5 Easy Ways to Split Excel Data into Sheets

Do you often find yourself sifting through large datasets in Microsoft Excel, only to realize that the data would be much more manageable if it was split into separate sheets? Whether you are analyzing sales figures, managing inventories, or organizing personal finance records, splitting data into different sheets can streamline your workflow and enhance productivity. Here, we'll explore five easy methods to split Excel data into multiple sheets, ensuring your data is both accessible and organized.
Method 1: Using Pivot Tables
Pivot Tables are not just for summarizing data; they can also help in sorting data into separate sheets:
- Select Your Data: Choose the data range or table.
- Insert Pivot Table: Go to ‘Insert’ > ‘PivotTable’ and ensure ‘New Worksheet’ is selected.
- Configure the Pivot Table: Drag your key column (the one you want to split by) to the Rows area. This will list each unique entry as a row.
- Split into Sheets: Right-click on each row label in the pivot table, select ‘Show Report Filter Pages’, and Excel will create new sheets for each item.

📊 Note: Pivot tables are dynamic, meaning updates in your source data will automatically reflect in the new sheets.
Method 2: Excel’s Advanced Filter

The Advanced Filter feature is perfect for when you need to split data based on specific criteria:
- Prepare Your Data: Ensure your data has headers for each column.
- Use Advanced Filter: Go to ‘Data’ > ‘Advanced’, choose ‘Copy to another location’.
- Define Criteria: Specify the range for your filter criteria, where you’ll list conditions for data to be filtered.
- Set Destination: Select a location for the filtered data to appear.
- Create Sheets: Manually or use a macro to copy this filtered data to new sheets.
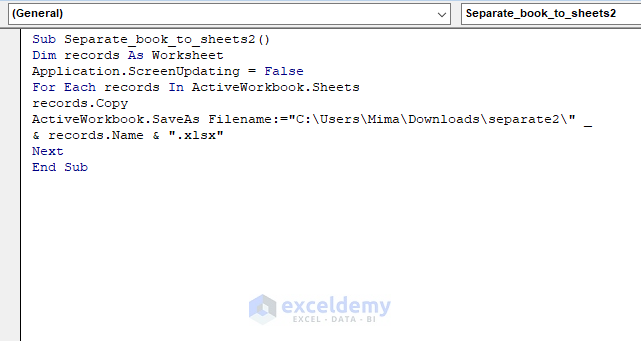
Method 3: VBA Macros

For those who are comfortable with programming, VBA macros provide a highly customizable solution:
- Open VBA Editor: Press Alt + F11 to access VBA in Excel.
- Insert New Module: Click ‘Insert’ > ‘Module’ to write your macro.
- Write the Macro: Use VBA to loop through data, check for conditions, and copy data to new sheets.
Sub SplitData() Dim wsSource As Worksheet Dim wsNew As Worksheet Dim rngSource As Range Dim cell As RangeSet wsSource = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Data") Set rngSource = wsSource.Range("A1").CurrentRegion For Each cell In rngSource.Range("B2:B" & rngSource.Rows.Count) If Not wsExists(cell.Value) Then Set wsNew = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Add wsNew.Name = cell.Value Else Set wsNew = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(cell.Value) End If rngSource.AutoFilter Field:=2, Criteria1:=cell.Value rngSource.Copy Destination:=wsNew.Range("A1") Next cell rngSource.AutoFilterMode = FalseEnd Sub
Function wsExists(wshName As String) As Boolean On Error Resume Next wsExists = CBool(Len(Worksheets(wshName).Name) > 0) End Function
Method 4: Using Formulas

You can also split data using Excel formulas, although this method requires more manual intervention:
- Use a Combination of Index and Match: Create a new sheet for each unique value, then use formulas to pull data based on your criteria.
=IF(EXACT(B2:B100,“Criteria”),INDEX(A2:C100,MATCH(ROW(),ROW(A2:A100)-ROW(A2)+1),COLUMN()))
Method 5: Power Query
Power Query (Get & Transform in Excel) provides a robust way to split data:
- Load Data: Connect to your data source or select your range.
- Group By: Use the ‘Group By’ feature to split data into separate tables.
- Load to Sheets: Each grouped table can be loaded into a new sheet.
In conclusion, splitting data in Excel can be approached in several ways, each offering its own advantages. From the simplicity of Pivot Tables to the power of VBA and the dynamic nature of Power Query, Excel provides versatile tools to cater to different levels of user expertise. Understanding these methods not only enhances your data management capabilities but also allows you to tailor your approach to the specific requirements of your project, making your data analysis and reporting more efficient.
Can I automate splitting data in Excel?
+
Yes, you can automate the process using VBA macros or Power Query. These methods can save time for repetitive tasks.
What if my dataset changes frequently?

+
Using Pivot Tables or Power Query is ideal for dynamic datasets as they automatically update with changes to the source data.
How can I split data without VBA?

+
You can use Advanced Filter or manually set up formulas to split data. These methods don’t require programming knowledge but might be less efficient for large datasets.
Is it possible to split data based on multiple criteria?

+
Yes, by combining different methods like Advanced Filter with VBA or Power Query, you can split data based on complex criteria.



