7 Proven Methods to Protect Your Excel Sheets

Understanding Excel Sheet Security

Microsoft Excel, a robust tool within the Microsoft Office Suite, empowers users to organize, manipulate, and analyze data efficiently. Whether for financial analysis, data tracking, or complex calculations, Excel sheets are invaluable. However, sharing sensitive information or safeguarding personal workbooks necessitates robust security measures. Here, we delve into seven proven methods to protect your Excel sheets, ensuring your data’s integrity and privacy.
1. Use Excel’s Built-in Protection Features


Excel provides several in-built options to lock down your spreadsheets:
- Password Protection: Add passwords to open or modify your workbook.
- Sheet Protection: Prevent users from editing specific cells or the structure of the sheet.
- Workbook Protection: Lock the structure and windows of your workbook to prevent unauthorized changes.
🔑 Note: If you forget your password, there is no default way to recover it. Consider storing passwords securely or using third-party recovery tools at your own risk.
2. Hide Sensitive Data

You can hide rows, columns, or entire sheets:
- Select rows/columns/sheets and right-click to hide.
- For sheets, you can use the
Format->Sheet->Hideoption.
3. Utilize Read-Only Mode

Distribute your workbook in read-only mode to prevent modifications:
- Save your workbook in a read-only format.
- Use “Mark as Final” to indicate the document is complete and should not be edited.
4. Cell Locking and Comments
| Action | How to Do It |
|---|---|
| Lock Cells | Select cells, use Format Cells -> Protection, and then lock the cells. Note: This only activates when you protect the sheet. |
| Add Comments | Use comments to provide instructions or explanations about the data or cell usage. |

📝 Note: Cell protection only applies when the sheet is protected. Users can still change unlocked cells or comment out your instructions.
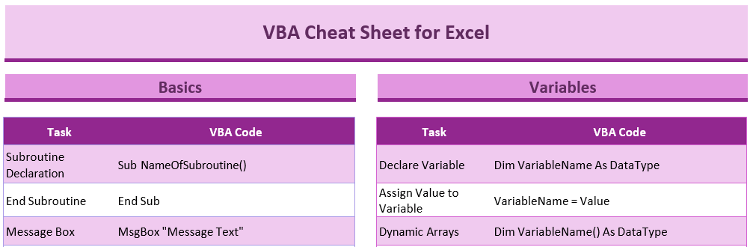
5. VBA Macros for Dynamic Security

Create Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macros to implement:
- User Authentication
- Dynamic Password Changes
- Automated Sheet Hiding
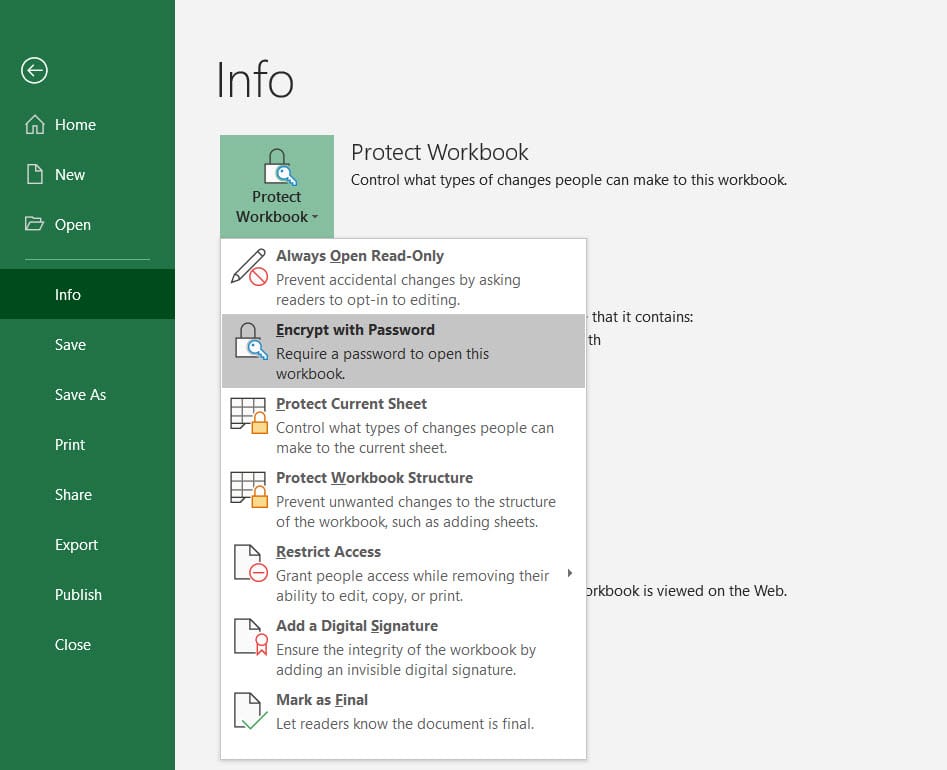
6. File Encryption

Encrypting your Excel files provides an extra layer of security:
- Select
File->Info->Protect Workbook->Encrypt with Passwordto secure your workbook with AES encryption. - External encryption tools like BitLocker or VeraCrypt can also be used.
🔒 Note: Strong encryption is key. Remember that once encrypted, file content is inaccessible without the password.
7. Third-Party Tools

Consider using additional software for enhanced security:
- Document tracking software for monitoring who opens or edits your files.
- Advanced password protection tools with features like password recovery or multi-factor authentication.
In conclusion, protecting your Excel sheets involves a combination of in-built Excel features, strategic data management, and possibly third-party tools. Implementing these methods not only prevents unauthorized access but also maintains the integrity of your data, ensuring it remains reliable for analysis and decision-making.
What happens if I forget the password for my protected Excel sheet?

+
If you forget your password, Excel does not offer a built-in password recovery mechanism. You may need to use third-party tools which can recover or reset the password, although this can come with risks or data loss.
Can I protect specific cells in Excel without locking the entire sheet?

+
Yes, you can lock individual cells while leaving the sheet unprotected. After formatting the cells you wish to lock, protect the sheet, but ensure you do not select “Protect worksheet and contents” option for the cells you want to remain editable.
Is it safe to encrypt my Excel files?

+
Yes, encryption significantly enhances security by making the file unreadable to anyone without the decryption key or password. However, ensure you use a strong password and consider the potential loss of access if the password is forgotten.