5 Easy Ways to Share Excel Formulas Across Sheets
Imagine the efficiency in your work if you could easily share Excel formulas across sheets. Whether you're a financial analyst, a project manager, or someone managing large datasets, the ability to replicate your work across different sheets can save time and reduce errors. In this post, we'll explore five straightforward methods to achieve this, enhancing your productivity with Excel.
Method 1: Using Defined Names

Defined names in Excel provide an easy way to reference data across sheets. Here’s how to do it:
- Select the cell containing the formula you want to share.
- Go to the ‘Formulas’ tab and click on ‘Define Name’.
- Give your formula a memorable name and click ‘OK’.
- Now, you can use this named formula in any cell on any sheet by simply typing the name.

🔍 Note: Using defined names makes your spreadsheet more manageable and reduces formula complexity.
Method 2: Copy and Paste Formulas

Perhaps the most straightforward way to share formulas is through copy and paste:
- Select the cell with the formula you want to share.
- Press Ctrl+C (Cmd+C on Mac) to copy.
- Go to the destination sheet and cell, then press Ctrl+V (Cmd+V on Mac).
- Alternatively, for pasting without changing cell references, use Paste Special (Alt+E, S).
📌 Note: Ensure you check formula references when pasting to avoid unintended changes.
Method 3: Utilize Excel’s External References

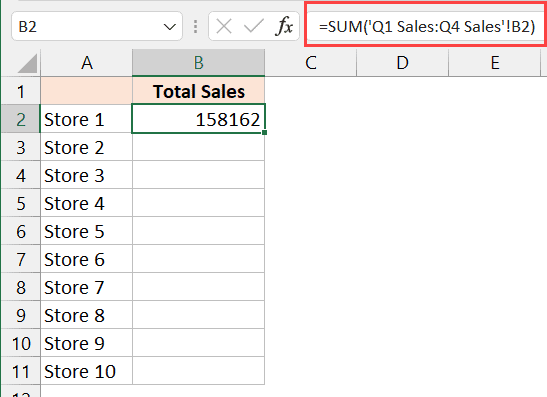
External references or 3D references allow you to pull data from other workbooks:
- Start typing the formula where you want the data to appear.
- Type the equal sign (=), then click on the cell from another sheet or workbook.
- Use square brackets for references from different workbooks, like =[Workbook.xlsx]Sheet1!A1.
| Workbook | Sheet | Cell |
|---|---|---|
| MyData.xlsx | Sheet1 | A1 |

⚠️ Note: External references require the referenced workbooks to be open when updating.
Method 4: Data Consolidation with Summarize Tools

The ‘Consolidate’ feature in Excel simplifies merging data from multiple sheets:
- Select the destination range on your worksheet.
- Go to ‘Data’ > ‘Consolidate’.
- Choose the function, add the ranges from different sheets, and click ‘OK’.

Method 5: Use Excel Tables and Structured References

By using Excel Tables, you can share data effortlessly across sheets:
- Convert your data range into a table (Ctrl+T or Insert > Table).
- Use structured references to refer to this table from other sheets.
- Your formulas will automatically adjust as data changes in the table.
🗃️ Note: Structured references provide a clean and dynamic way to reference data, which is particularly helpful with large datasets.
By leveraging these five methods, you can make your work with Excel not only more efficient but also more effective. Whether you're sharing intricate formulas or consolidating data from multiple sources, Excel offers a variety of tools to enhance your workflow. Remember, each method has its advantages, so choose the one that best fits your project requirements. With these techniques, your Excel sheets will not only become easier to manage but will also provide a seamless integration of data, reducing the risk of errors and making your data management tasks smoother.
What are the benefits of using defined names in Excel?

+
Using defined names helps in readability, simplifies formula writing, and makes it easier to manage and share complex spreadsheets.
Can I share formulas between workbooks?
+
Yes, you can share formulas between workbooks using external references, but keep in mind that the workbooks need to be open for updates to occur.
How do I ensure my formulas don’t change when pasting them in different sheets?

+
Use the ‘Paste Special’ feature with the ‘Values and Formulas’ option to paste formulas without changing cell references.
Why should I use Excel tables for sharing data?
+
Excel tables allow for structured references which dynamically adjust as data changes, ensuring that your formulas always pull the correct data.
Are there any limitations to using the consolidate tool?

+
The consolidate tool does not allow for referencing data from closed workbooks, and it might have issues with large datasets due to performance limitations.



