Mastering Excel: Link Cells Across Sheets Easily

Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis and management, but its true potential often lies in the ability to link cells across different sheets. This functionality not only saves time but also keeps your data organized and updates instantly reflected across your workbook. In this blog post, we will dive into the various methods of linking cells across sheets in Excel, ensuring that you can manage your data with ease and efficiency.
Understanding Cell References in Excel

Before we start linking cells, let’s briefly touch on how Excel references work:
- Absolute References (A1): These references remain constant even if you copy the formula to another cell.
- Relative References (A1): These change based on the relative position of rows and columns when copying formulas.
- Mixed References (A1 or A1): These are a combination of absolute and relative where either the row or the column remains fixed.
Basic Cell Linking Between Sheets

To link a cell in one sheet to another, follow these steps:
- Select the cell where you want to insert the link.
- Type the
=sign to start your formula. - Click on the sheet tab where the destination cell is located.
- Click on the cell you want to link to, or type its address manually like
‘Sheet2’!A1. - Press Enter to complete the link.

📝 Note: Always ensure that the sheet name you reference includes single quotes if the name contains spaces or special characters, like 'My Sheet'!A1.
Linking Ranges of Cells
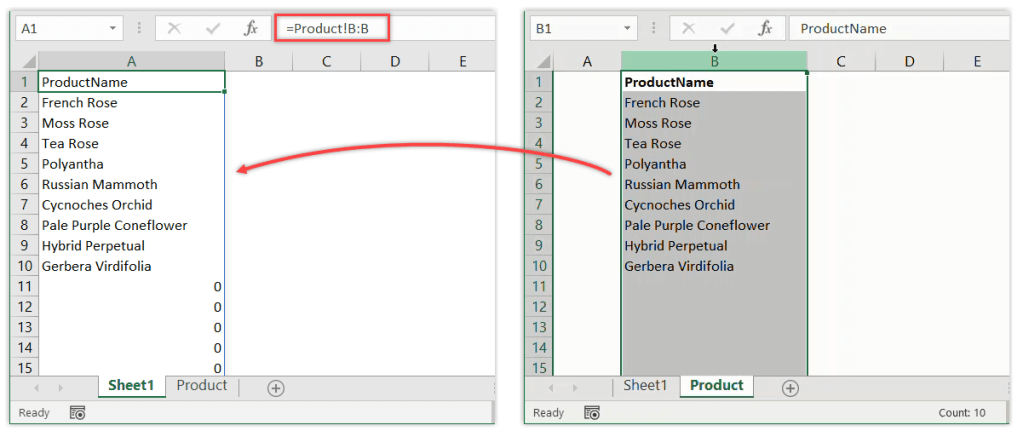
If you need to link entire ranges between sheets, the process is similar:
- Select the cell range on the source sheet.
- Copy it by pressing Ctrl+C or right-click and select Copy.
- Go to the destination sheet, select the top-left cell of the range you want to link to, then:
- Use Alt+E, then S, followed by V to paste as a link (this pastes the linked formula).
Advanced Linking Techniques

3D References

3D references allow you to link a range across several sheets:
| Usage | Description |
|---|---|
=SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1) |
This sums up the value of cell A1 from Sheet1 through Sheet3. |
=AVERAGE(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1:C10) |
Averages a range from A1 to C10 across multiple sheets. |

💡 Note: 3D references are particularly useful for summarizing data that is identically structured across multiple sheets.
Using Functions for Dynamic Linking

Functions like INDIRECT can make your links more dynamic:
- INDIRECT:
=INDIRECT(“‘” & B1 & “’!A1”)where B1 contains the sheet name to link from.
Automating Updates with Linked Data

When you link cells, any changes in the source cell will automatically update the linked cells:
- Editing the source cell value updates the linked cells in real-time.
- Deleting or moving the source cell might break the link, necessitating updates or use of the
Find Linkfeature in Excel.
Best Practices for Managing Linked Sheets

- Organize Your Workbook: Clearly label your sheets and use a naming convention to avoid confusion.
- Regular Updates: Periodically check for broken links, especially if sheets or files are moved or renamed.
- Documentation: Keep documentation or comments within your sheets explaining what each link does or represents.
By linking cells across sheets, you can streamline your data management, automate updates, and maintain consistency in your reports. This approach enhances productivity, allowing you to focus on analysis rather than manual data entry.
What is the difference between linking a single cell and a range?

+
Linking a single cell involves referencing one specific cell from another sheet, while linking a range refers to multiple cells or a block of cells. This allows you to synchronize data across various parts of your workbook efficiently.
Can I link cells between different Excel files?

+
Yes, you can link cells between different Excel files using external references. The format would be something like =[Book1.xlsx]Sheet1!A1.
How do I find and fix broken links in Excel?

+
Go to Data > Edit Links to view and manage all external links. You can update, open, or break links from there.



