Merge Excel Sheets Efficiently: Integration Guide

Imagine this: You have multiple Excel sheets, each filled with valuable data, but they're scattered across your device. How do you manage these data efficiently? Whether you're a data analyst, a project manager, or just someone who loves to keep their numbers straight, understanding how to integrate and merge Excel sheets efficiently can save you hours of manual labor. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk through various methods to merge Excel sheets, ensuring you can streamline your data management processes.
Understanding Excel Sheets and their Data Structures

Before we dive into merging, let’s understand what we’re dealing with:
- Workbooks: A collection of Excel files or books where sheets are stored.
- Worksheets or Sheets: Each tab within a workbook, containing rows, columns, and cells.
- Data Structures:
- Tabular Data: Data organized in rows and columns.
- Structured Reference: A way to refer to tables or ranges by name.
Manual Method: Copying and Pasting

Here’s how you can manually merge Excel sheets:
- Open the destination workbook where you want to merge all sheets.
- Switch to the source workbook and select all data or range from the sheet you wish to merge.
- Copy the data (Ctrl + C or Cmd + C).
- Return to the destination workbook, select the cell where you want to paste, and paste (Ctrl + V or Cmd + V).
- Adjust columns and rows if necessary.
💡 Note: This method works well for small datasets but can be error-prone and time-consuming with larger, more complex data structures.
Using Excel Formulas

When dealing with multiple sheets or datasets where data needs to be updated frequently, formulas can automate the merging process:
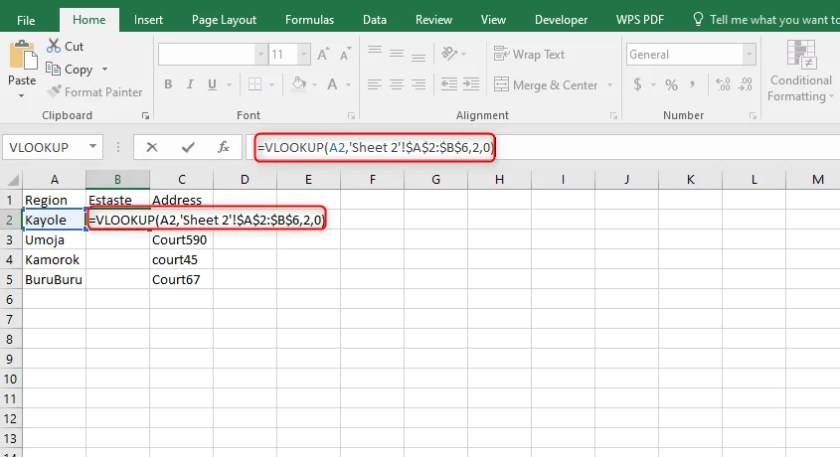
VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP Functions

- VLOOKUP: Use this to fetch data from another sheet based on a matching value. Here’s how it looks in practice:
=VLOOKUP(A2,Sheet2!A1:C100,2,FALSE) - XLOOKUP: Similar to VLOOKUP but more powerful, allowing for more complex lookup scenarios.
=XLOOKUP(A2,Sheet2!A:A,Sheet2!B:B)
Power Query for Advanced Merging

Power Query, available in newer versions of Excel, is an excellent tool for integrating data:
- Go to the Data tab and select “Get Data” > “From File” > “From Workbook”.
- Select your source Excel file, and choose the sheets you want to merge.
- Use the “Merge Queries” option to combine your datasets based on a common column.
Power Query will then allow you to manage, transform, and load your merged data back into Excel.
📝 Note: Power Query is available in Excel for Microsoft 365, Excel 2019, and later versions. If you're using an earlier version, consider upgrading or using an alternative method.
Using Macros and VBA for Automated Merging

If your workflow involves repetitive data merging, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can save you from manual labor:
- Create a Macro:
- Open the Developer Tab (if not visible, enable it from Excel Options).
- Click “Visual Basic” to open the VBA editor.
- Insert a new module and paste the following code:
Sub MergeSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim destWs As Worksheet Dim lastRow As Long Set destWs = Sheets(“MasterSheet”) For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> “MasterSheet” Then lastRow = destWs.Cells(destWs.Rows.Count, “A”).End(xlUp).Row ws.UsedRange.Copy destWs.Cells(lastRow + 1, “A”) End If Next ws End Sub
The above code will merge data from all sheets except the "MasterSheet" into one destination sheet.
Third-Party Tools for Data Integration

If Excel’s built-in tools aren’t enough, consider using:
- Excel Add-Ins: Tools like “Ablebits” or “ProWizard” provide extensive functionality for data merging.
- External Software: Applications like “Microsoft Power BI” or “Tableau” can handle data integration from multiple sources including Excel.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Accuracy

When merging data:
- Check for Duplicates: Use conditional formatting or functions like COUNTIF to spot duplicates.
- Verify Data Types: Ensure all data types (dates, numbers, etc.) are consistent across sheets.
- Manage Headers: Ensure headers are merged correctly; mismatching headers can cause data misalignment.
In conclusion, merging Excel sheets can transform your data management from tedious to efficient. By choosing the right method based on your data size, complexity, and frequency of updates, you can streamline your work processes significantly. Manual methods might suffice for small, one-time merges, but for regular updates or larger datasets, leveraging Excel's formulas, Power Query, VBA, or third-party tools will provide accuracy and time-saving benefits. Remember to always double-check your merged data for integrity, and with these tools and techniques at your disposal, you're well-equipped to manage even the most complex data integration tasks.
Can I merge Excel sheets from different workbooks?

+
Yes, you can merge sheets from different workbooks. Use Power Query for seamless integration or VBA for a custom solution.
How do I ensure data consistency when merging sheets?

+
Check for data types, normalize headers, and eliminate duplicates using conditional formatting or functions like COUNTIF or UNIQUE.
What if I need to merge sheets but keep them separate?

+
You can use the ‘Consolidate’ feature in Excel to combine data without losing individual sheet data. This can be found under the ‘Data’ tab.