Split Excel Sheet Names Easily: A Quick Guide

Excel is one of the most widely used tools in both professional and personal settings for data organization, analysis, and presentation. One of the common tasks users might encounter is splitting Excel sheet names. Whether you're organizing data for a project, managing records, or preparing reports, knowing how to manage your sheets efficiently can save time and reduce errors. This guide will walk you through the process step-by-step.
Understanding Excel Sheets
Before diving into the process of splitting Excel sheet names, it's important to understand what Excel sheets are. Excel workbooks contain sheets, which are essentially pages where you enter your data. Each sheet can be named, often corresponding to the type of data it contains (e.g., "Sales Q1", "Employee List", "Inventory").
Why Split Sheet Names?
- To improve the readability of the workbook by keeping related data together.
- To reduce clutter in the sheet tabs area.
- To enhance data management by allowing easier access to specific subsets of data.
Methods to Split Excel Sheet Names
Manual Method

This approach involves manually copying data from one sheet to another:
- Open your Excel workbook.
- Right-click on the sheet tab you wish to split.
- Select “Move or Copy…”
- Choose the location where you want to insert the new sheet. If you want a new workbook, select “(new book)”.
- Check the box labeled “Create a copy”.
- Click “OK”.
- Rename the new sheet appropriately.
- Delete or copy the data as required from the original sheet to the new one.
⚠️ Note: Ensure you do not delete essential data in the original sheet unless you've verified the copy is accurate.
VBA Macro Method

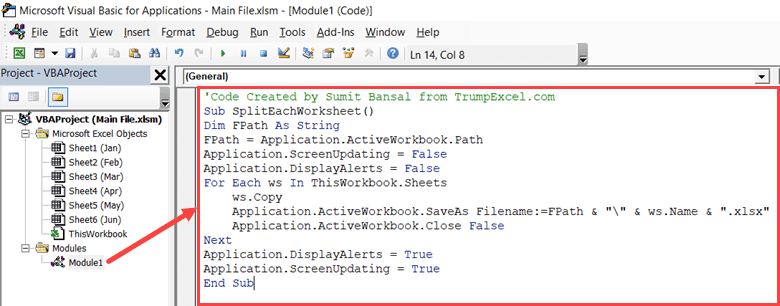
For those familiar with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), using macros can automate the process:
| VBA Code |
|---|
Sub SplitSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim newWb As Workbook
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim lastCol As Long
Dim dataArray As Variant
' Loop through all sheets
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
With ws
' Determine the last row and column with data
lastRow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
lastCol = .Cells(1, .Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
' Read the entire data range into an array
dataArray = .Range(.Cells(1, 1), .Cells(lastRow, lastCol))
' Create a new workbook for each sheet
Set newWb = Workbooks.Add
' Set the first sheet's name to be the same as the original
newWb.Sheets(1).Name = ws.Name
' Copy data to the new workbook
newWb.Sheets(1).Range("A1").Resize(UBound(dataArray, 1), UBound(dataArray, 2)) = dataArray
' Save and close the new workbook
newWb.SaveAs ThisWorkbook.Path & "\" & ws.Name & ".xlsx"
newWb.Close
End With
Next ws
End Sub
|

Here's how to use this macro:
- Open the Excel VBA editor by pressing Alt + F11.
- Insert a new module (Insert > Module).
- Paste the above code into the module.
- Run the macro by going back to Excel, selecting Developer > Macros, selecting your macro, and clicking "Run".
📍 Note: Always backup your workbook before running any VBA script.
Third-Party Tools

If you are not comfortable with VBA or prefer a visual approach, several third-party tools can split Excel sheets:
- Ablebits Excel Add-in: Offers tools for splitting, merging, and converting data.
- Kutools for Excel: Provides utilities for enhancing Excel productivity, including data splitting.
📝 Note: Always ensure the third-party tools you use are compatible with your Excel version and comply with your organization's IT policies.
After managing your Excel sheets, whether through manual, VBA, or third-party methods, you'll find your workflow streamlined. Splitting sheets allows for better organization, which means easier access to the data you need when you need it. Keep in mind that while splitting sheets, maintaining data integrity and consistency across your Excel workbooks is crucial.
Why should I split Excel sheet names?

+
Splitting Excel sheet names helps in organizing data better, reducing clutter, and making data management more efficient by keeping related data in separate sheets.
Is it safe to use VBA to split sheets?

+
Yes, VBA is generally safe if used correctly. However, always back up your data before running any macro, and ensure your VBA scripts are written or sourced from trusted places.
Can I undo the splitting of sheets in Excel?

+
If you manually split sheets, you can manually combine them by copying data back to the original workbook. For VBA or third-party tools, ensure you have a backup to revert changes.
What’s the benefit of using third-party tools for sheet splitting?

+
Third-party tools often provide user-friendly interfaces, more robust functionality for data manipulation, and might offer additional features like merging sheets or advanced data analysis options.
How do I manage multiple sheets with the same name?

+
Excel does not allow duplicate sheet names within the same workbook. If you are splitting sheets to another workbook, you can give them the same name, but for clarity, it’s better to give each new sheet a unique name or a naming convention.