5 Ways to Merge Excel Sheets Easily

Managing and consolidating data from multiple Excel sheets can often be a daunting task, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex spreadsheets. Whether you're compiling financial reports, combining customer data, or merging inventory lists, having a streamlined method for merging Excel sheets can significantly improve productivity. Here are five easy methods to help you merge Excel sheets effortlessly.
1. Using VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP for Simple Data Merge
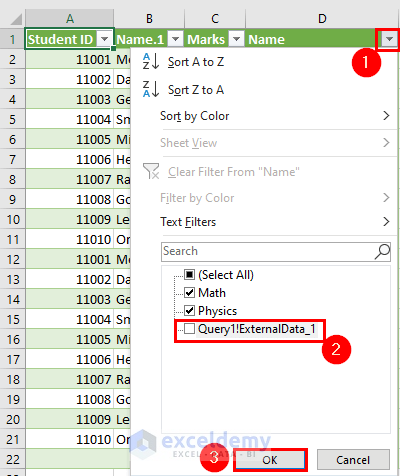
The VLOOKUP or the newer XLOOKUP functions are invaluable when you need to merge data based on a common identifier, like employee IDs or product codes. Here’s how:
- Step 1: Ensure your source sheets have a unique identifier in one of the columns.
- Step 2: In your target sheet, write the VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP formula to pull data from the source sheets.
VLOOKUP Formula Example:

=VLOOKUP(A2,SourceSheet!A:B,2,FALSE)
🔍 Note: Make sure to specify the exact location of the data in the SourceSheet and adjust the column index accordingly.
2. Consolidate Data by Position or Category

Excel provides a feature called ‘Consolidate’ which allows you to merge data from different sheets using functions like Sum, Average, etc., based on position or labels:
- Step 1: Open your target Excel workbook and go to the “Data” tab.
- Step 2: Select ‘Consolidate’, choose your function (e.g., Sum), and specify the ranges from the source sheets.
Settings for Consolidation:

| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Sum | Adds up values |
| Count | Counts the number of cells with data |
| Average | Calculates the average of values |
| Min/Max | Finds the minimum or maximum value |

📝 Note: Use the 'Use labels in' options to specify whether to consolidate by row or column labels.
3. Power Query for Advanced Merging

Power Query in Excel is a powerful tool for merging sheets, especially when dealing with multiple or large datasets:
- Step 1: Open a new Excel workbook or use an existing one. Click on ‘Data’ then ‘New Query’, select ‘From File’, and choose ‘From Excel Workbook’.
- Step 2: Load all sheets you want to merge into the Power Query Editor.
- Step 3: Use the ‘Append Queries’ or ‘Merge Queries’ functions to combine the data as needed.
⚙️ Note: Power Query provides flexibility in data transformation, allowing for custom merging logic based on various criteria.
4. VBA Script for Custom Merging

For those comfortable with coding, VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) offers the ultimate customization for merging Excel sheets:
- Step 1: Press ALT+F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Step 2: Create a new module and write a script to open multiple Excel workbooks, access different sheets, and merge the data into one.
- Step 3: Run the script to perform the merge.
Example VBA Script:

Sub MergeSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim lastColumn As Long
' Assuming you want to merge data from Sheet1 of each workbook into 'DestinationSheet'
Sheets("DestinationSheet").Activate
lastRow = Sheets("DestinationSheet").Cells(Sheets("DestinationSheet").Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
lastColumn = Sheets("DestinationSheet").Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
' Loop through all open workbooks
For Each wb In Workbooks
If wb.Name <> ThisWorkbook.Name Then
wb.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:Z100").Copy _
Destination:=ThisWorkbook.Sheets("DestinationSheet").Cells(lastRow + 1, 1)
lastRow = Sheets("DestinationSheet").Cells(Sheets("DestinationSheet").Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
End If
Next wb
MsgBox "Merge completed."
End Sub
💡 Note: This script needs to be customized for your specific workbook and sheet names.
5. Using Excel Macros

If VBA seems too daunting, Excel macros can simplify the process:
- Step 1: Record a macro that performs the necessary steps for merging sheets.
- Step 2: Playback the macro whenever you need to merge sheets with similar structures.
📌 Note: Macros can automate repetitive tasks but are less flexible for varied data structures.
Merging Excel sheets efficiently can streamline your workflow, reduce errors, and save time. Whether you choose simple formulas like VLOOKUP or dive into the complexity of Power Query or VBA, the key is to select the method that best fits your data merging needs. Each approach has its own set of advantages, tailored to different levels of Excel proficiency and data complexity. By mastering these techniques, you empower yourself to handle data consolidation with ease and accuracy, making your data analysis tasks much more manageable and insightful.
Can VLOOKUP handle multiple criteria?

+
Standard VLOOKUP function cannot handle multiple criteria directly. However, by combining VLOOKUP with CHOOSE or helper columns, you can work around this limitation.
Is there a limit to how many sheets I can merge with Power Query?

+
There’s no defined limit by Excel, but practical limits might arise from system memory or processing power when dealing with very large datasets or too many sheets.
How can I ensure data consistency when merging sheets?

+
Ensure that all source sheets have identical structures, including matching column headers and data types, before merging. Use data validation and checks within Excel to maintain consistency.
What should I do if I encounter errors during the VBA merge?

+
Check for common issues like incorrect sheet references, workbook names not matching, or mismatches in data types. Debug your script by stepping through the code with the VBA editor.



