VBA Guide: Rename Excel Sheets Easily

Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is a powerful tool within Microsoft Excel that allows users to automate repetitive tasks and enhance their spreadsheets with custom functionalities. One common task in Excel is the renaming of worksheet tabs, which can be particularly useful in organizing data or aligning worksheets with a dynamic dataset or a report's content. In this guide, we'll explore how to leverage VBA to make the process of renaming Excel sheets both easy and efficient.
Why Use VBA for Renaming Excel Sheets?
Renaming Excel sheets manually can be tedious, especially when working with large numbers of sheets or when sheets need to be renamed frequently. Here are some reasons why using VBA can be advantageous:
- Automation: With VBA, you can rename multiple sheets with a single command.
- Consistency: Ensuring uniform naming conventions across your workbook becomes effortless.
- Efficiency: Saves time by automating a potentially repetitive task.
- Customization: You can tailor the renaming process to fit specific needs or patterns.
Basic VBA Syntax for Renaming Sheets
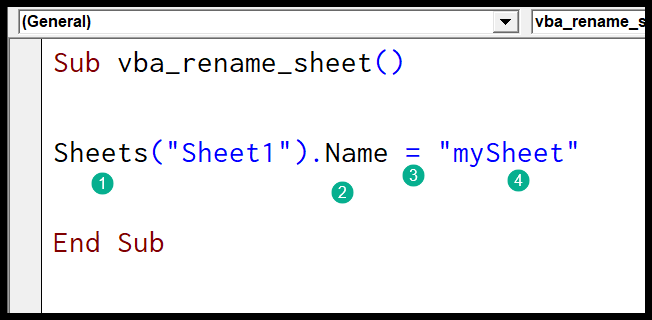
The VBA code to rename a sheet is relatively straightforward. Here’s the basic syntax:
Sheets(“SheetName”).Name = “NewSheetName”⚠️ Note: Ensure that the “SheetName” and “NewSheetName” do not already exist in the workbook to avoid errors.
Renaming a Single Sheet

To rename a single sheet:
- Press
ALT + F11to open the VBA editor. - Go to Insert > Module to create a new module.
- Insert the following code to rename “Sheet1” to “SalesData”:
Sub RenameSingleSheet()
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Name = “SalesData”
End SubRenaming Multiple Sheets at Once

If you need to rename several sheets, you can use a loop to cycle through each sheet in your workbook:
Sub RenameMultipleSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim i As Integeri = 1 For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> "Summary" Then 'Exclude "Summary" sheet from renaming ws.Name = "Sheet" & i i = i + 1 End If Next ws
End Sub
Here, the loop will rename all sheets except "Summary" by assigning sequential numbers to them.
Dynamic Sheet Renaming

You might want to rename sheets based on some criteria or values in the sheets themselves:
Sub RenameSheetsDynamically() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim i As Integeri = 1 For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> "Control" Then ' Rename the sheet based on cell A1's value in each sheet If ws.Range("A1").Value <> "" Then ws.Name = Left(ws.Range("A1").Value, 31) Else ws.Name = "Sheet" & i i = i + 1 End If End If Next ws
End Sub
Renaming Sheets with User Input

For flexibility, you can allow users to input the new name for sheets:
Sub RenameSheetsWithInput() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim NewName As StringFor Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> "Control" Then NewName = InputBox("Enter new name for " & ws.Name) If NewName <> "" Then ws.Name = Left(NewName, 31) End If End If Next ws
End Sub
✅ Note: The function `Left` is used to ensure the new sheet name doesn't exceed the 31-character limit set by Excel.
Error Handling and Best Practices

Here are some best practices to follow when renaming sheets with VBA:
- Use
On Error Resume Next: To handle errors when renaming sheets:
Sub RenameWithErrorHandling()
On Error Resume Next
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Name = “NewSheetName”
If Err.Number <> 0 Then MsgBox “Error renaming sheet: ” & Err.Description
On Error GoTo 0
End SubWrapping Up

Renaming Excel sheets using VBA can significantly enhance your workflow. From single sheet renaming to bulk operations, VBA provides the flexibility to manage your workbook in ways that Excel’s interface alone does not allow. By applying these methods, you can:
- Automate the process of naming or renaming sheets to reflect their content or current data.
- Create dynamic naming conventions that respond to changes within your data.
- Reduce errors by enforcing naming rules through VBA scripts.
- Allow users to interact with and customize sheet names in real-time.
Incorporating these techniques into your Excel usage will not only streamline your work but also ensure that your workbooks are well-organized and follow a logical structure, making them easier to understand and maintain over time.
Can I rename hidden sheets with VBA?

+
Yes, VBA can rename hidden sheets just as easily as visible ones. You would use the same Name property for the sheet object, regardless of its visibility.
What are the limitations to renaming sheets with VBA?

+
The primary limitations include: the new sheet name cannot exceed 31 characters, cannot contain certain characters like \/?*[], and a sheet cannot have the same name as another within the workbook.
Is it possible to undo renaming with VBA?

+
VBA does not inherently provide an “undo” feature for renaming. However, you could write VBA code to keep track of previous names and provide a way to revert them.



