5 Proven Ways to Import CSV Files to Excel

Importing CSV files into Microsoft Excel can streamline data management and analysis for individuals and businesses alike. This guide will explore five proven methods to import CSV data into Excel, ensuring your data import process is efficient and error-free.
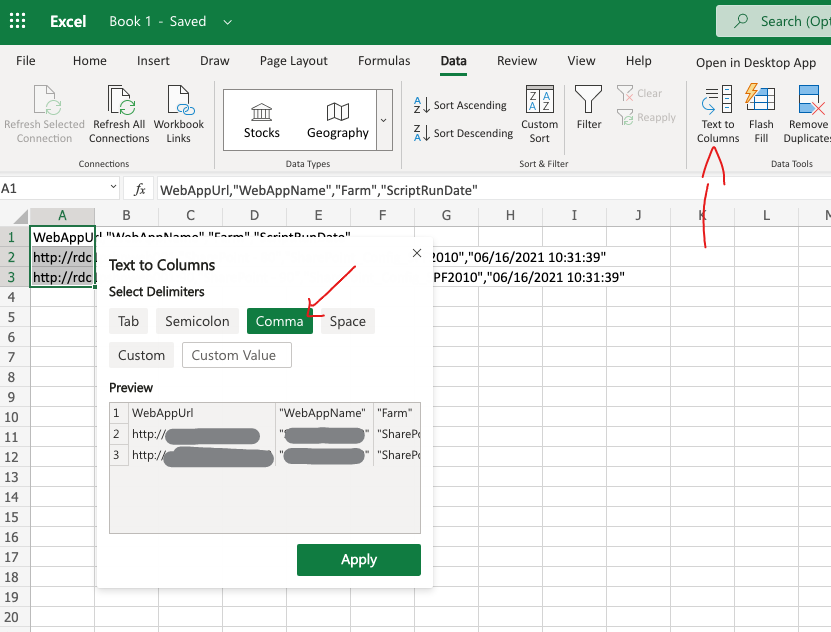
1. The Default Import Wizard

Excel comes with a built-in tool called the Text Import Wizard, which is perfect for handling a variety of data formats:
- Open Excel and click on ‘Data’ from the ribbon.
- Select ‘From Text’ or ‘Get Data’ depending on your Excel version.
- Locate and open your CSV file.
- Follow the wizard, choosing ‘Delimited’ and then selecting your delimiter (commonly a comma).
- Adjust column formats in Step 3 if necessary.
⚠️ Note: If your data contains special characters, consider the next method for better control.
2. Using Power Query

Power Query is an Excel feature designed for data transformation and provides more robust options:
- Go to the ‘Data’ tab and select ‘Get Data’ > ‘From File’ > ‘From CSV’.
- Navigate to and select your CSV file.
- The Power Query Editor will open, where you can:
- Transform your data.
- Filter and clean up as needed.
- Load the data into your worksheet.
Power Query is especially useful when you need to import data frequently or clean up your dataset extensively before analysis.
3. The CSV File Conversion Approach

This method involves converting your CSV file into a format Excel readily accepts:
- Rename the CSV file to have a .txt extension.
- Open Excel, then click ‘File’ > ‘Open’.
- Choose ‘All Files’ from the drop-down, locate your .txt file, and open it.
- The Text Import Wizard will guide you through importing the data.
4. VBA Scripting

For advanced users or those needing automation, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can be a powerful tool:
- Open Excel and press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor.
- Insert a new module (Insert > Module).
- Use the following script to import your CSV file:
Sub ImportCSV() Dim ws As Worksheet, filePath As String, fileName As String Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1) filePath = Application.GetOpenFilename("CSV Files (*.csv), *.csv", , "Open CSV File") If filePath = "False" Then Exit Sub With ws.QueryTables.Add(Connection:="TEXT;" & filePath, Destination:=ws.Range("A1")) .TextFileParseType = xlDelimited .TextFileCommaDelimiter = True .Refresh End With End SubExecute the macro by running ‘ImportCSV’.
5. Manual Copy-Paste Method

While not as sophisticated, this method can be quick and straightforward:
- Open your CSV file in Notepad or any text editor.
- Copy the entire text content.
- In Excel, paste the data into a cell (A1, for example).
- Excel will auto-detect the CSV format and ask for your preferences. Choose ‘Data in the first row’ if that’s where your headers are.
This method is best for small datasets and when you need a quick import.
💡 Note: Ensure your data is well-organized and headers are clearly defined to avoid import issues.
In summary, choosing the right method for importing CSV files into Excel depends on the size of your data, how often you need to perform this task, and the level of control you require. The Default Import Wizard and Power Query offer great ease of use, while VBA scripting provides automation and flexibility for complex or recurring tasks. Whether you are a novice or an expert, there's a method here that will suit your needs, ensuring your data management remains seamless and efficient.
How can I import a CSV file with special characters?
+
For CSV files with special characters, using Excel’s Power Query or the manual copy-paste method can help preserve the data integrity by allowing you to define the encoding type.
Can I automate the CSV import process?

+
Yes, VBA scripting in Excel can automate the import process, making it ideal for recurring tasks.
Does Excel keep the original formatting from the CSV?

+
Excel will not preserve the formatting from the CSV file upon import. You’ll need to reapply any formatting within Excel after the import is complete.
How do I handle large CSV files?

+
Use the Power Query for larger files as it can handle substantial datasets with more efficiency than the default import wizard.



