5 VBA Tricks to List Excel Sheet Names Instantly

Excel is a powerful tool widely used for data analysis, but managing multiple sheets within a workbook can often be tedious. Knowing how to list sheet names instantly can streamline your workflow, save time, and reduce errors. Here are five Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) tricks to help you quickly obtain the names of sheets within your Excel workbook.
1. Using the VBA Immediate Window

The Immediate Window in VBA is a straightforward way to display the names of sheets:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Press Ctrl + G to display the Immediate Window.
- Type
?ActiveSheet.Nameand press Enter. This will list the current active sheet’s name. - For listing all sheets, use:
Sub ListSheetNames()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Sheets
Debug.Print ws.Name
Next ws
End Sub
💡 Note: If you do not see the Immediate Window, you can toggle it by navigating through View > Immediate Window in the VBA Editor.
2. Creating a List on a Worksheet

Instead of using the Immediate Window, you might want to list sheet names on an actual worksheet:
- In the VBA editor, click Insert > Module.
- Enter the following code:
Sub ListSheetsOnSheet() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim targetWs As Worksheet Set targetWs = ThisWorkbook.Sheets.AddDim rowIndex As Integer rowIndex = 1 For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Sheets If ws.Name <> targetWs.Name Then targetWs.Cells(rowIndex, 1).Value = ws.Name rowIndex = rowIndex + 1 End If Next ws
End Sub
This script adds a new worksheet and populates it with the names of all sheets in the workbook, excluding the sheet on which the list is being created.
📝 Note: The new sheet is added at the end of the existing sheets. You can adjust the code to change where the sheet is inserted if required.
3. Sorting Sheet Names Alphabetically

If you have a large workbook with many sheets, sorting them alphabetically can help you find what you need faster:
- Utilize the following macro to create a sorted list:
Sub ListSheetsSorted() Dim wsList As Variant Dim wsNames As Worksheet Set wsNames = ThisWorkbook.Sheets.AddDim i As Integer i = 1 ReDim wsList(1 To ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count) For Each Sheet In ThisWorkbook.Sheets wsList(i) = Sheet.Name i = i + 1 Next Sheet QuickSort wsList, 1, UBound(wsList) For i = 1 To UBound(wsList) wsNames.Cells(i, 1).Value = wsList(i) Next iEnd Sub
Sub QuickSort(arr, first, last) Dim lo As Long, hi As Long Dim midValue As Variant lo = first hi = last midValue = arr((first + last) \ 2) Do While lo <= hi Do While arr(lo) < midValue And lo < last lo = lo + 1 Loop Do While arr(hi) > midValue And hi > first hi = hi - 1 Loop If lo <= hi Then Swap arr, lo, hi lo = lo + 1 hi = hi - 1 End If Loop If first < hi Then QuickSort arr, first, hi If lo < last Then QuickSort arr, lo, last End Sub
Sub Swap(arr, a, b) Dim temp As Variant temp = arr(a) arr(a) = arr(b) arr(b) = temp End Sub
This VBA script sorts the sheet names alphabetically and lists them on a new worksheet.
4. Creating a Dropdown List of Sheet Names

For an interactive experience, you can add a dropdown list to select and navigate between sheets:
- Set up a dropdown with Data Validation on a cell and populate it using VBA:
Sub CreateDropdownOfSheets() Dim wsList As String Dim i As Integer Dim ws As WorksheetFor Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Sheets wsList = wsList & ws.Name & "," Next ws ' Trim the last comma wsList = Left(wsList, Len(wsList) - 1) With Sheet1.Range("A1").Validation .Delete .Add Type:=xlValidateList, AlertStyle:=xlValidAlertStop, Operator:= _ xlBetween, Formula1:=wsList .IgnoreBlank = True .InCellDropdown = True .InputTitle = "Select Sheet" .ErrorTitle = "Incorrect Selection" .InputMessage = "Choose a Sheet from the dropdown" .ErrorMessage = "Please select an existing sheet from the list" End With
End Sub
When a user selects a sheet name from this dropdown, you can then have VBA navigate to that sheet.
5. Automatically Renaming Sheets
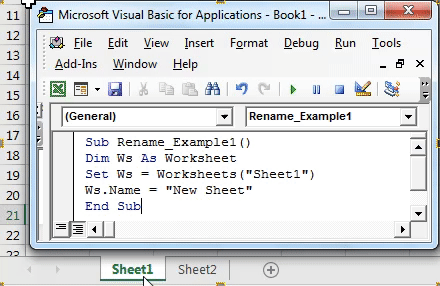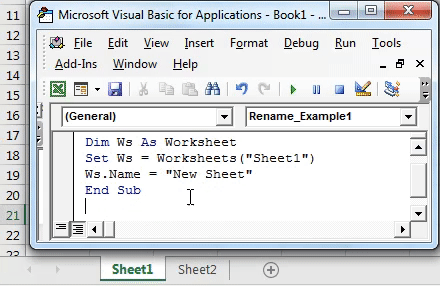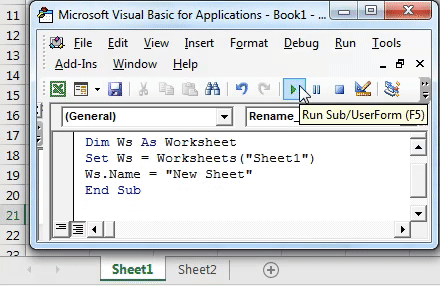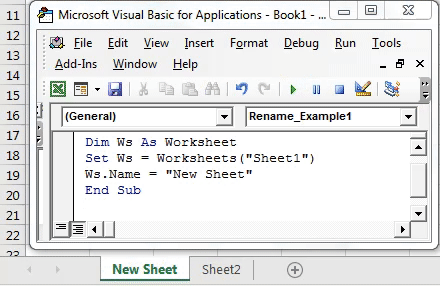
Imagine you want to rename sheets based on specific conditions or rules. Here’s how:
- Use the following script to rename sheets with a prefix or suffix:
Sub RenameSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim prefix As String Dim i As Integerprefix = "Sheet_" i = 1 For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name <> ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Name Then ' Exclude first sheet ws.Name = prefix & i i = i + 1 End If Next ws
End Sub
This can be modified to add any prefix or suffix you need.
In these VBA tricks, we've covered various techniques for managing sheet names, from simple listing to interactive dropdowns and automated renaming. These methods not only help in organizing your workbook but also in making it user-friendly and dynamic. Remember, while these scripts are straightforward, their implementation in your Excel workbooks can significantly enhance your productivity. Take the time to explore and customize these macros to fit your specific needs, which might include error handling, user prompts, or additional functionalities.
How do I run a VBA macro?

+
To run a VBA macro, press Alt + F8 to open the Macro dialog box, select your macro from the list, and click ‘Run’.
Can these macros be used on all versions of Excel?

+
Yes, these VBA macros should work on all versions of Excel that support VBA (which includes Excel 2007 and later versions).
What are the common errors when working with VBA macros?

+
Common errors include syntax errors, runtime errors due to missing references, worksheet naming conflicts, and security settings blocking macros from running.



