5 Ways to Spot Duplicate Values in Excel Sheets

Excel is an incredibly powerful tool used by millions to organize, analyze, and manipulate data. However, when dealing with large datasets, it's common to encounter duplicate values, which can skew your analysis or disrupt your data integrity. Here's how you can effectively identify these duplicates, ensuring your data remains clean and accurate.
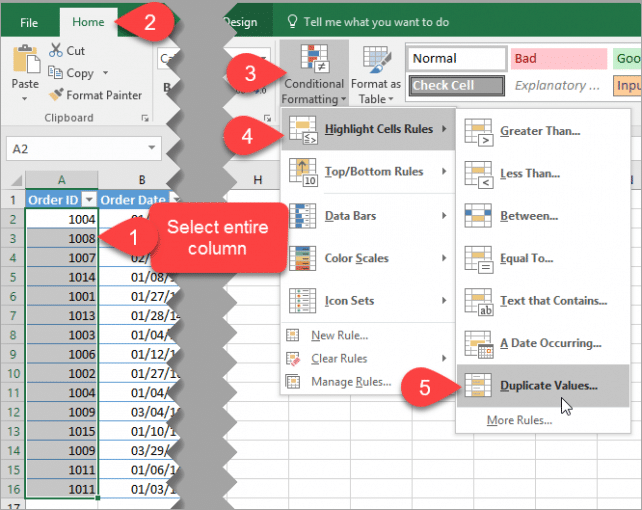
Using Conditional Formatting

One of the simplest ways to spot duplicates is through Excel’s Conditional Formatting feature:
- Select the range of cells where you want to find duplicates.
- Go to the ‘Home’ tab, click on ‘Conditional Formatting’, then select ‘Highlight Cells Rules’ > ‘Duplicate Values’.
- Choose how you want the duplicates to be highlighted, typically with a color fill.

Advantages:

- Immediate visual feedback helps in quickly identifying duplicates.
- It’s non-intrusive; your data remains unchanged.
📝 Note: Conditional Formatting only helps to visually mark duplicates, not to remove or organize them.
Advanced Filter

The Advanced Filter feature can sort or display duplicate records:
- Select the data range you are analyzing.
- Navigate to ‘Data’ > ‘Sort & Filter’ > ‘Advanced’.
- Choose ‘Filter the list, in-place’ or ‘Copy to another location’, then click on ‘Unique records only’ to exclude duplicates or see only duplicates by unchecking this option.
Benefits:
- Can extract unique values or identify duplicates with or without grouping.
- Allows for the creation of a new, duplicate-free dataset.
📝 Note: This method will alter your original dataset if you choose 'Filter the list, in-place', so consider using 'Copy to another location' for safekeeping.
Removing Duplicates with Excel’s Built-in Tool

Excel provides a straightforward method to remove duplicates:
- Select the range or table where duplicates reside.
- Go to ‘Data’ > ‘Remove Duplicates’.
- Select which columns to check for duplicates and hit ‘OK’.
Advantages:

- Quickly cleans data by removing duplicate rows.
- Allows for selective column-based comparison.
📝 Note: This action is not undoable, so ensure you have a backup of your data before proceeding.
Using Pivot Tables

Pivot Tables offer a dynamic way to check for duplicates:
- Select your data range.
- Navigate to ‘Insert’ > ‘Pivot Table’.
- Set up the Pivot Table with columns for checking duplicates, then in the ‘Value’ field, choose ‘Count of [Column Name]’.
Benefits:

- Provides a structured approach to see frequency counts.
- Can be expanded to sort and filter for further analysis.
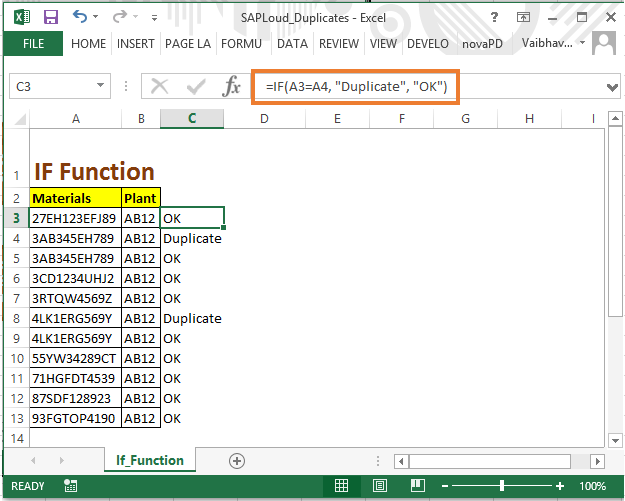
Using Formulas
If you need more control, formulas can be your allies:
- COUNTIF - Counts occurrences in a range:
=COUNTIF(Range, Criteria) - VLOOKUP - To check if a value appears elsewhere in the dataset:
=IF(COUNTIF(A:A, A2) > 1, “Duplicate”, “Unique”)
Considerations:
- Formulas are flexible but require basic understanding of Excel functions.
- They can be cumbersome to set up for large datasets but are powerful once configured.
In essence, these methods offer a comprehensive approach to dealing with duplicate values in Excel. Whether you need a quick visual check, a deeper analysis, or even data cleaning, Excel has tools tailored to your needs. Keeping your datasets free from duplicates enhances data accuracy, streamlines your work, and supports better decision-making processes.
Can I undo removing duplicates in Excel?

+
Once you remove duplicates, Excel does not provide an automatic way to undo this action. Ensure you save your data before removing duplicates or use ‘Copy to another location’ in the Advanced Filter method for a reversible approach.
How can I find duplicates based on multiple columns?

+
When using the ‘Remove Duplicates’ or ‘Conditional Formatting’ tools, you can choose multiple columns to identify duplicates based on combinations of these columns.
Is there a way to highlight duplicates automatically as I enter data?

+
You can use Conditional Formatting with a formula like =COUNTIF(A:A, A2) > 1 to highlight duplicates automatically as you input data. This will apply to the whole column.