Combine Excel Data from Two Sheets Easily

Managing data in Excel often involves bringing together information from multiple sources. Whether you're consolidating financial reports, merging customer databases, or aggregating survey results, combining data from different sheets into one can streamline your work significantly. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various methods to combine Excel data from two sheets with ease and efficiency.
Understanding Excel Workbooks and Sheets

Before diving into the methods, let’s briefly review the structure of an Excel workbook:
- A Workbook is the Excel file that can contain multiple sheets.
- A Sheet (or worksheet) is a single page within a workbook where you enter data.
📘 Note: It's vital to understand this structure, as all methods discussed will involve working across these elements.
Method 1: Manual Copy-Paste
This is the simplest method for beginners or when dealing with small datasets:
- Open both Excel files or ensure both sheets are in one workbook.
- Click on the first cell of the destination sheet where you want to combine data.
- Switch to the source sheet, select the data range you wish to copy, and press Ctrl + C.
- Return to your destination sheet, and paste with Ctrl + V or right-click and choose “Paste”.
Pros:

- Easy to understand and implement.
Cons:

- Time-consuming for large datasets.
- Risk of errors in large data sets due to manual selection and copying.
💡 Note: If you're only moving a small amount of data, this can be sufficient. However, for extensive or repeated tasks, consider more automated methods.
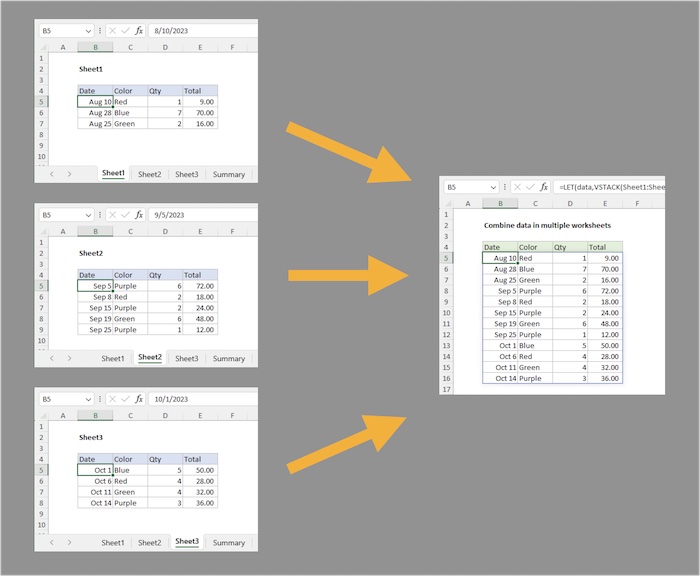
Method 2: Excel Formulas

For dynamic data linking, using Excel formulas like =Sheet1!A1 can be quite effective:
- Place your cursor in the first cell of your destination sheet where you want data to appear.
- Type the formula to reference the data from another sheet, for example,
=Sheet1!A1for the first sheet’s A1 cell. - Copy the formula down and across to fill in the rest of your data.
Pros:

- Data automatically updates when the source data changes.
- Useful for creating dynamic reports or dashboards.
Cons:

- Performance issues with very large datasets.
- Can be complex to manage many formulas, especially if sheets are in different workbooks.
✅ Note: Use this method when you need your destination data to stay current with the source.
Method 3: Power Query

For advanced users, Power Query offers a robust solution for merging and manipulating data:
- Access Power Query via the “Data” tab, then choose “Get Data”.
- Select “From Other Sources” -> “From Microsoft Query” or “From File” if sheets are in different workbooks.
- Load both sheets into Power Query, then use the “Append Queries” option to combine them.
- Refine your data with Power Query’s tools, and load the result back into Excel.
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Capable of handling large datasets | Requires learning a new interface |
| Offers extensive data manipulation options | Can slow down Excel if not used carefully |
| Automates repetitive data combining tasks | Might require manual steps for data refresh |

🚀 Note: Power Query is your go-to when you need more than just simple copy-pasting or formula linking.
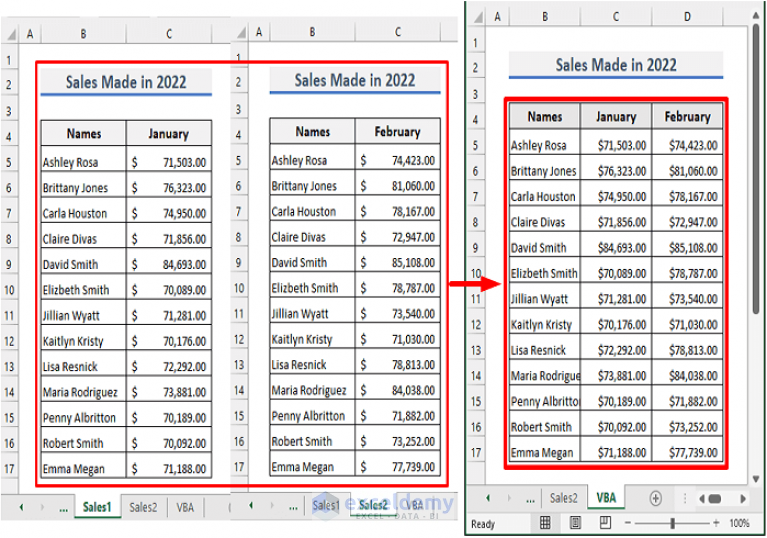
Method 4: Using Excel Macros (VBA)

For automation and flexibility:
- Open the VBA editor by pressing Alt + F11.
- Insert a new module (Insert -> Module).
- Write or record a macro that copies and pastes or links data between sheets.
- Run your macro when needed, or set it to run automatically with triggers.
Pros:

- Automates repetitive tasks completely.
- Can handle complex scenarios and interact with external applications.
Cons:

- Requires knowledge of VBA programming.
- Macros can be disabled for security reasons on some systems.
🛠 Note: VBA is excellent for those who need custom solutions or want to automate their workflows extensively.
Each method for combining data from two Excel sheets has its strengths and is suited for different scenarios. Manual copy-paste suits small, infrequent tasks, while Excel formulas offer real-time updates for dynamic data sets. Power Query stands out for its ability to manage and manipulate large datasets with ease, and VBA macros provide unparalleled flexibility and automation for complex tasks.
Remember, the choice depends on your specific needs, the size of your data, how often you need to perform the operation, and your comfort level with Excel's more advanced features. By mastering these methods, you can significantly boost your efficiency in handling data in Excel, making your data analysis and reporting tasks more manageable and less time-consuming.
Can I combine data if the sheets are in different workbooks?
+
Yes, you can combine data from sheets in different workbooks using all four methods described above. For Power Query and VBA, you might need to define file paths or use Excel’s external data connection features.
How do I ensure data accuracy when combining data?

+
Use formulas or Power Query with strict column matching, and always perform a reconciliation check. Additionally, using Excel’s data validation rules and cross-referencing can help maintain accuracy.
What if my datasets have different structures?

+
If datasets differ structurally, you’ll need to use Power Query or VBA to align data. Power Query can be particularly useful in such cases as it allows for transforming data before combining it.



