Effortlessly Sum Values Across Excel Sheets: A Simple Guide

Managing large datasets often involves working with multiple Excel spreadsheets. For data analysts, accountants, or anyone who relies on spreadsheets for tracking or reporting, the ability to sum values across different sheets can be incredibly useful. This guide will walk you through a simple method to sum values across different sheets, making your data compilation and reporting more efficient.
Understanding Excel Sheets and Ranges

Before diving into the summing process, let's first understand the basics of Excel sheets and cell ranges:
- Sheets: Excel documents are composed of sheets, which are essentially separate pages within one file.
- Ranges: A group of cells can be defined as a range, which can be referenced in formulas to sum or manipulate data.
🔍 Note: It's essential to organize your data consistently across sheets to make summing easier.
Step-by-Step Guide to Sum Values
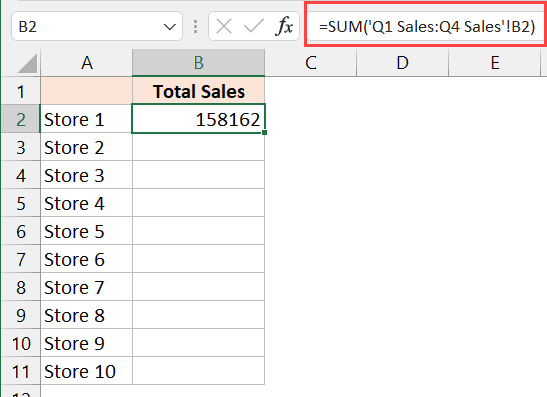
Consistent Structure
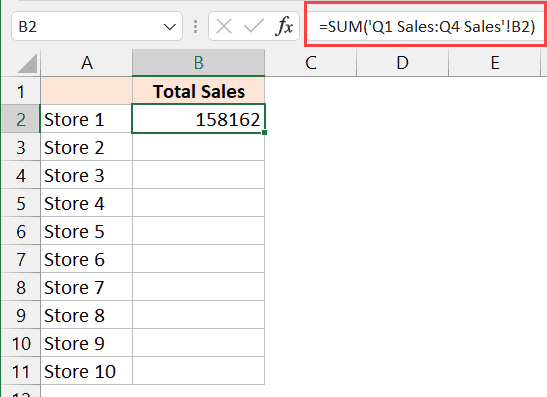
Ensure that each sheet has:
- A consistent layout with data in the same format or position.
- Correct cell references for data you wish to sum.
Using the SUM Function Across Sheets

Here is how to sum values across different sheets:
- Navigate to the sheet where you want to display the total sum.
- Click on the cell where you want the result to appear.
- Type in the SUM formula as follows:
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| =SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1) | Sum the values in cell A1 from Sheet1 through Sheet3. |
| =SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1:A5) | Sum the range A1 through A5 from Sheet1 through Sheet3. |

🔍 Note: The colon in the formula represents the range of sheets from the first named to the last named sheet.
Using 3D References

For summing across a range of sheets:
- Select the cell where you want the sum to appear.
- Type the formula:
=SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!B5)whereSheet1toSheet3are the names of your sheets, andB5is the cell you want to sum.
Using Excel Functions for Efficiency

If you're dealing with more complex data, you might benefit from:
- INDIRECT function to dynamically reference sheets.
- SUMIF or SUMIFS for conditional summing across sheets.
- Named Ranges for more manageable formulas.
Advanced Techniques
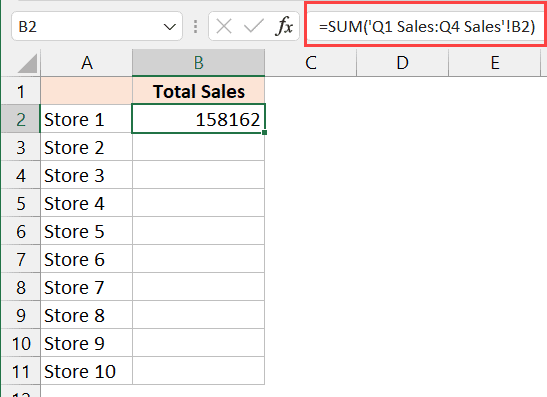
Dynamic Summation

Use functions like INDIRECT to refer to sheets whose names change:
- Create a formula like:
=SUM(INDIRECT(“‘”&A1&“’”&“!B2:B10”))where A1 contains the sheet name you want to reference.
Using Macros and VBA

For complex summing or automation:
- Create a macro or use VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) to loop through sheets and sum values. Here’s a simple example:
Sub SumAcrossSheets()
Dim sumValue As Double
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
sumValue = sumValue + ws.Range(“B2:B10”).Value
Next ws
MsgBox sumValue
End Sub
🔍 Note: VBA can automate repetitive tasks, saving time for extensive data analysis or reporting.
In this comprehensive guide, we've explored straightforward ways to sum values across multiple Excel sheets, from basic SUM formulas to using dynamic references and automation. By mastering these techniques, you enhance your ability to manage, analyze, and report data efficiently, turning complex tasks into manageable ones.
Can I sum values across non-adjacent sheets?

+
Yes, but you would need to sum each sheet separately in your formula or use VBA for more flexibility.
What if my sheets have different names?

+
You can use the INDIRECT function with a named range or reference cell to dynamically pull in sheet names for your SUM formula.
How can I sum values with conditions across sheets?

+
Use SUMIF or SUMIFS across multiple sheets by naming a range of cells or using an array formula to handle the conditions.



