How Long Should You Keep Income Tax Returns?

In the intricate world of personal finance, one question frequently echoes: how long should you retain your income tax returns? This inquiry isn't trivial, as tax documents are crucial for both legal and practical reasons, including tax audits, loan applications, and financial planning. Let's delve into the intricacies of tax return retention policies to help you navigate this essential aspect of financial management.
Legal Requirements for Keeping Tax Records

Legislation in many countries mandates the retention of financial records for a certain period. Here’s what you need to know:
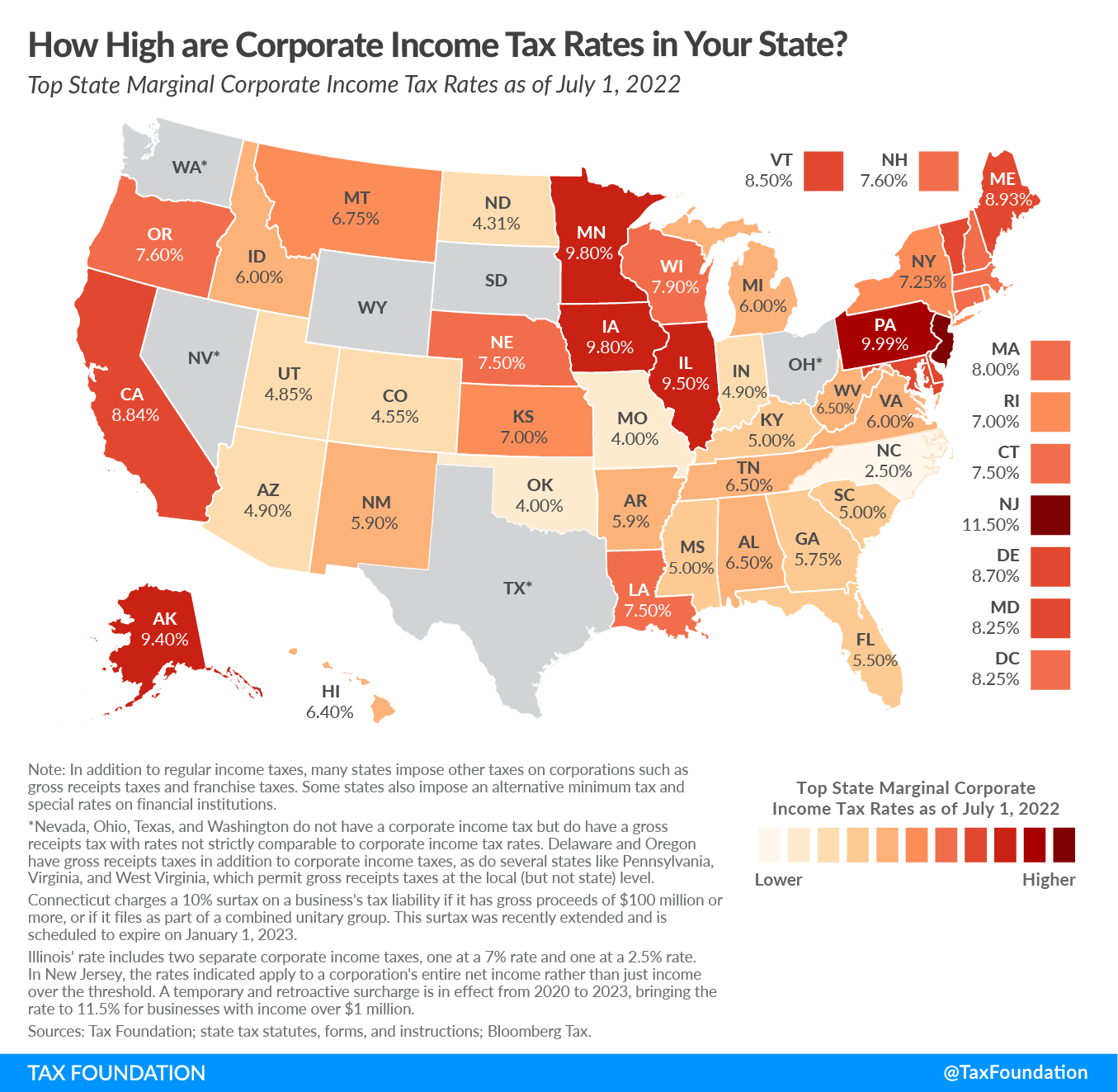
- United States: The IRS typically has three years from when you file your taxes to audit your return. However, in cases involving significantly under-reported income or fraud, this period extends to six years or indefinitely. Therefore, keeping tax returns and their related documents for at least seven years is generally advisable.
- Canada: The Canada Revenue Agency suggests keeping records for at least six years from the year-end of the tax year in question, but if you’ve claimed capital losses or have property transactions, you should keep records indefinitely.
- United Kingdom: HM Revenue & Customs requires individuals to keep records for at least five years from the 31st of January following the tax year, or longer if necessary.
Practical Reasons for Retaining Tax Returns
Beyond legal mandates, there are several practical reasons why you might want to keep your tax returns longer:
- Future Tax Filings: Older returns can serve as a reference when preparing your current or future tax filings, providing insights into past deductions and income reports.
- Financial Planning: Tax returns are a comprehensive record of your financial history, which can be invaluable for financial planning and managing wealth.
- Loan Applications: Lenders often request tax returns as part of loan applications for mortgages, car loans, or personal loans. Having a complete set of tax records can streamline this process.
- Retirement Planning: If you have a retirement account like an IRA or 401(k), your tax returns can help in understanding your tax implications during retirement.
Strategies for Efficient Tax Document Storage

To manage your tax documents effectively:
- Digital Storage: Consider scanning and saving your tax documents electronically. This approach reduces clutter and makes retrieval easy. Use a secure cloud service or external hard drive with backups.
- Physical Storage: If you prefer physical copies, use a fireproof, waterproof safe. Organize them by year and ensure they are easily accessible.
- Periodic Review: Annually or biennially, review your storage strategy to dispose of documents past their retention period or update your digital archives.
💡 Note: Ensure that your digital storage is secure and encrypted to protect sensitive financial data.
Conclusion

Retaining your income tax returns and related documents goes beyond mere legal compliance. It aids in financial planning, tax preparation, and even securing loans. While the legal minimums vary by country, adopting a seven-year retention period generally covers most scenarios. Implementing a robust storage strategy can save time, ensure your documents are safe, and provide peace of mind knowing your financial history is well-organized and accessible.
Can I shred tax returns after a certain number of years?

+
Once the legal retention period has passed and you no longer need the documents for financial planning or legal proof, you can shred your tax returns. Ensure that you are not disposing of documents prematurely if they are still needed for tax purposes.
What should I do if I’ve lost my tax returns?

+
Contact the relevant tax authority (e.g., IRS for the US, CRA for Canada) to request a copy or transcript of your tax returns. This service usually incurs no fee and can be an invaluable resource for past financial data.
Are electronic copies of tax returns valid during audits?

+
Yes, in most jurisdictions, electronic copies, particularly those with a secure audit trail, are acceptable during audits, provided they are legible and complete.