Combine Multiple Excel Sheets into One Easily

Merging multiple Excel sheets into a single, organized spreadsheet can significantly improve efficiency when dealing with large datasets or preparing comprehensive reports. Whether you are managing data across different departments or consolidating monthly sales figures from various stores, the process can be streamlined to save time and reduce errors. Here's how you can combine multiple Excel sheets into one with ease:
Preparation Steps

Before diving into the technical aspect, ensure:
- All sheets are in the same Excel file or accessible via network sharing if they are in separate files.
- The structure of data in each sheet is consistent (column headers match).
- Backup your data to prevent loss during the process.
Using Excel's Built-in Functions
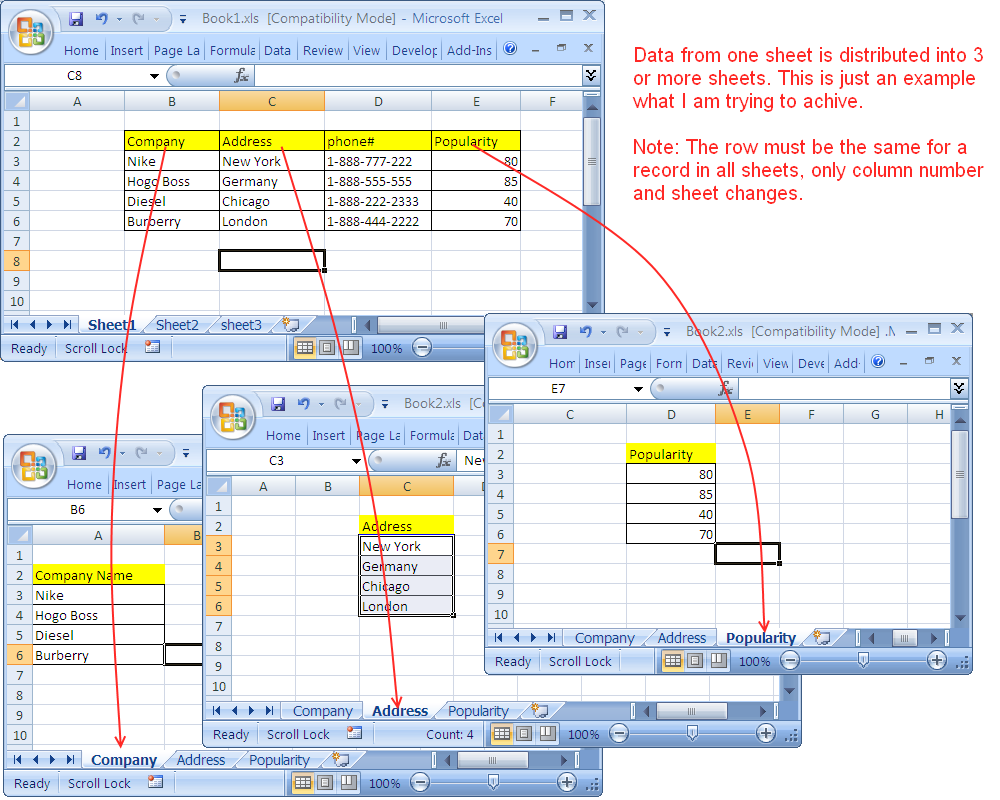
Excel offers several native functions that make combining sheets straightforward:
Power Query

Power Query is one of the most powerful tools for data manipulation in Excel:
- Open Excel and go to the Data tab.
- Click on Get Data, then From File, and select From Workbook.
- Navigate to and select your Excel file containing the sheets.
- In the Navigator window, check the sheets you want to combine, then click Load or Transform Data.
- If you choose Transform Data, you'll be able to:
- Append sheets: Use Append Queries from the Home tab in Power Query Editor.
- Merge sheets: Use Merge Queries to join data based on common columns.
- Click Close & Load to apply changes and bring data into Excel.
⚠️ Note: Ensure column names are identical across all sheets for seamless appending or merging.
VBA Macro

If you're comfortable with VBA, here's a basic script to merge sheets:
Sub CombineSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim combinedWs As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long, copyRow As Long
Set combinedWs = ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count))
combinedWs.Name = "CombinedSheet"
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name <> combinedWs.Name Then
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
copyRow = combinedWs.Cells(combinedWs.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row + 1
If copyRow = 2 Then ' Copy headers only once
ws.Range("A1:I1").Copy Destination:=combinedWs.Range("A1:I1")
End If
ws.Range("A2:I" & lastRow).Copy Destination:=combinedWs.Range("A" & copyRow)
End If
Next ws
MsgBox "Sheets combined successfully into " & combinedWs.Name
End Sub
Using Third-Party Tools or Add-ins

Several software solutions and add-ins can help with this task:
- XLSTAT - A statistical add-in for Excel with data merging capabilities.
- Merge & Combine Multiple Excel Files - An Excel add-in specifically for this purpose.
- PowerTools for Excel - Offers tools for data management including merging capabilities.
Automation and Best Practices

Once you've learned how to combine sheets, consider:
- Automating the process with Power Automate or scheduled scripts if you deal with recurring data.
- Standardizing data entry across departments to ensure consistency.
- Documenting the process for future reference and training.
Wrapping Up

Combining Excel sheets not only organizes your data but also opens up new avenues for data analysis, reporting, and decision-making. Whether through Excel's own tools like Power Query or VBA scripting, or using specialized third-party add-ins, the process can be adapted to various needs and levels of technical expertise. With the steps provided, you can now merge your Excel data efficiently, saving time, and enhancing data integrity.
Can I merge sheets from different Excel files?

+
Yes, you can use Power Query or VBA to combine data from multiple Excel files if they are accessible within the same network or loaded into Excel.
What should I do if the column headers do not match?

+
Standardize your data structure. Use Power Query or manually align headers before merging, or adjust your script to handle discrepancies.
How do I avoid duplicating data when combining sheets?

+
Before appending, use Power Query to remove duplicates, or structure your VBA script to check for existing entries in the destination sheet.



