How to Add a Dropdown Menu in Excel Easily
In today's digital age, spreadsheets are indispensable tools for organizing and analyzing data. Microsoft Excel, with its vast array of features, makes data management not only possible but intuitive. Among the many features that Excel offers, dropdown menus stand out for their ability to enhance efficiency in data entry, reduce errors, and streamline user interaction with the spreadsheet. Here, we delve into the practical steps for adding a dropdown menu in Excel, guiding users from novices to advanced learners.
Understanding Dropdown Menus in Excel
A dropdown menu, or dropdown list, in Excel, provides a list of options from which users can select one or more items. This functionality is useful in various scenarios, from simple data entry tasks to complex financial models where consistency and accuracy are paramount.
- Data Validation: Ensuring that only predefined items are entered.
- User Experience: Simplifying data input by guiding the user through a list of choices.
- Data Analysis: Making data sorting and filtering easier when dropdowns are used consistently across datasets.
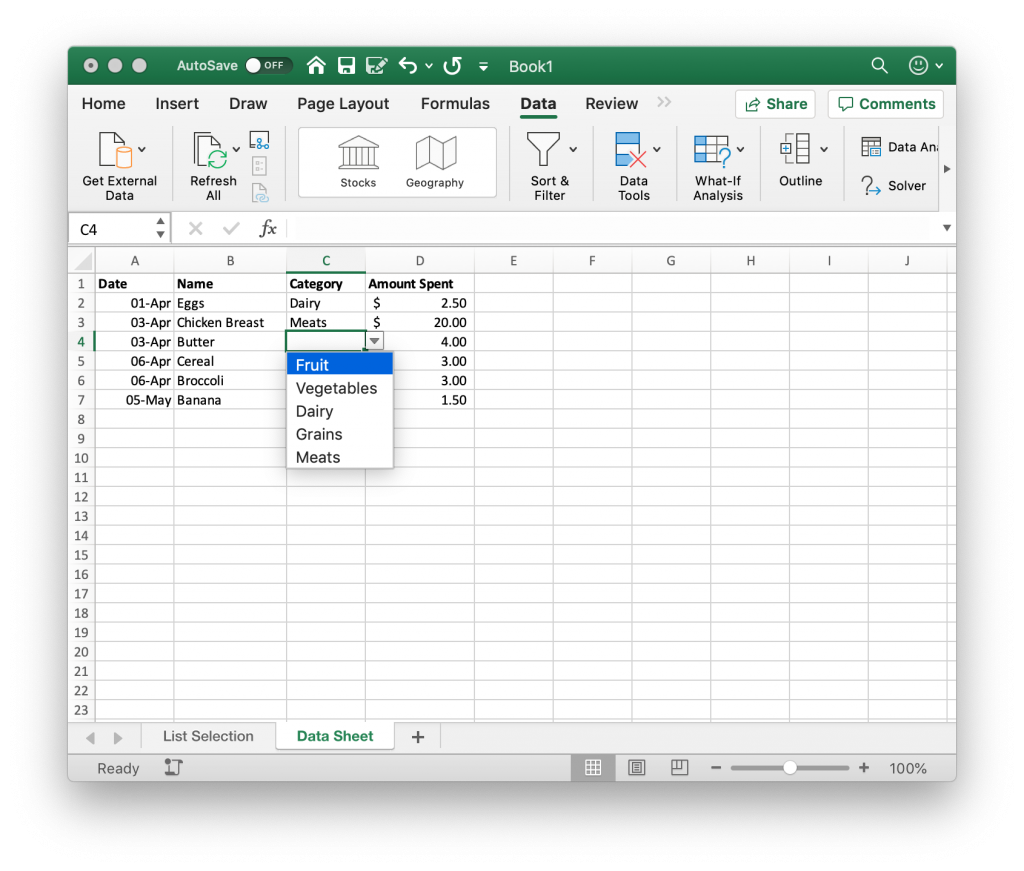
How to Create a Dropdown List

To create a basic dropdown list in Excel, follow these steps:
-
Select the Cell

Choose the cell where you want the dropdown to appear. For this example, let’s say it’s cell A1.
-
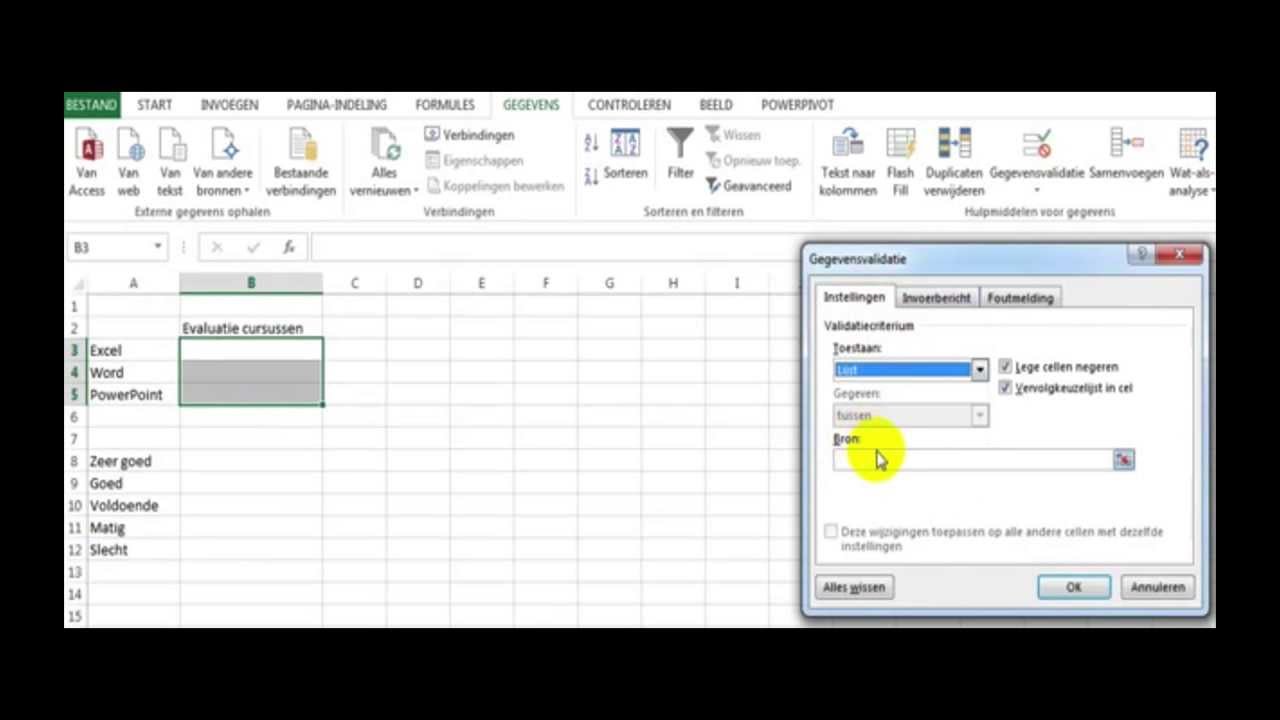
Data Validation Setup

Go to the Data tab on the Excel ribbon and select Data Validation.
-
Configure Validation

In the Data Validation dialog box, set these parameters:
- Allow: Choose List from the dropdown menu.
- Source: Enter the items for your dropdown, separated by commas. Alternatively, click the Expand Dialog button to select a range from the sheet.
-
Finalize Settings

Decide if you want to allow Empty or None (not recommended) for the dropdown and click OK.
🌟 Note: You can also include a source range from another sheet or workbook, but ensure it remains accessible when you move or share the workbook.
Advanced Dropdown List Options

Excel offers several enhancements to basic dropdown lists:
-
Dynamic Lists

Create a list that updates automatically with new entries using Named Ranges and OFFSET formulas.
-
Color-Coded Dropdowns

Use Conditional Formatting to change the dropdown’s background color based on the selected option.
-
Cascading Dropdowns
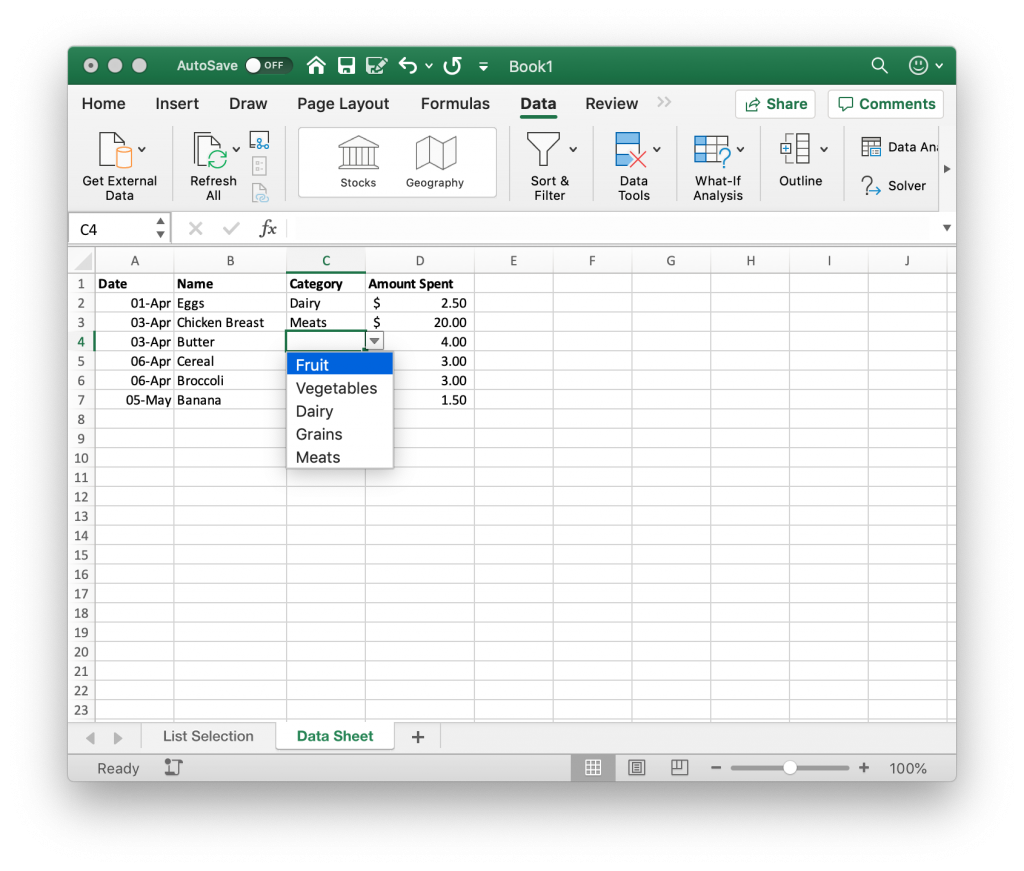
Set up dropdown menus that change based on previous selections, allowing for hierarchical data entry.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While setting up dropdown menus is generally straightforward, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Dropdown Not Appearing: Ensure you’ve used the comma correctly or that the source range isn’t empty or inaccessible.
- Items Not Updating: If using dynamic lists, check if the named range formula or data validation settings are set correctly.
- Multiple Selections: Excel doesn’t natively support multiple selections in a single cell. Consider using checkboxes or a helper column for multiple entries.
As we conclude this guide, remember that dropdown menus are a powerful feature in Excel that not only increase productivity but also ensure data integrity. By following the steps outlined here, you can empower your spreadsheets with this dynamic functionality, catering to various data entry and analysis needs.
Can I create a dropdown list from another workbook?

+
Yes, you can reference a range from another workbook as the source for your dropdown list. However, ensure that the workbook is open when you set up the list, and always keep it accessible when the main workbook is in use.
How do I add dropdown menus to an entire column?

+
To apply a dropdown list to an entire column, first select all the cells in the column, then follow the steps to create the list, ensuring the Source range is correctly referenced.
Can I create a cascading dropdown menu?

+
Yes, with some setup using Data Validation, Named Ranges, and formulas like INDIRECT to dynamically change the list based on previous selections.
What if I want to limit dropdown menu options?
+You can use Excel’s Data Validation settings to set limits on the number of selections, but for multiple selections, consider using separate cells or helper columns.