Excel Magic: Linking Two Sheets in Seconds

Mastering the art of data management in Microsoft Excel can significantly enhance your productivity and data analysis capabilities. A pivotal skill in this regard is the ability to link data between two sheets within an Excel workbook. Whether you're consolidating financial reports, tracking project progress, or managing inventory across departments, linking sheets can streamline your workflow and ensure data consistency. This guide will walk you through the process of linking two sheets in Excel, ensuring that your data updates dynamically and efficiently.
Why Link Sheets in Excel?
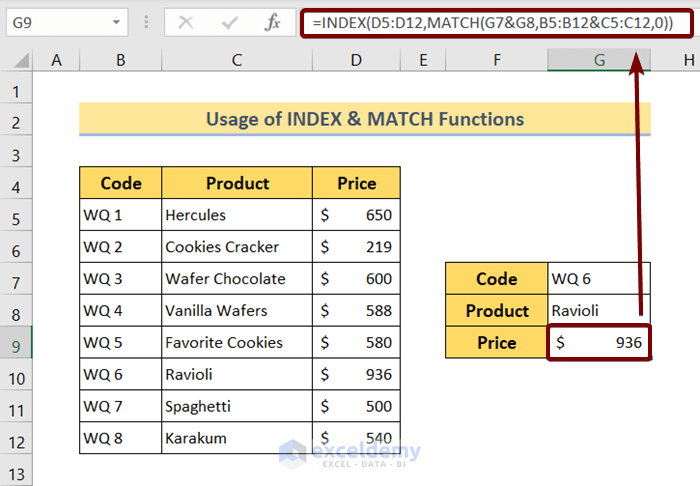
Linking sheets in Excel offers multiple benefits:
- Reduced Errors: Data changes only need to be entered once, reducing the chances of manual transcription errors.
- Efficiency: Automate data transfer, saving time in data entry and updates.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring consistency across related data sets.
- Real-time Updates: Any changes in the source sheet reflect immediately in linked sheets, making your data more dynamic.
Step-by-Step Guide to Linking Sheets

1. Preparing Your Sheets

Before you start linking, ensure:
- Both sheets are within the same workbook for simplicity.
- You have the source data ready where you want to pull information from.
2. Initiate the Link
Here’s how you can link data from one sheet to another:
- Click on the cell where you want the linked data to appear in the destination sheet.
- Press ‘=’ on your keyboard. This activates formula mode.
- Switch to the source sheet. You can click on the tab or use the shortcut Ctrl + Page Up/Page Down.
- Select the cell or range of cells you wish to link.
- Hit Enter. You’ll see the data from the source cell appear in your destination cell.
The formula in the formula bar will look like this: =SheetName!CellReference, where SheetName is the name of your source sheet, and CellReference is the cell or range you linked from.
3. Understanding the Formula

The formula you see in the formula bar indicates:
=initiates the formula.SheetName!specifies which sheet the data comes from.CellReferenceindicates the cell or range you’ve linked to.
When using the mouse to select cells, Excel automatically creates this formula for you. However, if you want to manually enter the formula, ensure you use the correct sheet name and cell reference.
4. Editing and Managing Links

Once the link is established:
- Updating Links: Any changes made to the source data will automatically reflect in the linked cell.
- Modifying Links: Click on the cell with the link, adjust the formula in the formula bar to point to a new cell or range if needed.
- Breaking Links: If you no longer need the link, simply enter a new value or formula directly into the cell.
Using Advanced Linking Techniques

For more complex scenarios:
Named Ranges

Named ranges can simplify linking and make formulas more readable:
- In the source sheet, select the range you want to name.
- Go to Formulas > Define Name and create a name for your range.
- In the destination sheet, instead of referencing cells, you can now use this name in your formulas:
=SheetName!RangeName.
Linking Across Workbooks

To link data between different Excel workbooks:
- Ensure both workbooks are open.
- In the destination workbook, enter the formula:
=[SourceWorkbook]SheetName!CellReference, whereSourceWorkbookis the name of the other workbook.
🔍 Note: When linking across workbooks, changes must be saved in the source workbook for the links to update in the destination workbook.
Using 3D References

3D references are useful when you want to link data across multiple sheets:
- The formula would look like
=SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1), summing A1 across Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3.
Linking sheets in Excel can transform the way you manage and analyze data, offering a level of automation and consistency that is invaluable in today's data-driven environment. By understanding how to link data efficiently, you can make your spreadsheets more dynamic and reduce the workload associated with data updates. This guide not only covers the basics of linking sheets but also delves into advanced techniques that can further enhance your Excel proficiency, making you adept at managing complex data sets with ease. Whether you're a beginner looking to grasp the fundamentals or an intermediate user aiming to harness Excel's full potential, linking sheets is a skill that will undoubtedly elevate your data management capabilities.
What is the benefit of linking sheets in Excel?

+
The primary benefits include reduced errors, increased efficiency, maintaining data integrity, and real-time updates across sheets.
Can I link data across different workbooks?

+
Yes, you can link data between different Excel workbooks by referencing the workbook name in your formula, for instance: =[SourceWorkbook]SheetName!CellReference.
What happens if I rename a sheet that is linked to another?

+
Excel will display a warning, and you’ll need to update all formulas manually to reflect the new sheet name. It’s best to rename sheets before setting up links or use named ranges for more stability.



