5 Quick Ways to Filter Data in Excel

Introduction to Data Filtering

Before diving into the technical ways, let's understand why filtering data is important in Excel. Data filtering allows you to isolate and analyze specific subsets of your data, making it easier to draw insights and perform detailed analysis without the clutter of unnecessary information. This is particularly useful in business analysis, research, or any scenario where large datasets need to be managed efficiently.
Basic Filtering Techniques

Excel provides several methods to filter data quickly:
- AutoFilter: The simplest method available through Excel's ribbon.
- Advanced Filter: For more complex filtering needs.
Using AutoFilter

Here's how to apply AutoFilter:
- Select your dataset.
- Go to the Home tab, then Sort & Filter, and click Filter.
- Click the arrow next to any column header to choose filter options.

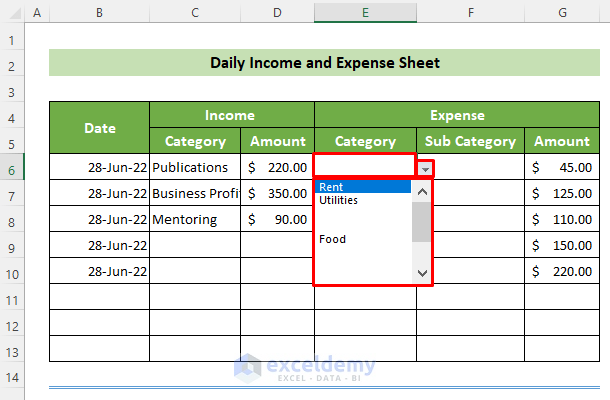
Advanced Filter

For criteria-based filtering:
- Select your dataset.
- Go to Data > Advanced under the Sort & Filter group.
- Specify the Criteria Range where you define your filter criteria.
🔍 Note: The Advanced Filter can work with complex criteria and even use formulas, but ensure your criteria are correctly formatted for accurate results.
Custom Filters

Custom filters allow for greater specificity:
- Text Filters: Begin with, ends with, contains, does not contain, etc.
- Number Filters: Greater than, less than, between, etc.
- Date Filters: Before, after, between, in the last, etc.
Filtering with Formulas

Excel’s formula-based filtering allows for dynamic filtering:
Using FILTER Function (Excel 365/Excel 2019 and later)

The FILTER function simplifies data filtering:
=FILTER(A2:B10, A2:A10=“Product A”, “No Match”)
💡 Note: This function dynamically filters data based on the specified criteria, adjusting as the data changes.
Using Dynamic Arrays

Excel’s dynamic array functionality can be leveraged:
=FILTER(A2:C10, (A2:A10=“Product A”)*(B2:B10>100))
This example filters for Product A with a sales value greater than 100.
Conditional Formatting

Although not a traditional filter, conditional formatting can visually filter data:
- Select your data range.
- Go to Home > Conditional Formatting.
- Choose a rule that highlights cells based on specific conditions.
Table Feature

Excel’s Table feature comes with built-in filtering options:
- Convert your data range into a table using Insert > Table.
- The filter dropdowns will appear automatically for each column header.
Quick Tips for Efficient Filtering

- Keyboard Shortcut: Use
Ctrl+Shift+Lto toggle filter on/off. - Clear Filters: Use Home > Sort & Filter > Clear to reset filters.
- Reapply Filters: Refresh filters after data changes by clicking the filter arrow and selecting “Reapply.”
To wrap up, the ability to filter data in Excel is an essential skill for anyone dealing with data analysis or management. By mastering these five quick methods—AutoFilter, Advanced Filter, Custom Filters, Filtering with Formulas, and utilizing the Table Feature—you can efficiently sort through large datasets to find the information you need. This not only enhances productivity but also ensures that you can derive meaningful insights from your data swiftly. Filtering helps in focusing on specific data points, making analysis easier, and ultimately leads to more informed decision-making processes in any field where data plays a crucial role.
Can I use multiple filters in Excel?

+
Yes, you can apply multiple filters by selecting filters from different columns or by using advanced filter criteria to refine your search further.
How can I filter by color in Excel?
+
Go to the filter dropdown arrow, select “Filter by Color”, and choose the color you’ve applied with conditional formatting or manual cell color selection.
What is the difference between AutoFilter and Advanced Filter?

+
AutoFilter is more user-friendly for basic filtering, whereas Advanced Filter allows for complex criteria using logical expressions or even formulas for precise filtering needs.
Is it possible to filter data based on text content?

+
Absolutely. Use custom text filters to find cells that contain, do not contain, begin with, or end with specific text.