Limit Your Excel Sheet: A Step-by-Step Guide

In the ever-evolving world of data management, Microsoft Excel has remained a steadfast tool, offering a blend of simplicity and depth that appeals to a wide range of users. Whether you're managing inventory, tracking project progress, or simply organizing personal data, Excel is often the go-to software. However, as your Excel sheets grow larger, managing and navigating through them can become challenging. This is where understanding how to limit your Excel sheet comes into play. Limiting an Excel sheet can streamline your workflow, reduce file size, enhance performance, and ultimately, make your data handling more efficient.
Understanding Excel Sheet Size Limitations

Before we delve into methods of limiting your Excel sheet, it's crucial to understand the built-in limitations. Microsoft Excel does not impose strict limits on row and column sizes, but practical limits do exist due to:
- Performance Issues: Large datasets can slow down processing times.
- Memory Constraints: Sheets with excessive data may consume too much memory.
- File Size: Larger Excel files become cumbersome to share and save.
Excel allows up to:
| Number of Rows | 1,048,576 |
| Number of Columns | 16,384 (Column XFD) |
| File Size | Approximately 2 GB |

Steps to Limit Your Excel Sheet

1. Remove Unnecessary Data
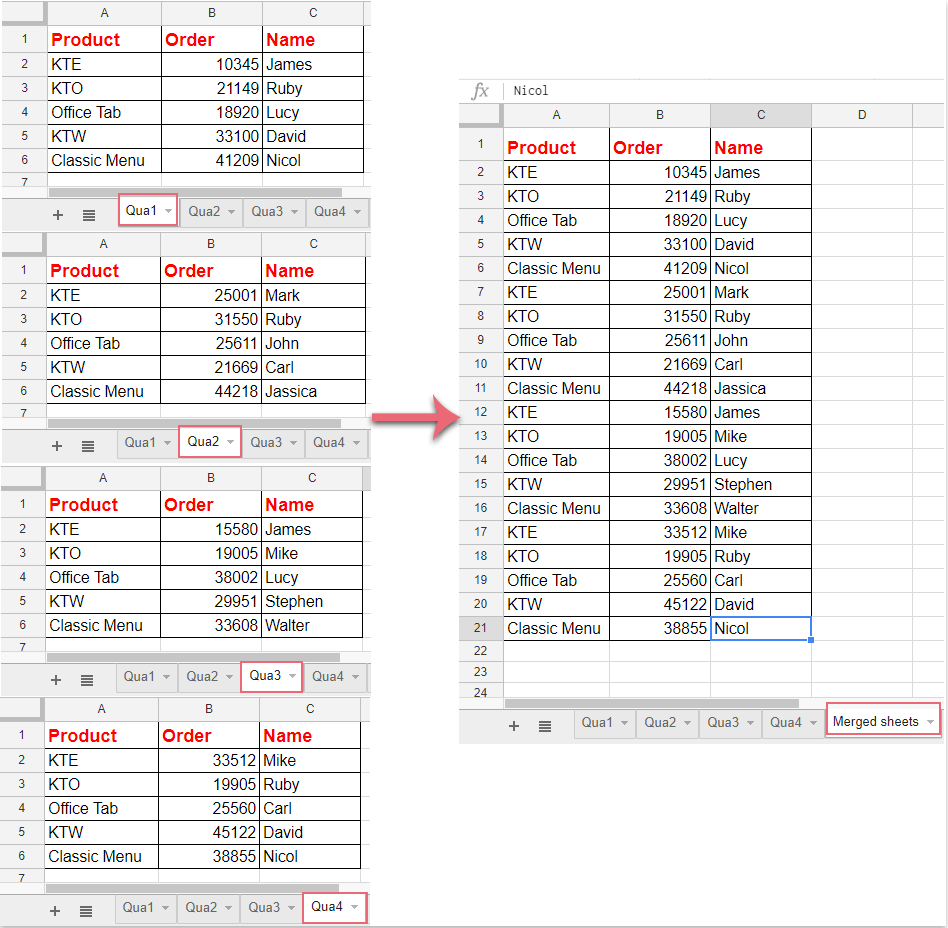
The most straightforward approach to limit your Excel sheet involves reviewing your data:
- Delete Irrelevant Columns and Rows: Go through your sheet and remove any columns or rows that are no longer needed or contain outdated information.
- Trim Unnecessary Formats: Often, old data retains formatting that isn’t required. Use Excel’s Clear Formats function (Home Tab > Clear > Clear Formats) to eliminate superfluous formatting.
2. Optimize Data Storage

Excel offers various features to optimize how your data is stored:
- Use Data Validation: Limit the data entry to predefined lists or ranges, which not only saves space but also ensures data integrity.
- Employ Lookup Tables: Instead of duplicating data, use VLOOKUP, INDEX/MATCH, or XLOOKUP functions to reference data stored in lookup tables.
- Convert to Named Ranges: Assign names to cell ranges frequently used, reducing cell addresses clutter in formulas.
3. Manage Formulas and Functions

Formulas can significantly increase the size and complexity of your workbook:
- Replace Formulas with Values: Once calculations are complete, you can replace formulas with their results to save on recalculation time.
- Use Volatile Functions Sparingly: Functions like NOW(), TODAY(), RAND(), and INDIRECT recalculate every time the workbook is opened or changed, affecting performance.
💡 Note: After replacing formulas with values, remember to save a copy of your workbook with the original formulas for reference or future edits.
4. Work with Excel’s Limitations

Excel has built-in settings to help manage file size and performance:
- Workbook Calculation Options: Set calculation to manual (Formulas Tab > Calculation Options) to control when your formulas are recalculated.
- Limit Number of Sheets: Only include necessary sheets in your workbook.
- Reduce Workbook Size: Compress or reduce the number of images and charts.
5. Use External Data Sources

Instead of storing all data within Excel:
- Import External Data: Use Excel’s data import features (Get & Transform Data) to periodically refresh from external sources.
- Link to External Files: Excel supports linking directly to other Excel files, allowing you to work with linked data rather than copying it over.
Enhancing Performance

Beyond limiting the size of your Excel sheet, here are steps to enhance overall performance:
- Close Unnecessary Files: Keep only the workbook you’re working on open to maximize available memory.
- Disable Add-Ins: If they’re not in use, turn off Excel add-ins through File > Options > Add-Ins.
- Use Conditional Formatting Sparingly: While useful, overuse of conditional formatting can slow down your workbook.
As we wrap up our guide on limiting your Excel sheet, remember that the key to effective Excel usage is balance. By managing the size of your Excel files, you can ensure a smoother workflow, faster calculation times, and less strain on system resources. These techniques not only enhance performance but also make your data management more sustainable and less error-prone.
Why should I limit my Excel sheet size?

+
Limiting your Excel sheet size reduces file size, speeds up calculations, and improves overall performance. It also makes your data more manageable and reduces the risk of errors or data corruption.
What if I need to keep all my data?

+
If you need to retain all your data, consider linking to external files or using external data sources to keep your Excel workbook lean while maintaining access to the information you need.
Can limiting my Excel sheet affect my data analysis?

+
Limiting your Excel sheet by removing unnecessary data or optimizing storage can actually enhance your data analysis by making it more focused and reducing the likelihood of errors. Ensure you maintain important data through proper documentation or backups.