5 Simple Steps to Translate Excel Sheets to English
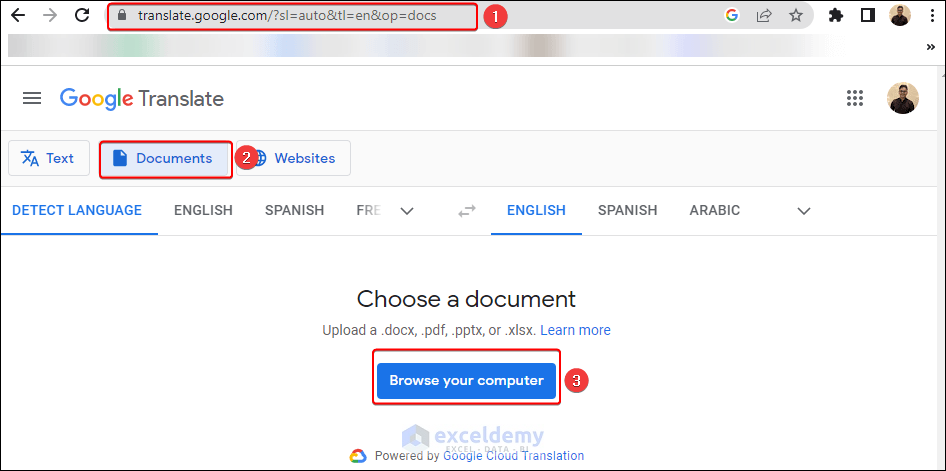
Translating Excel sheets from one language to another can be an essential task for businesses operating globally. Whether you're working on financial reports, customer data, or project management, ensuring everyone involved has access to the information in a language they understand is vital. In this guide, we'll explore five simple steps to translate Excel sheets to English, making your data accessible and clear to English-speaking audiences.
Step 1: Identify What Needs Translation

Before you begin translating, it’s crucial to determine which parts of your Excel workbook require translation. Here’s how:
- Open your Excel file and review the worksheets to find non-English text.
- Note specific cell ranges or sheets that contain text, formulas, or comments that need translation.
This step helps you to create a focused translation strategy, avoiding unnecessary work on already English or non-text elements.
Step 2: Use Automated Translation Tools

Leveraging automated translation tools can save time, especially when dealing with large datasets. Here’s what you can do:
- Select the cells with text you wish to translate.
- Use Microsoft’s built-in translation features or external add-ons like Google Translate for Excel or Translator++.
These tools can automatically detect source languages and translate content to English with just a few clicks.
Step 3: Manual Translation for Contextual Accuracy

Automated translations can sometimes miss the nuances or context of certain phrases. For precise accuracy, manual translation might be necessary:
- Review the machine-translated text for errors or misinterpretations.
- Consider having a fluent speaker or professional translator verify and correct the translations.
📝 Note: Some translations require an understanding of cultural or industry-specific context to ensure accuracy.
Step 4: Implement Translation in Excel
Once translations are ready, it’s time to integrate them back into your Excel sheet:
- Update the cells with the new translations.
- Ensure that the translated data is formatted correctly to maintain the integrity of your workbook.
- Consider using conditional formatting or macros to simplify the process.
| Action | Example |
|---|---|
| Original Text | “Este es un informe.” |
| Translated Text | “This is a report.” |
Step 5: Review and Quality Check

Translation is not just about changing words from one language to another; it’s also about ensuring the message retains its original intent. Here are some checkpoints:
- Proofread for spelling, grammar, and punctuation.
- Verify if formulas and functions still work correctly after translation.
- Check that the translated sheet maintains the same data structure.
🔍 Note: Regular quality checks are crucial, especially when dealing with sensitive data or critical business information.
To sum it up, translating Excel sheets to English involves identifying what needs to be translated, using automated tools for bulk translation, ensuring contextual accuracy through manual review, updating Excel with the new translations, and performing thorough quality checks. These steps ensure that your data is not only translated but also retains its functionality and relevance in an English-speaking environment.
What if my Excel file contains formulas that depend on the original language?

+
Formulas in Excel typically use cell references which remain constant regardless of the language in the cell content. However, ensure that any text within formulas (like sheet or named range references) is also translated, as some functions might use different names in different languages.
Can I automate the translation process for multiple Excel files?

+
Yes, with the help of macros or VBA scripts, you can automate the translation process across multiple Excel files. This requires some knowledge of programming in Excel, but it can significantly streamline the process.
Are there any limitations to using automated translation tools?

+
Automated tools might not always capture idiomatic expressions or industry-specific terminology correctly. Moreover, they can sometimes misunderstand the context, leading to translations that might need manual correction to maintain accuracy and cultural relevance.