5 Steps to Master Your Excel Balance Sheet Setup

Creating a balance sheet in Microsoft Excel involves much more than just entering numbers. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the 5 key steps to master your Excel balance sheet setup, ensuring your financial reports are both accurate and insightful.
1. Understanding the Balance Sheet Structure

Before delving into Excel, you need a solid understanding of what a balance sheet represents:
- Assets: Everything your business owns.
- Liabilities: Everything your business owes.
- Equity: What remains after subtracting liabilities from assets.
These components form the foundation of your balance sheet, which should balance with the equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
📌 Note: Ensure you understand the accounting principles behind each category for accurate setup.
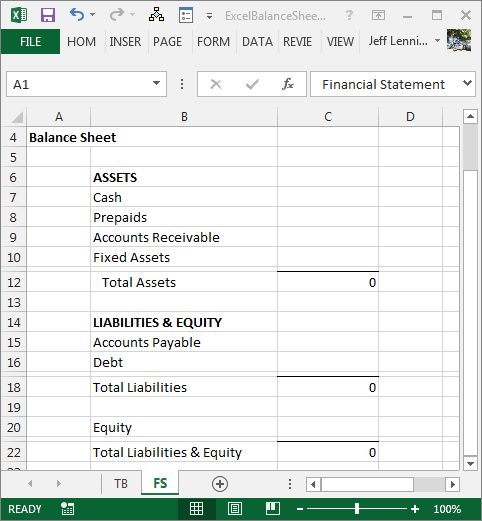
2. Setting Up Your Excel Workbook

Here’s how you can set up your Excel environment for balance sheet creation:
- Start with a Template: If you’re new, using a pre-built template can be helpful, but customizing it for your business is key.
- Organize Sheets: Use separate sheets for different sections like Assets, Liabilities, and Equity, or combine them into one sheet with clear headings.
- Formatting: Use bold text for headers, borders for cell separation, and conditional formatting to highlight important figures.
💡 Note: Customizing templates or using existing ones helps in setting up the basic structure without errors.
3. Entering Data Correctly
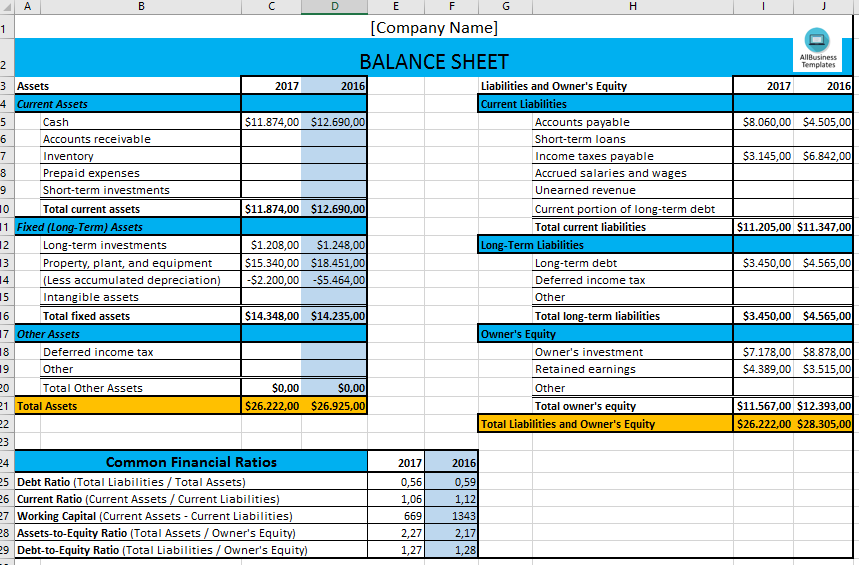
Inputting data with precision is vital:
- Data Accuracy: Double-check every figure entered.
- Date Handling: Use Excel’s date functions for consistency.
- Categorization: Place entries in the appropriate categories to maintain the balance sheet structure.
| Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Current Assets | Cash and items that can be converted to cash within one year | Cash, Accounts Receivable |
| Non-Current Assets | Items expected to provide economic benefits beyond one year | Property, Plant & Equipment |
| Current Liabilities | Debts due within one year | Accounts Payable, Short-term Loans |
| Non-Current Liabilities | Debts not due within one year | Long-term Loans, Bonds Payable |
| Equity | Shareholder's investment in the company | Common Stock, Retained Earnings |

🛠 Note: Ensure correct categorization to maintain the accuracy of financial reporting.
4. Calculating Balances and Formulas
Once your data is entered:
- Totaling Columns: Use SUM function to add up each column.
- Balance Verification: Ensure Assets equals Liabilities plus Equity using Excel formulas.
- Error Checking: Set up data validation and error checking rules.
🔍 Note: Double-check formulas to avoid miscalculations that can skew your financial reports.
5. Visualizing and Analyzing Data

Making your balance sheet data accessible and understandable:
- Charts: Use Excel’s charting tools to visualize trends in assets, liabilities, or equity.
- Conditional Formatting: Apply colors or icons to highlight key financial changes or potential issues.
- Data Tables: Create pivot tables for in-depth analysis of your financial data.
📊 Note: Visualization aids in understanding complex financial data quickly and effectively.
In this guide, we've explored how to master your Excel balance sheet setup. From understanding the structure and setting up your workbook to entering data, calculating balances, and visualizing your financial data, you're now equipped to handle your balance sheets with confidence. Keep in mind the importance of maintaining accuracy and integrity in your financial reporting to ensure your business thrives on solid financial insights.
How often should I update my balance sheet?

+
It's recommended to update your balance sheet at least monthly to keep track of your business's financial health. For dynamic businesses, weekly or even daily updates might be necessary.
Can I use Excel for my official financial reports?

+
Yes, Excel can be used for official financial reports. However, ensure your spreadsheet follows GAAP or IFRS standards and has internal controls for accuracy.
What if the balance sheet doesn't balance?

+
If your balance sheet doesn't balance, recheck your data entry for accuracy, ensure all formulas are correct, and verify the categorization of entries. Common issues include misclassification or clerical errors.
🔗 Note: This comprehensive guide aims to elevate your understanding of Excel balance sheet setup. Practice these steps, and your financial reporting will benefit from heightened accuracy and clarity.



