5 Ways to Rename Sheets in Excel VBA Easily

When working with extensive Excel workbooks, managing and organizing multiple sheets becomes crucial for efficient data handling. VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) in Excel offers a plethora of methods to streamline this process. Here are five simple yet effective ways to rename sheets in Excel using VBA.
Method 1: Rename Sheet with a Fixed Name
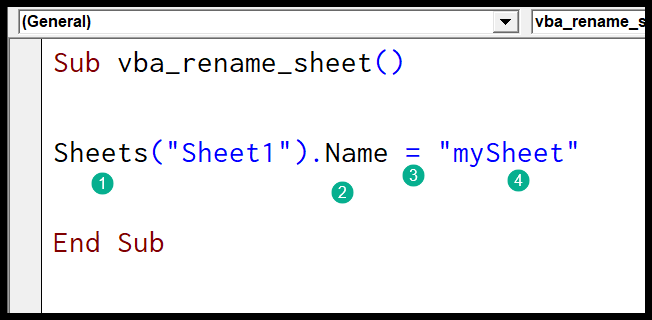
Begin by opening the VBA editor with Alt + F11. Here’s a straightforward VBA code to rename a sheet with a specific name:
Sub RenameSheet()
ThisWorkbook.Sheets(“Sheet1”).Name = “NewName”
End Sub
This code will rename “Sheet1” to “NewName”.
💡 Note: Ensure the sheet name already exists before attempting to rename it to avoid errors.
Method 2: Rename Multiple Sheets Based on a Pattern

If you have several sheets you wish to rename in a consistent pattern, VBA can automate this task:
Sub RenameMultipleSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim i As Integer
i = 1
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Sheets
If ws.Name Like “Report” Then
ws.Name = “Product Report ” & i
i = i + 1
End If
Next ws
End Sub
- This subroutine searches for sheets named like “Report” and renames them as “Product Report [Number]”.
- The number increments with each sheet renamed.
Method 3: Rename Sheets Using Input Box
To give users the ability to rename sheets interactively:
Sub RenameSheetInteractively()
Dim NewName As String
NewName = InputBox(“Enter the new sheet name”, “Rename Sheet”)
If NewName <> “” Then
ThisWorkbook.ActiveSheet.Name = NewName
Else
MsgBox “No name provided. The sheet remains unchanged.”
End If
End Sub
- This script prompts the user to enter a new name for the active sheet.
- If the user cancels or provides no name, it informs them that the sheet remains unchanged.
Method 4: Rename Sheets from an Array or List

When you have predefined names, you can use an array or a list to rename sheets:
Sub RenameSheetsFromList() Dim NewNames As Variant NewNames = Array(“Overview”, “Details”, “Summary”)Dim i As Integer For i = 0 To UBound(NewNames) ThisWorkbook.Sheets(i + 1).Name = NewNames(i) Next i
End Sub
- The sheet at index 1 gets renamed to “Overview”, index 2 to “Details”, and so on.
Method 5: Rename Sheets Based on Cell Content
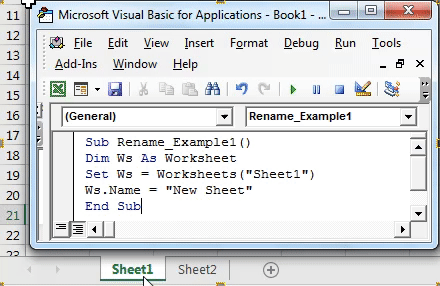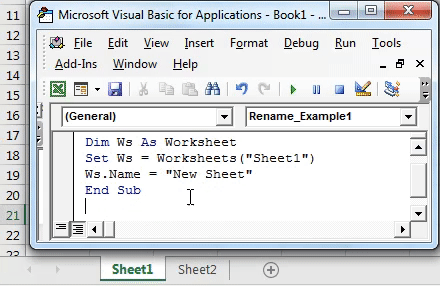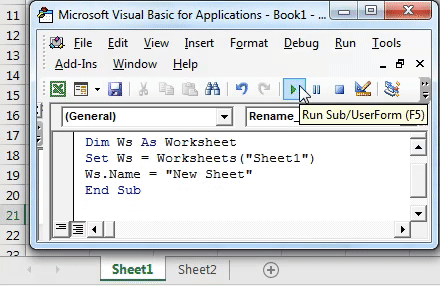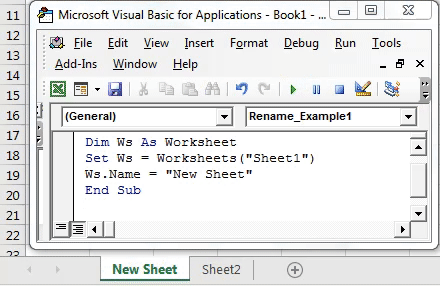
Here’s how to rename sheets dynamically based on the contents of a cell:
Sub RenameSheetFromCell()
Dim sh As Worksheet
For Each sh In ThisWorkbook.Sheets
If sh.Name <> “Summary” Then
sh.Name = sh.Range(“A1”).Value
End If
Next sh
End Sub
- Each sheet, except for “Summary”, gets renamed to the value in cell A1 of that sheet.
💡 Note: Excel has naming restrictions; names must not start with numbers or spaces, nor exceed 31 characters.
In summary, renaming sheets in Excel with VBA offers a wealth of options to automate and enhance your workbook management. Whether it's applying static names, using patterns, or dynamically basing names on cell content, these methods provide flexibility and efficiency. This can drastically improve productivity by reducing manual sheet management tasks, allowing users to focus on more analytical work.
Can VBA rename sheets in other workbooks?

+
Yes, by changing ThisWorkbook to the specific workbook you want to modify, like Workbooks(“OtherWorkbook.xlsx”).
How do I handle sheet names with special characters?

+
Excel restricts sheet names to certain characters. VBA can use the Replace() function to handle special characters by substituting them with acceptable ones.
What if the new sheet name already exists?

+
VBA will raise an error if you attempt to rename a sheet to a name that already exists. You can use error handling to manage such scenarios, perhaps by appending numbers to make names unique.
Is it possible to undo a VBA sheet rename?

+
No automatic undo option exists for VBA changes, but you can save the original names in an array before renaming and revert to those names if needed.
What is the maximum length for a sheet name in Excel?
+
A sheet name in Excel can be up to 31 characters long. VBA automatically truncates any name that exceeds this limit.