5 Ways to Read Excel in ASP.NET C#

Excel files are ubiquitous in the business world, serving as a standard medium for data exchange and reporting. For ASP.NET developers working with C#, integrating Excel functionality into web applications can significantly enhance data handling capabilities. This post will guide you through five effective ways to read Excel files in ASP.NET using C#, catering to different needs, skill levels, and project requirements.
1. Using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel

The Microsoft Office Interop libraries allow you to interact with Excel files directly through COM interop.
Setting Up

- Ensure that Microsoft Excel is installed on the server.
- Add a reference to Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel in your project.
Code Example

using Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;public void ReadExcelFile(string filePath) { Application excelApp = new Application(); Workbook wb = excelApp.Workbooks.Open(filePath); Worksheet ws = wb.Worksheets[1] as Worksheet;
for (int i = 1; i <= ws.Rows.Count; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= ws.Columns.Count; j++) { Range cell = ws.Cells[i, j]; if (cell.Value != null) Console.WriteLine(cell.Value); } } wb.Close(); excelApp.Quit();
}
⚠️ Note: This method requires an Office installation on the server and can be resource intensive.
2. Using ClosedXML

ClosedXML is a library for reading and writing Excel files without relying on Excel itself.
Setting Up

- Install the NuGet package:
Install-Package ClosedXML.
Code Example

using ClosedXML.Excel;public void ReadExcelFile(string filePath) { using (var workbook = new XLWorkbook(filePath)) { var worksheet = workbook.Worksheet(1);
foreach (var row in worksheet.Rows()) { foreach (var cell in row.Cells()) { if (cell.GetValue<string>() != null) Console.WriteLine(cell.GetValue<string>()); } } }
}
📝 Note: ClosedXML is lightweight and does not require Excel installation.
3. Using EPPlus
EPPlus is another excellent library for handling Excel files, which supports both xlsx and xls formats.
Setting Up

- Install the NuGet package:
Install-Package EPPlus.
Code Example
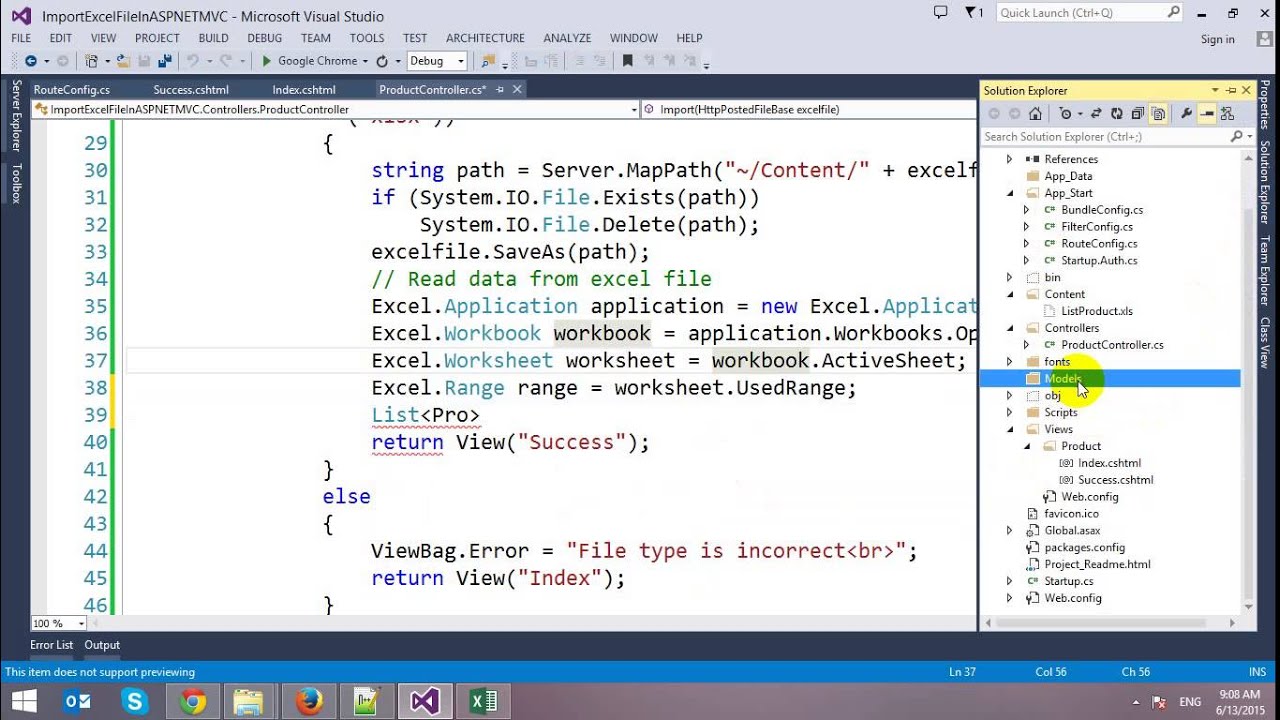
using OfficeOpenXml;public void ReadExcelFile(string filePath) { FileInfo existingFile = new FileInfo(filePath); using (ExcelPackage package = new ExcelPackage(existingFile)) { // Get the first worksheet ExcelWorksheet worksheet = package.Workbook.Worksheets[1]; int rowCount = worksheet.Dimension.Rows; int ColCount = worksheet.Dimension.Columns;
for (int row = 1; row <= rowCount; row++) { for (int col = 1; col <= ColCount; col++) { if (worksheet.Cells[row, col].Value != null) Console.WriteLine(worksheet.Cells[row, col].Value); } } }
}
4. Using ExcelDataReader

ExcelDataReader is perfect for reading .xls and .xlsx files without requiring Excel to be installed.
Setting Up
- Install the NuGet package:
Install-Package ExcelDataReader.DataSet.
Code Example
using ExcelDataReader;public void ReadExcelFile(string filePath) { using (var stream = File.Open(filePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { using (var reader = ExcelReaderFactory.CreateReader(stream)) { var result = reader.AsDataSet(new ExcelDataSetConfiguration { ConfigureDataTable = (_) => new ExcelDataTableConfiguration { UseHeaderRow = true } });
DataTable table = result.Tables[0]; foreach (DataRow row in table.Rows) { for (int i = 0; i < row.ItemArray.Length; i++) { if (row[i] != null) Console.WriteLine(row[i].ToString()); } } } }
}
5. Using ASP.NET Excel Libraries

There are commercial libraries like Aspose.Cells for .NET or GemBox.Spreadsheet, which offer advanced Excel manipulation capabilities.
Setting Up

- Obtain a license from the respective provider.
- Install the relevant NuGet package or reference the DLL.
Code Example (Aspose.Cells)

using Aspose.Cells;public void ReadExcelFile(string filePath) { // Instantiate a Workbook Workbook workbook = new Workbook(filePath);
//Access the first worksheet Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0]; //Get the number of rows and columns in the worksheet int rowCount = worksheet.Cells.MaxDataRow + 1; int colCount = worksheet.Cells.MaxDataColumn + 1; for (int row = 0; row < rowCount; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < colCount; col++) { string cellValue = worksheet.Cells[row, col].StringValue; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(cellValue)) Console.WriteLine(cellValue); } }
}
Each method for reading Excel files in ASP.NET C# comes with its own set of pros and cons, tailored to different scenarios:
- Interop.Excel is direct but resource-heavy.
- ClosedXML and EPPlus are lightweight and do not require Excel installation.
- ExcelDataReader offers simplicity and efficiency.
- Commercial libraries like Aspose.Cells provide extensive features but come at a cost.
In the pursuit of integrating Excel functionality into your ASP.NET applications, selecting the right tool or library depends on various factors including server resources, project scope, and financial considerations. The methods outlined above cover a spectrum from free, open-source solutions to powerful, paid options, enabling you to choose what best fits your project needs. Always ensure that your chosen method aligns with your application's architecture, security protocols, and maintenance strategy for the most seamless integration.
Can I use these methods for reading both .xls and .xlsx files?
+Yes, most of the libraries mentioned (ClosedXML, EPPlus, ExcelDataReader) support both .xls and .xlsx formats. Interop.Excel can also handle both, but remember it needs Excel installed on the server.
Are there any licensing issues I should be aware of?
+Commercial libraries like Aspose.Cells require licensing, which could be an additional cost. Make sure to check the terms for each library regarding commercial and production use.
How can I ensure data security when processing Excel files in ASP.NET?
+Ensure files are uploaded securely, validate file types before processing, handle exceptions properly, and sanitize any input data to prevent script injection or other vulnerabilities.
What are some common errors when reading Excel files?
+Common errors include file format incompatibility, Excel version issues, data type mismatches, memory leaks from unclosed resources, and server-side issues when using Interop.Excel.
Can these libraries handle large files?
+Yes, libraries like EPPlus and ClosedXML are optimized for performance and can handle large files, although streaming options should be used for very large datasets to manage memory effectively.