3 Simple Ways to Import Data from Another Excel Sheet

Working with data across multiple Excel spreadsheets is often necessary for businesses, researchers, and anyone who relies on data analysis. Importing data from one Excel sheet to another can seem daunting at first, but Excel provides several straightforward methods to accomplish this task. Let's explore three simple and effective ways to import data from another Excel sheet, enhancing your data management capabilities.
Using the Copy and Paste Feature

The simplest method to transfer data is through the age-old technique of copy and paste. Here's how to do it:
- Open both Excel workbooks - One should contain the data you wish to import, and the other should be where you want the data to go.
- Select the range of cells or entire sheet you want to copy in the source workbook.
- Press Ctrl + C to copy or right-click and choose 'Copy'.
- Switch to the destination workbook.
- Select the starting cell where you want to paste the data.
- Press Ctrl + V to paste or right-click and select 'Paste'.
📝 Note: Ensure that the formatting and data types are preserved while copying, especially if dealing with date values or numbers that require specific formatting.
Utilizing Excel's Get & Transform Tools

Excel 2016 and later versions offer powerful tools under the 'Get & Transform' section (also known as Power Query). Here’s how you can use it:
1. Open Power Query Editor

- From the Data tab in Excel, select 'Get Data' > 'From Other Sources' > 'From Microsoft Query'.
2. Choose the Data Source
- Choose 'Microsoft Excel' as the data source and select the workbook with the data you want to import.
3. Transform Data
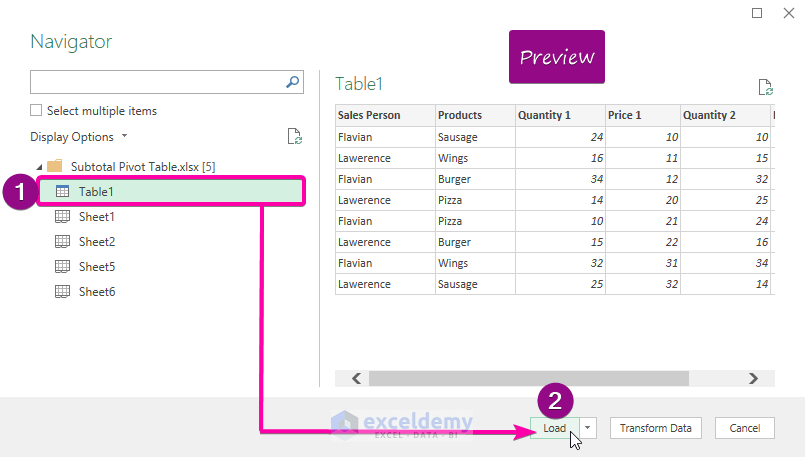
- Once the data is loaded, you can filter, sort, or clean the data before importing. This step is crucial for ensuring data integrity.
4. Load to Excel

- Click 'Close & Load' or 'Close & Load To' to bring the transformed data back into Excel.
This method is particularly useful for large datasets or when you need to perform data transformations before importing. Here's a visual guide:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Choose 'From Other Sources' |
| 2 | Select Workbook |
| 3 | Transform Data |
| 4 | Load Data |

👀 Note: Power Query is excellent for regular imports as it allows you to refresh data with just a click.
Using VBA for Dynamic Imports

Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can provide a more automated solution for those who need to import data frequently. Here's how to set up a VBA script:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA editor.
- Insert a new module (Insert > Module).
- Enter the following VBA code:
Sub ImportDataFromAnotherSheet()
Dim sourceWorkbook As Workbook
Dim destinationWorkbook As Workbook
Dim sourceSheet As Worksheet
Dim destinationSheet As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long, lastCol As Long
'Define the source and destination workbooks
Set sourceWorkbook = Workbooks("SourceWorkbook.xlsx")
Set destinationWorkbook = ThisWorkbook
'Select sheets
Set sourceSheet = sourceWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
Set destinationSheet = destinationWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1")
'Find the last row and column with data in the source sheet
lastRow = sourceSheet.Cells(sourceSheet.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
lastCol = sourceSheet.Cells(1, sourceSheet.Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
'Copy data from source to destination
sourceSheet.Range(sourceSheet.Cells(1, 1), sourceSheet.Cells(lastRow, lastCol)).Copy _
destinationSheet.Range("A1")
MsgBox "Data has been imported!"
End Sub
- Close the VBA editor and run the macro from Excel’s 'Developer' tab (you might need to enable it).
VBA allows for customization, enabling you to import data based on conditions, specific ranges, or even external events like a button click or a time-based trigger.
End Note

Importing data from another Excel sheet can be as simple or as complex as your workflow demands. From the basic copy-paste method suitable for small, occasional tasks to the advanced capabilities of Power Query or VBA for repetitive, large-scale data management, Excel provides a toolset for all levels of user proficiency. By choosing the right method, you can streamline your data analysis process, ensure data accuracy, and save time. Remember, the key to effective data management is not just importing data but also maintaining its integrity, ensuring its relevance, and keeping your workflow efficient. Whether it's for business analysis, research, or personal use, mastering these import methods can significantly enhance your productivity and data handling skills. In your data journey, these techniques serve as fundamental tools to harness the full potential of Excel, making it an indispensable resource in your data manipulation arsenal. Let these methods be your guide to more organized, accurate, and streamlined data management.
Can I import data from a closed workbook without opening it?

+
Yes, you can use VBA to import data from a closed workbook by using the ‘ADODB.Connection’ object to connect to the Excel file without opening it. This method requires a bit more setup but can be very useful for automating data imports from multiple files.
How do I handle errors when importing data with VBA?
+
VBA provides error handling with ‘On Error Resume Next’ and ‘On Error GoTo [label]’ which allows you to manage unexpected issues. You can also use ‘Err.Number’ and ‘Err.Description’ to log or handle specific errors gracefully.
What should I do if the source workbook changes its structure frequently?

+
If the source workbook’s structure changes often, it’s advisable to use Power Query. It has options for handling changes in structure, allowing you to dynamically adjust to new data layouts with minimal intervention.