Excel Lookup Guide: Find Values Across Sheets Easily

In today's fast-paced work environment, Microsoft Excel remains a crucial tool for data analysis and management. One of Excel's most powerful features is its ability to perform lookups across different sheets. This Excel Lookup guide will walk you through how to easily find values in different sheets, enhancing your productivity and accuracy in data handling.
Understanding Excel Lookup Functions

Before diving into specifics, let's understand some of the key lookup functions in Excel:
- VLOOKUP - Searches for a value in the first column of a range and returns a value in the same row from another column.
- HLOOKUP - Similar to VLOOKUP, but searches horizontally across rows instead of vertically.
- INDEX and MATCH - A more versatile lookup combination than VLOOKUP, allowing you to look up both rows and columns.
These functions are foundational for any Excel user who needs to reference data from multiple sheets or workbooks.
How to Use VLOOKUP Across Sheets

Here's a step-by-step guide on using VLOOKUP to find values in another sheet:
1. Set Up Your Sheets

Ensure you have your source data in one sheet and the sheet where you want to place the lookup results.
2. Write the VLOOKUP Formula

The syntax for VLOOKUP is:
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
- lookup_value: The value you want to find.
- table_array: The range of cells that contains the data.
- col_index_num: The column number in the table array from which to retrieve the value.
- range_lookup: TRUE for an approximate match or FALSE for an exact match.
When referencing data from another sheet, include the sheet name in the table_array:
=VLOOKUP(A2, 'SheetName'!A:B, 2, FALSE)
3. Drag Down or Copy the Formula
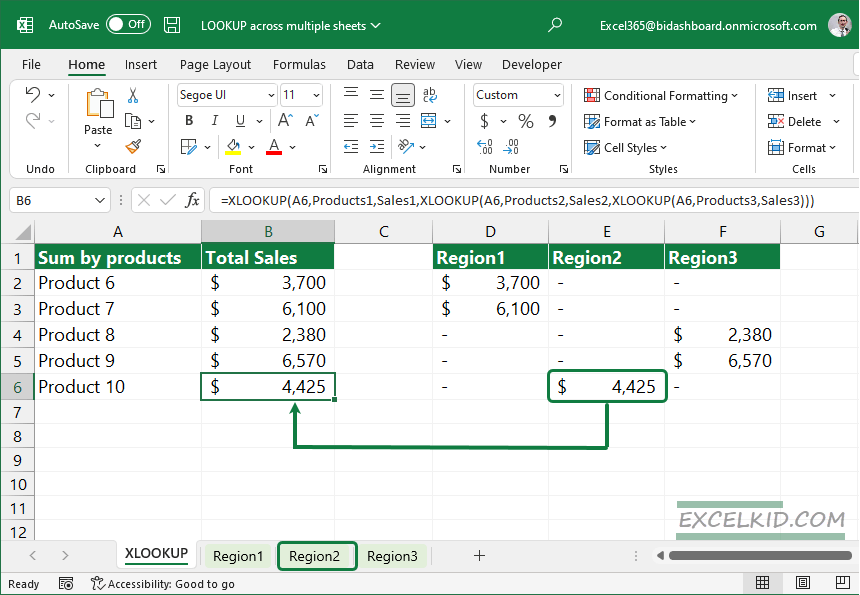
Once you have the formula, drag it down or copy it to fill the column.
💡 Note: Remember, if the sheet name contains spaces, use single quotes around it like 'Sheet Name'!
Using HLOOKUP Across Sheets

HLOOKUP is less common but can be very useful when dealing with horizontal data:
1. Set Up Your Sheets

Similar to VLOOKUP, ensure you have the source data and the sheet for lookup results.
2. Write the HLOOKUP Formula

The syntax for HLOOKUP is:
=HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, [range_lookup])
Where:
- row_index_num: The row number in the table array from which to retrieve the value.
Example:
=HLOOKUP(B1, 'SheetName'!A1:D4, 2, FALSE)
3. Drag Across or Copy the Formula

Copy or drag this formula across rows where needed.
Combining INDEX and MATCH Functions
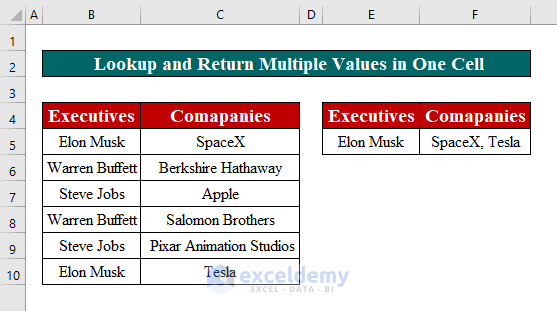
While VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP are straightforward, INDEX and MATCH provide more flexibility:
1. INDEX and MATCH Syntax

The INDEX function returns the value of a cell in a table based on the row and column number:
=INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num])
MATCH returns the position of a value within a range:
=MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type])
2. Combine for Lookup

Example for vertical lookup:
=INDEX('SheetName'!B:B, MATCH(A2, 'SheetName'!A:A, 0))
And for a horizontal lookup:
=INDEX('SheetName'!2:2, MATCH(B1, 'SheetName'!1:1, 0))
💡 Note: This method is especially useful when your table's columns or rows might change, as it dynamically finds the position of the value you need.
Advanced Tips for Efficient Lookups

- Named Ranges: Define named ranges to simplify your formulas. For example, if 'Sheet1' has a column named 'Data', you can reference it as:
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, Data, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(lookup_value, Data, 2, FALSE), "Not Found")
In wrapping up this guide on Excel lookups across sheets, it’s clear that mastering these functions can significantly enhance your efficiency with Excel. Whether you’re performing simple lookups with VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP or using the more flexible INDEX and MATCH, understanding how to navigate through different sheets is vital.
These techniques not only streamline your workflow but also ensure accuracy in data analysis, saving you time and potential errors. By applying the steps outlined, you’ll be better equipped to manage large datasets, perform dynamic lookups, and maintain organized spreadsheets.
Remember that practice will improve your proficiency with these functions. Experiment with different scenarios to see how each lookup method can benefit your specific data management tasks. With these tools in your Excel toolkit, you’re well on your way to becoming a data management wizard.
Can I use VLOOKUP to find values across multiple sheets simultaneously?

+
VLOOKUP by itself does not support looking up across multiple sheets at once. However, you can nest multiple VLOOKUPs or use helper columns to achieve this functionality.
What is the advantage of using INDEX and MATCH over VLOOKUP?

+
INDEX and MATCH are more flexible because they can look up values both horizontally and vertically. They’re also more efficient when dealing with large datasets, as MATCH can perform faster searches, and INDEX can retrieve data without shifting columns.
How can I handle errors when using Excel lookup functions?
+
Use the IFERROR function to wrap your lookup formulas. This allows you to return a custom message or value when the lookup function encounters an error, like if the lookup value is not found.
Why does my VLOOKUP return #N/A when I know the value exists?
+
This can occur for several reasons: The lookup value might not match exactly, including formatting like trailing spaces or case sensitivity. Also, check if your table array includes the column with the lookup value as its first column.