Link Multiple Excel Sheets: A Step-by-Step Guide

If you've ever found yourself managing complex data across multiple Excel sheets, you know the importance of organizing this information efficiently. Linking sheets is a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to connect different sheets within the same workbook or even across different workbooks. This tutorial will guide you through the process of linking multiple Excel sheets with step-by-step instructions, ensuring you can manage and analyze your data with ease.
Understanding the Basics of Excel Sheet Linking
Linking in Excel essentially means connecting two or more cells or ranges from different worksheets or workbooks in such a way that data entered into one cell automatically updates in another. This is incredibly useful for:
- Summarizing data from multiple sources.
- Consolidating data for analysis or reporting.
- Maintaining consistency across datasets.
Preparatory Steps Before Linking

Before you start linking sheets, make sure:
- You have your workbooks saved to avoid losing unsaved data.
- All workbooks you intend to link are open.
- Your data is structured and organized for linking.
Linking Sheets Within the Same Workbook

Step 1: Identify the Source Data

Select the cell or range of cells you want to link from. Let’s say we are linking from a sheet named “Sales” with data in cell B2.
Step 2: Navigate to the Destination Sheet

Go to the sheet where you want the linked data to appear. Suppose this sheet is named “Summary.”
Step 3: Create the Link
In the “Summary” sheet, click on the cell where you want the linked data to show. Type an equal sign (=) to start a formula, navigate back to the “Sales” sheet, and click on the cell B2. Now press Enter. The formula should look like:
=Sales!B2
This formula tells Excel to display the data from cell B2 in the “Sales” sheet in the selected cell in the “Summary” sheet.
Step 4: Verify the Link

Check that the data updates correctly by making a change in the source cell. The destination cell should reflect this change immediately.
🔄 Note: Always verify links after creation to ensure they are working as expected.
Linking Sheets Between Different Workbooks

Step 1: Open Both Workbooks
Ensure both the source and destination workbooks are open.
Step 2: Select the Source Data

Go to the source workbook and select the cell you want to link from.
Step 3: Create the Link

Move to the destination workbook, select a cell, and type an equal sign (=). Now, either manually type the full path to the source workbook followed by the sheet name or use the Windows File Explorer to find and select the workbook:
’[Source Workbook Name.xlsx]Sheet1’!A1
Or, with the source workbook in focus, select the cell, type ‘=’, then switch to the destination workbook and click the cell where you want the link to appear. The link should look like:
‘C:[Source Folder\Source Workbook Name.xlsx]Sheet1’!A1
Press Enter. Excel will create the link.
Step 4: Verify the Cross-Workbook Link
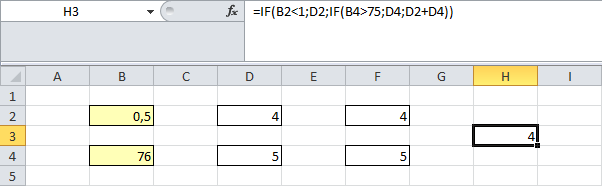
Make changes in the source workbook to ensure the data reflects in the destination workbook. Remember that workbooks must be opened at the same time for updates to happen automatically.
🔗 Note: When linking across workbooks, both files must be open for the links to update dynamically.
Advanced Linking Tips

Dynamic Linking with Named Ranges

Instead of cell references, you can use named ranges for better readability and manageability. Here’s how:
- Define a named range in the source sheet (e.g., “SalesData”).
- Link using the named range:
’[Source Workbook Name.xlsx]Sheet1’!SalesData
Or within the same workbook:
=Sheet1!SalesData
Using 3D References

When dealing with similar data across multiple sheets, 3D references can consolidate data. Here’s how:
=SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1)
This formula would sum the value in cell A1 from Sheet1 through Sheet3.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

- Broken Links: Ensure file paths are correct and files exist.
- Updating Links: In Excel, go to Data > Edit Links to refresh links.
- Performance: Large numbers of links can slow down Excel. Consider using VLOOKUP or other functions for large datasets.
This guide should equip you with the necessary skills to link multiple Excel sheets, ensuring that your data management is streamlined and your analysis is more effective. Remember to always organize your data structure before linking to ensure the best results, and take advantage of Excel's dynamic linking capabilities to enhance your workflow.
Why are my links not updating automatically?
+Links won’t update automatically if workbooks are closed, files are moved, or permissions are restricted. Ensure all linked files are open, paths are correct, and check for any Excel settings that might prevent automatic updates.
How do I create a two-way link between cells?
+Excel does not natively support two-way linking. However, you can use VBA scripting or manually update both cells when a change occurs in either one.
Can I link sheets across different versions of Excel?
+Yes, you can link sheets across different versions of Excel, but be aware of potential compatibility issues, especially with new functions or features in newer versions that might not be supported in older ones.
What happens to the link if I move or rename a workbook?
+If you move or rename a workbook, the links might break unless you update the file path manually. Excel will prompt you to update or break the links during such changes.
How do I prevent users from editing my linked data?
+Lock the cells or protect the sheet/workbook where the source data resides. Use cell protection options under the Review tab in Excel.