Import Excel Sheets into MATLAB: A Simple Guide

How to Import Excel Sheets into MATLAB: A Comprehensive Guide

If you’re delving into data analysis or simulation, MATLAB’s powerful computing capabilities make it an excellent tool for handling complex mathematical operations and visualizations. Among its many features, importing data from external sources like Excel sheets is crucial. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you import Excel files into MATLAB with ease.
Preparing Your Excel Sheet for MATLAB Import

Before diving into MATLAB, ensure your Excel file is formatted correctly:
- Check that all required data is in tabular form.
- Ensure no merged cells exist in the data region.
- Format numbers, dates, and texts appropriately to prevent misinterpretation.
Using MATLAB’s Import Tool

MATLAB provides an intuitive interface for importing data:
- Open MATLAB and navigate to the Home tab.
- Click on Import Data or readtable for a more programmatic approach.
- Select your Excel file from the file selection dialog.
- Choose the specific sheet if your Excel file contains multiple sheets.
- Preview the data in the Import Tool, where you can adjust:
- Range selection.
- Column headers.
- Data types and formatting.
- Click Import Selection to bring the data into your MATLAB workspace.
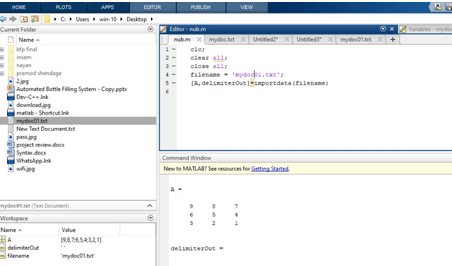
Programmatic Import with MATLAB Functions
If you prefer scripting or need to automate the import process:
Using xlsread Function

The xlsread function reads numeric and text data from an Excel file:
% Importing data from the first sheet
[num, txt, raw] = xlsread(‘path_to_your_file.xlsx’, 1);
Using readtable for Structured Data

For more complex data structures, readtable is preferable:
% Importing the entire worksheet named ‘Sheet1’
T = readtable(‘path_to_your_file.xlsx’, ‘Sheet’, ‘Sheet1’);
Handling Large Files or Ranges

If you’re dealing with large datasets, you might specify ranges:
% Importing a specific range from sheet 2
[,,rawData] = xlsread(‘path_to_your_file.xlsx’, 2, ‘A1:D20’);
⚠️ Note: The `xlsread` function is less optimal for large datasets due to memory constraints. Consider using `readtable` or `readcell` for more efficient processing of extensive data.
Post-Import Data Manipulation

Once you’ve imported your data, MATLAB offers tools to manipulate and analyze it:
- Data cleaning: Use functions like
ismissing,fillmissing, anduniqueto clean your dataset. - Type Conversion: Convert data types using
cell2mat,num2cell, ordatetimefunctions. - Indexing: Subset your data with logical indexing for quick filtering.
💡 Note: When cleaning data, consider backup versions of your dataset to preserve the original data integrity.
Understanding how to efficiently import and manipulate Excel data in MATLAB opens up numerous possibilities for data analysis, from statistical computations to time-series forecasting. Here's how you can sum up your learning:
The process of importing Excel data into MATLAB involves preparation, selection of tools, and post-import handling. By following the steps outlined, you can easily integrate Excel data into your MATLAB workflows. Remember, selecting the right function for your task and understanding data manipulation techniques will significantly enhance your MATLAB experience.
Can I import only a specific range of cells from an Excel sheet?

+
Yes, you can specify a range when using functions like xlsread. For example, xlsread('file.xlsx', 1, 'A1:D20') imports data from cells A1 to D20.
What if my Excel file has multiple sheets?
+
MATLAB’s import functions allow you to specify which sheet to import. Use the Sheet parameter with readtable or the second argument in xlsread.
Is it possible to import data from .xlsb files?
+
Directly importing .xlsb files is not supported by MATLAB. Convert the .xlsb file to an .xlsx or .csv format before importing.
How can I handle errors during data import?

+
Use try...catch statements around your import function calls to manage exceptions or errors gracefully.
Does MATLAB support importing from other formats like CSV?

+
Yes, MATLAB can import from CSV, TXT, and other common data formats using functions like csvread, dlmread, or readtable with appropriate delimiters specified.