5 Ways to Spot Duplicates in Excel Sheets

Understanding Duplicate Entries

Before diving into the methods of detecting duplicates, let’s define what constitutes a duplicate entry in Excel. Duplicates can range from identical rows to partial matches based on selected columns or criteria.
Method 1: Conditional Formatting for Visual Identification
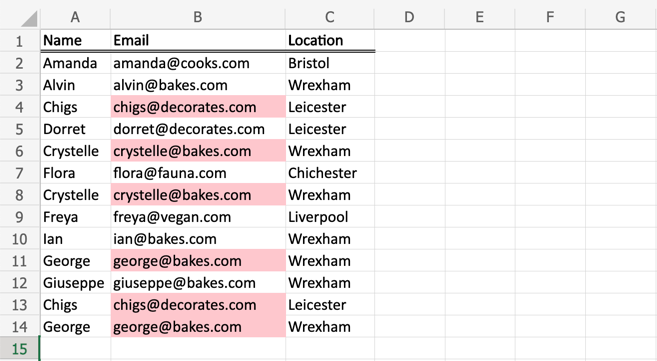
Excel’s Conditional Formatting tool provides a visual approach to identifying duplicates:
- Select the Range: Choose the cells you want to check for duplicates.
- Access Conditional Formatting: Go to Home > Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules > Duplicate Values.
- Choose Formatting: Select a color or format that will stand out, like red fill or bold text.
📌 Note: This method visually highlights duplicates but does not remove or list them. It is best for quick visual checks rather than detailed analysis.
Method 2: The Remove Duplicates Feature

If you need to not just find but also remove duplicate entries from your data:
- Select the Data: Highlight the range containing potential duplicates.
- Go to Data > Remove Duplicates: Choose whether to remove duplicates based on all columns or specific ones.
- Confirm Action: Excel will prompt you with the number of duplicates found and removed.
📌 Note: Remember that once duplicates are removed, there's no way to undo this action unless you saved a copy before making changes.
Method 3: Using Advanced Filter for More Detailed Control
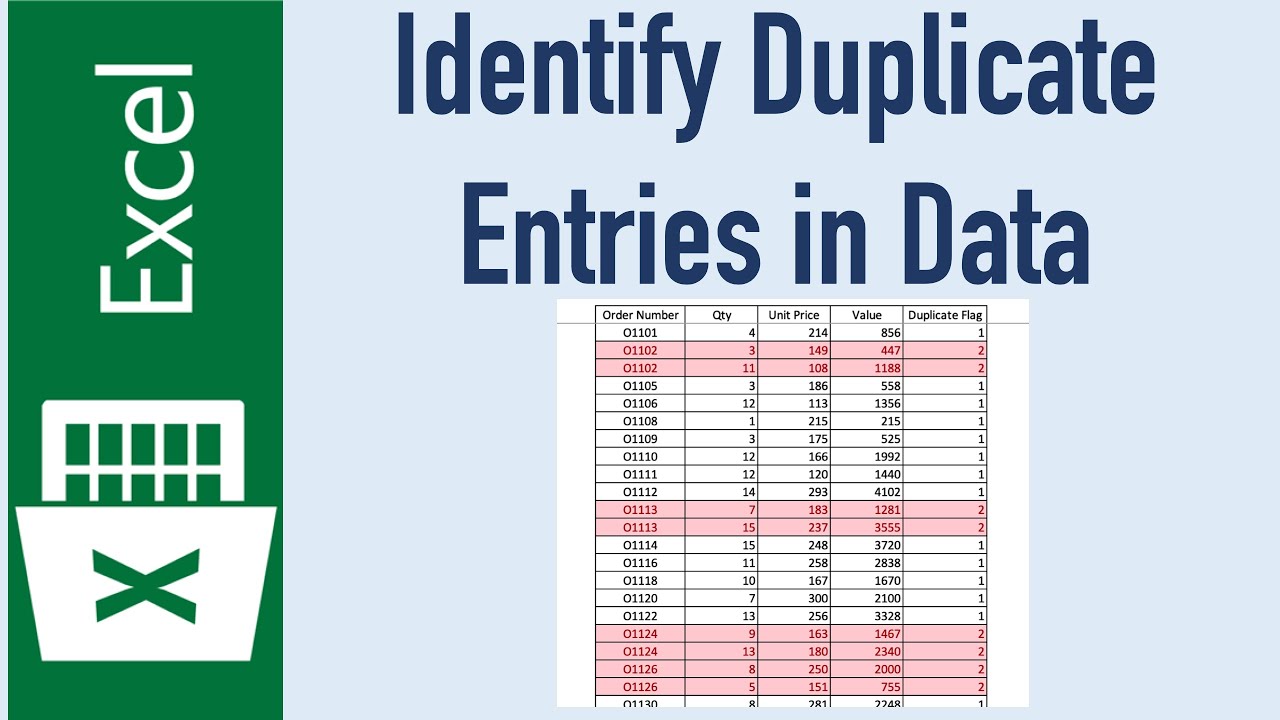
The Advanced Filter tool allows for filtering out unique or duplicate records with more control:
- Prepare Criteria: If needed, set up criteria in a separate area of the worksheet.
- Select Data and Go to Data > Advanced: Choose 'Filter the list, in-place' or 'Copy to another location'.
- Specify Criteria: Set up the filter options to show unique records only.
Method 4: Formulas for Identifying Duplicates

For users comfortable with formulas, here are some ways to detect duplicates:
- COUNTIF: Use =COUNTIF(range, cell)>1 to check if a value appears more than once.
- IF and EXACT: Combine =IF(EXACT(A2,A1), "Duplicate", "Unique") to mark identical consecutive rows.
Method 5: PivotTables for Grouping and Counting

PivotTables offer a powerful way to group and summarize data, helping identify duplicates:
- Create a PivotTable: Select your data range and go to Insert > PivotTable.
- Add Data to Rows: Drag the columns you wish to analyze into the Rows section.
- Count Duplicates: Use the 'Count' value field to see how many times each value appears.
📌 Note: PivotTables can provide insights beyond just spotting duplicates; they can help you understand patterns and distributions within your data.
To wrap up, we’ve explored various techniques for spotting duplicates in Excel sheets. Whether you prefer visual cues, need to eliminate duplicates, want detailed control, require formulas, or desire data summarization, Excel has tools to suit your workflow. Always back up your data before making significant changes to ensure you can revert to the original if needed.
Can I use these methods to find duplicates across multiple sheets?
+
Yes, but you’ll need to consolidate data from multiple sheets into one before applying these methods or use formulas to reference other sheets in your formulas for identifying duplicates.
What should I do after finding duplicates?

+
Once you’ve identified duplicates, you might want to remove them, merge them into unique records, or analyze why they exist. Depending on your needs, you can use tools like ‘Remove Duplicates’ or keep them for reference.
Can Conditional Formatting identify duplicates based on specific conditions?

+
Yes, you can set up conditions within Conditional Formatting to highlight duplicates based on partial matches or custom formulas.
Is it possible to automate the duplicate checking process?

+
Yes, using macros or scripting in VBA, you can automate the process of checking for duplicates based on your specific criteria.
How can I keep track of which duplicates have been processed?

+
You can use a helper column to mark duplicates as processed, or use filtering options to hide duplicates that have been dealt with.