5 Easy Ways to Spot Duplicates Across Excel Sheets

Identifying duplicates across multiple Excel sheets is essential for maintaining data integrity, particularly in large datasets. Whether you're combining data from different sources or cleaning up a cluttered database, recognizing duplicate entries saves time and ensures accuracy. In this guide, we will explore five easy methods to efficiently spot duplicates in Excel.
Method 1: Conditional Formatting
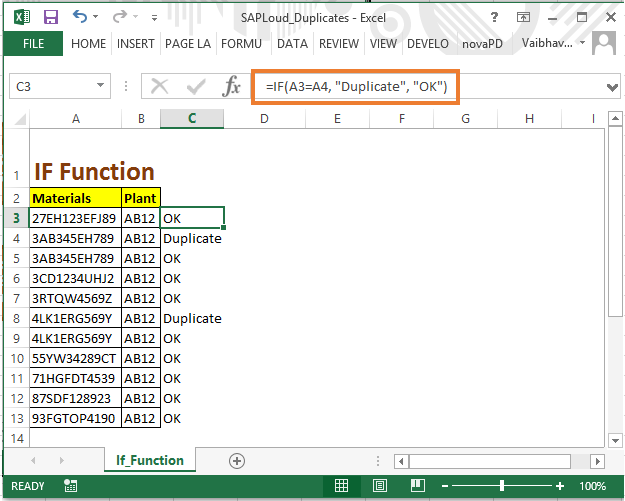
Conditional Formatting in Excel allows you to highlight duplicate values, making them stand out visually. Here’s how to do it:
- Select the entire dataset or the column where you want to identify duplicates.
- Go to the Home tab, click on Conditional Formatting, then Highlight Cells Rules, and finally Duplicate Values.
- Choose the format for highlighting, such as red fill with dark red text.
💡 Note: This method is quick but limited to highlighting duplicates within a single sheet.
Method 2: Using Excel Formulas


Formulas provide a robust way to search for duplicates across sheets:
- Use
COUNTIFto count how many times a value appears: - If the count exceeds 1, it’s a duplicate. Use conditional formatting or a helper column to highlight these values.
=COUNTIF(Sheet1:Sheet3!A:A, A2) > 1
Method 3: Combining Data from Multiple Sheets
Sometimes, the first step is to combine data before identifying duplicates:
- Copy and paste or use Consolidate under the Data tab to merge data from multiple sheets.
- Then, apply one of the above methods to find duplicates in the consolidated data.
Method 4: Power Query

Power Query in Excel provides advanced data manipulation capabilities:
- From the Data tab, select Get Data > From Other Sources, then choose Blank Query.
- In the Query Editor, load the data from all sheets.
- Merge the queries and then use the Remove Duplicates feature to clean your dataset.
Method 5: Using VBA Scripts

Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can automate the process of finding duplicates across multiple sheets:
- Open the VBA Editor with ALT + F11.
- Insert a new module and paste a script designed to find duplicates, like:
Sub FindDuplicates()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim rng As Range
Dim cel As Range
Dim dict As Object
Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
For Each rng In ws.UsedRange
If Not dict.Exists(rng.Value) Then
dict.Add rng.Value, 1
Else
rng.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0) ' Highlight duplicates in red
End If
Next rng
Next ws
End Sub
💡 Note: VBA can be complex. Ensure to save backups before running scripts that alter your data.
In summary, whether you're dealing with small datasets or complex databases, Excel provides several tools and methods to spot duplicates across multiple sheets. From simple conditional formatting to advanced VBA scripts, you can choose the method that best suits your data management needs. Each technique offers its own set of benefits, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in data handling.
Can Conditional Formatting spot duplicates in more than one sheet?

+
No, Conditional Formatting in Excel can only identify duplicates within the same worksheet.
Is it necessary to combine data before using formulas to find duplicates?

+
Not necessary, but it can be more efficient if you’re dealing with a lot of sheets. Formulas can reference multiple sheets, but having the data consolidated might simplify the process.
What’s the advantage of using Power Query over other methods?

+
Power Query allows for repeatable and automated data transformations, which is ideal for large or regularly updated datasets. It also provides a graphical interface for data manipulation, making complex operations more accessible.
Can I safely use VBA scripts on any Excel file?

+
Yes, but you should always back up your data first. VBA can change data, and if not written correctly, it might lead to data loss or corruption. Test scripts in a non-critical environment first.