Master Excel Editing: Quick Guide
Do you often find yourself struggling with managing large datasets in Excel? Whether it's organizing, analyzing, or simply formatting your data, mastering Excel can significantly boost your productivity and accuracy in data handling. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through essential Excel editing techniques to streamline your workflow, making you an Excel pro in no time.
Understanding Excel Basics


Before diving into advanced techniques, let's ensure we're all on the same page with some fundamental Excel features:
- Workbooks and Worksheets: An Excel file is a workbook which can contain multiple worksheets.
- Cells, Rows, and Columns: Data is entered into cells, organized by rows and columns.
- Formulas and Functions: Excel's core for calculations and data manipulation.
Data Entry and Formatting

The way data is entered and formatted in Excel not only affects readability but also efficiency in data processing:
- Cell Formatting: Change text style, size, color, and alignment for better presentation.
- Data Validation: Set rules for what data can be entered into specific cells, preventing errors.
- Conditional Formatting: Automatically format cells based on the data they contain, making trends or outliers visually identifiable.
Mastering Excel Formulas

Formulas are the backbone of Excel's analytical capabilities. Here are some key formulas and functions you should know:
Basic Formulas

- SUM: Adds values in a range.
- AVERAGE: Computes the mean of selected numbers.
- COUNT: Counts how many cells in a range contain numbers.
Advanced Functions

- VLOOKUP: Looks for a value in the leftmost column of a table and returns a value in the same row from another column.
- INDEX and MATCH: More flexible than VLOOKUP, used for locating information in a table or range based on specific criteria.
- SUMIF/SUMIFS: Sum cells that meet single or multiple criteria.
🌟 Note: Learning to use relative vs. absolute cell references (e.g., $A$1 vs. A1) is crucial for effective formula usage.
Power Features for Data Analysis

Excel offers advanced tools for those delving deeper into data analysis:
Sorting and Filtering

- Organize data with ease, allowing you to view only what you need.
- Apply filters to focus on specific entries based on criteria.
PivotTables

- Summarize, analyze, and explore data interactively.
- Create dynamic reports that can be updated as data changes.
Data Analysis Tools

- What-If Analysis: Use for scenario modeling.
- Solver: Find an optimal value for a formula in one cell, subject to constraints on the values of other cells.
Macros and VBA: Automating Excel

For repetitive tasks, Excel’s VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) allows you to:
- Create macros to automate repetitive processes.
- Customize Excel to meet specific business needs.
Creating a Simple Macro

Here’s how to record a basic macro:
- Go to the “Developer” tab (enable if it’s not visible).
- Click “Record Macro.”
- Name your macro and assign it to a keyboard shortcut if desired.
- Perform the actions you want to automate.
- Stop recording the macro.
Editing VBA Code

Once you’ve recorded a macro, you can edit the VBA code:
- Open the Visual Basic Editor (Alt+F11 or through “Developer” tab).
- Locate your macro under “Modules.”
- Modify the code to customize its behavior.
Data Validation and Error Checking

Data integrity is paramount in Excel. Use:
- Error Checking: Locate and fix formula errors.
- Data Validation: Set rules for data entry to prevent mistakes.
💡 Note: Regularly check for and correct errors to ensure data accuracy.
Advanced Charting Techniques
Visual representation of data can be immensely helpful. Here are some techniques:
- Create custom chart templates for consistent branding.
- Use dynamic range names to update charts automatically as data changes.
- Employ secondary axes to compare different data scales on the same chart.
| Chart Type | Best Used For |
|---|---|
| Column/Bar Charts | Comparing values across categories or time periods. |
| Line Charts | Tracking changes over continuous intervals like time. |
| Pie Charts | Displaying proportions of a whole. |
| Scatter Plots | Showing relationships between two variables. |

Troubleshooting Common Issues

Excel can sometimes behave unexpectedly. Here are tips for common issues:
- File Not Saving: Check if Excel is in “read-only” mode or if there are issues with file permissions.
- Formula Errors: Ensure cell references are correct, and you’re using the appropriate formula syntax.
- Slow Performance: Reduce large datasets or consider using Power Query to manage data more efficiently.
In wrapping up our journey through Excel editing, mastering these techniques will not only make you more efficient but also provide a solid foundation for further exploration into Excel's vast capabilities. Remember, regular practice and curiosity are key to becoming an Excel adept. Keep refining your skills, and soon, Excel will have no more secrets to offer you.
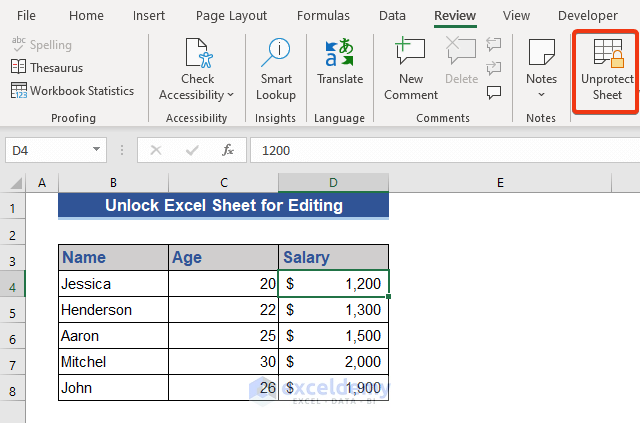
How do I protect my Excel worksheet?

+
You can protect your worksheet by selecting “Review” > “Protect Sheet” or “Protect Workbook” to prevent unauthorized changes. Choose a password and set permissions for users.
What are the best practices for large datasets in Excel?
+
Use Power Query to manage large datasets, avoid volatile functions that can slow down Excel, and consider using Table formats for better data handling.
Can I recover an unsaved Excel file?

+
Yes, go to “File” > “Info” > “Manage Versions” > “Recover Unsaved Workbooks” to locate and open any unsaved files.