How To Delete A Sheet In Excel Using Vba

Managing large datasets in Microsoft Excel often involves the need to restructure or clean up workbooks. This task can become repetitive and time-consuming, especially if you're dealing with numerous sheets. To streamline this process, VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) can be your ally. In this article, we'll explore how to use VBA to delete a specific sheet in Excel with precision and efficiency.
Why Use VBA for Deleting Sheets?

VBA provides several advantages when it comes to deleting sheets in Excel:
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors and increasing productivity.
- Consistency: Ensure that the deletion of sheets is performed uniformly across all workbooks.
- Control: Provide more control over which sheets are deleted, based on conditions, or in bulk.
- Integration: VBA scripts can be integrated with other Excel functionalities for a seamless workflow.
Step-by-Step Guide to Delete a Sheet with VBA

Here’s how you can write a VBA script to delete a specific sheet in your Excel workbook:
- Open the VBA Editor:
- Press
Alt + F11to open the VBA editor in Excel.
- Press
- Insert a New Module:
- Right-click on any of the objects in the 'Project Explorer' on the left.
- Choose 'Insert' > 'Module' to add a new module where you can write your VBA code.
- Write the VBA Code:
- Use the following code to delete a sheet:
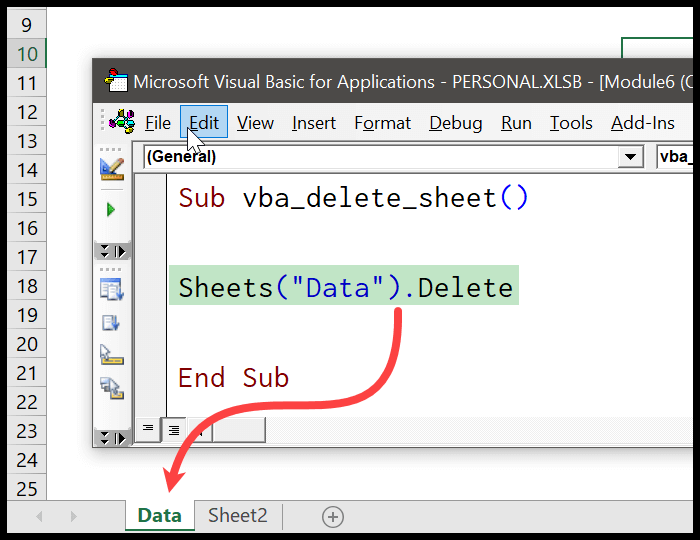
Sub DeleteSpecificSheet() Dim ws As Worksheet ' Replace "SheetName" with the name of the sheet you want to delete On Error Resume Next Application.DisplayAlerts = False Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("SheetName") If Not ws Is Nothing Then ws.Delete End If Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub- This script disables alerts to prevent prompts about deleting the sheet, then attempts to find and delete a sheet named "SheetName". If the sheet does not exist, it does nothing.
- Run the Macro:
- Place your cursor inside the subroutine and press
F5or click ‘Run’ to execute the macro.
- Place your cursor inside the subroutine and press
🎯 Note: Always ensure that you have a backup of your workbook before deleting sheets, as this operation cannot be undone without a backup.
Advanced VBA Techniques

If you need more complex operations for deleting sheets, consider these advanced techniques:
- Conditional Deletion: Delete sheets based on certain criteria, like sheet names containing specific text:
Sub DeleteSheetsConditionally()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Sheets
If InStr(1, ws.Name, “OldData”, vbTextCompare) > 0 Then
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ws.Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End If
Next ws
End Sub
Sub DeleteAllButOne()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Sheets
If ws.Name <> “SheetToKeep” Then
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ws.Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
End If
Next ws
End Sub
🚀 Note: Be cautious with bulk deletion as it can have significant consequences on your workbook's structure.
Error Handling and Best Practices
When dealing with VBA code to delete sheets, consider these best practices:
- Error Handling: Use On Error Resume Next judiciously. Understand what errors might occur, like attempting to delete the last remaining sheet or the sheet currently active.
- Prompt for Confirmation: In production environments, consider adding a confirmation prompt to ensure users don’t accidentally delete important data.
- Save Beforehand: Ensure your VBA scripts save the workbook before performing operations that can’t be undone.
Here's an example of incorporating confirmation and error handling:
Sub DeleteWithConfirm()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim ans As VbMsgBoxResult
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("SheetName")
If Not ws Is Nothing Then
ans = MsgBox("Are you sure you want to delete this sheet?", vbYesNo)
If ans = vbYes Then
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ws.Delete
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
MsgBox "Error: " & Err.Description
End If
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Else
MsgBox "Deletion cancelled by user."
End If
Else
MsgBox "The sheet does not exist."
End If
End Sub
To conclude, mastering how to delete sheets in Excel with VBA not only enhances your data management capabilities but also significantly improves productivity by automating what would otherwise be a tedious task. This method ensures accuracy, allows for conditional deletions, and gives you the control to manage your Excel environment effectively. Remember to handle errors wisely, always backup your work, and consider implementing user prompts in critical operations to prevent unintended data loss.
Can I recover a sheet deleted with VBA?

+
No, once a sheet is deleted with VBA, it is permanently removed from the workbook. Always ensure you have backups if you need to restore sheets.
How can I run this VBA script automatically when opening the workbook?

+
You can add a Workbook_Open event to the ThisWorkbook object’s code module. This event runs when the workbook opens, where you can call your deletion script.
Is it possible to delete sheets based on content or formulas?

+
Yes, by iterating through each cell in a sheet and checking for specific content or formula conditions, you can conditionally delete sheets. However, this requires more advanced VBA scripting.