Mastering Excel: Linking Cells Across Sheets Easily

If you use Microsoft Excel regularly for organizing, analyzing, or reporting data, you know how important it is to keep your spreadsheets interconnected and easily manageable. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is by learning how to link cells across different sheets within your workbook. This technique not only makes your work more efficient but also helps in maintaining consistency across large datasets. In this detailed guide, we'll explore how to link cells effortlessly, the benefits of doing so, and some advanced techniques to enhance your Excel productivity.
Understanding Cell Linking

Cell linking in Excel is the process of referencing a cell from one sheet into another. This creates a dynamic connection where changes in the source cell are automatically reflected in all linked cells. Here’s why cell linking is crucial:
- Data Consistency - Ensures that data is uniform across multiple sheets.
- Time-Saving - Reduces the need for repetitive data entry.
- Error Reduction - Minimizes the chances of manual errors when updating data.

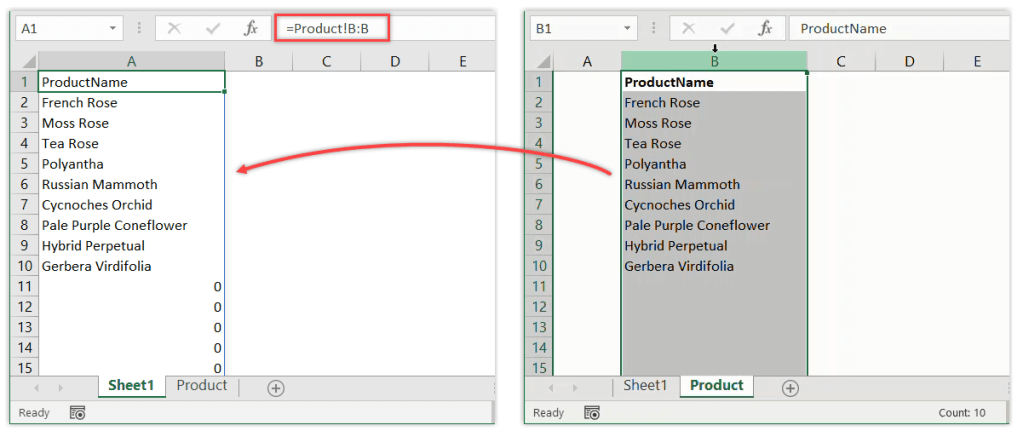
How to Link Cells Across Sheets

Linking cells across sheets involves simple steps but can be incredibly powerful. Here’s how you can do it:
Step 1: Identify the Source Cell

First, locate the cell on the sheet that contains the data you want to link. Let’s assume this cell is B2 on Sheet1.
Step 2: Open the Destination Sheet

Switch to the sheet where you want to display the linked data. Assume this sheet is named ‘Summary’.
Step 3: Select the Destination Cell

Click on the cell where you wish to show the linked data. For our example, let’s choose cell D2.
Step 4: Enter the Formula

Type the equals sign (=) to begin your formula, then click on the source sheet tab (Sheet1 in this case), select the source cell (B2), and press Enter. The formula should look like this:
=Sheet1!B2
Now, any updates made to B2 on Sheet1 will automatically appear in D2 on the Summary sheet.
💡 Note: Ensure you're not adding a space after the equals sign to avoid formula errors.
Step 5: Copy the Formula

If you need to link multiple cells, simply drag the fill handle or copy and paste the formula across other cells.
Advanced Techniques for Cell Linking

While basic cell linking is straightforward, there are advanced techniques that can make your work even more efficient:
Named Ranges

Create named ranges for frequently used data sets to make your formulas more readable and easier to manage.
- Go to Formulas > Define Name.
- Give a name to a specific range or cell.
- Reference this named range in your formulas across different sheets.
Dynamic Links

Use Excel’s INDIRECT function for more complex linking scenarios:
=INDIRECT(“‘Sheet1’!”&“B2”)
This function lets you construct the reference dynamically, allowing for more flexible linking.
Linking Across Workbooks

To link cells across different workbooks, use:
=‘[WorkbookName.xlsx]Sheet1’!B2
Make sure both workbooks are open, or you might see #REF! errors.
| Function | Use Case |
|---|---|
| INDIRECT | Dynamic cell referencing |
| DEFINE NAME | Creating readable named ranges |
| Workbook Link | Linking data across different Excel files |

💡 Note: Avoid using spaces or special characters in workbook names to prevent link issues.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

Linking cells can be straightforward, but there are common pitfalls:
- Incorrect Sheet References - Make sure you’re referencing the correct sheet.
- Workbook Path Issues - Changes in file location can break external links.
- Deleting or Renaming Sheets - Can cause #REF! errors in linked formulas.
💡 Note: Regularly check and update external links, especially if moving or renaming workbooks.
Troubleshooting Tips
If your links aren’t working, consider:
- Checking for sheet or workbook names in formulas.
- Verifying that the source workbook is open for external links.
- Using Find and Replace (Ctrl+H) to update references if sheets were renamed.
💡 Note: Use Excel’s Trace Precedents feature to visually track cell dependencies.
In summary, linking cells across sheets in Excel not only improves your workflow but also ensures data integrity across complex spreadsheets. By mastering these techniques, you'll save time, reduce errors, and make your data analysis more powerful. Whether it's for personal finance, business reporting, or data management, the ability to link cells effectively is a game-changer.
What happens if I delete a source cell or sheet with linked data?

+
Deleting a source cell or sheet will result in #REF! errors in the cells that are linked to them. You’ll need to update or remove these references to resolve the errors.
Can I link cells across different workbooks?

+
Yes, you can link cells across workbooks using the formula structure =‘[WorkbookName.xlsx]Sheet1’!B2. Ensure both workbooks are open when setting up the link, or you’ll see errors.
How do I update all links when moving a workbook?
+If you move the linked workbook, Excel will prompt you to update the links when you open the file containing the links. Ensure you update all references to avoid #REF! errors.