5 Ways to Merge Excel Sheets and Remove Duplicates
5 Ways to Merge Excel Sheets and Remove Duplicates
Excel is an incredibly versatile tool that many professionals and hobbyists use for data analysis, project management, and record keeping. One common task when working with Excel is the need to merge different sheets into one cohesive dataset, often while ensuring there are no duplicate entries. Here, we'll explore five effective methods to merge Excel sheets while also removing any duplicates.
Method 1: Using Excel's Built-In Features

Excel provides several in-built features that can help you merge sheets and remove duplicates:
- Consolidate: This tool lets you consolidate data from multiple sheets into one place while performing basic operations like Sum, Average, Count, Max, or Min on the values.
-
Consolidate Steps:
- Open the Excel workbook containing the sheets to merge.
- Select a blank worksheet where you want to consolidate data.
- Go to Data > Consolidate.
- In the Consolidate dialog, choose the function you want to use.
- Select the ranges from the different sheets using the Reference box, clicking Add for each range.
- Click OK.
-
Remove Duplicates:
- After consolidating, click any cell in the dataset.
- Go to Data > Remove Duplicates.
- Select the columns to check for duplicates.
- Click OK to remove duplicate entries.
⚠️ Note: Be cautious when using the Consolidate feature, as it might not preserve the original data's context if not set up properly.
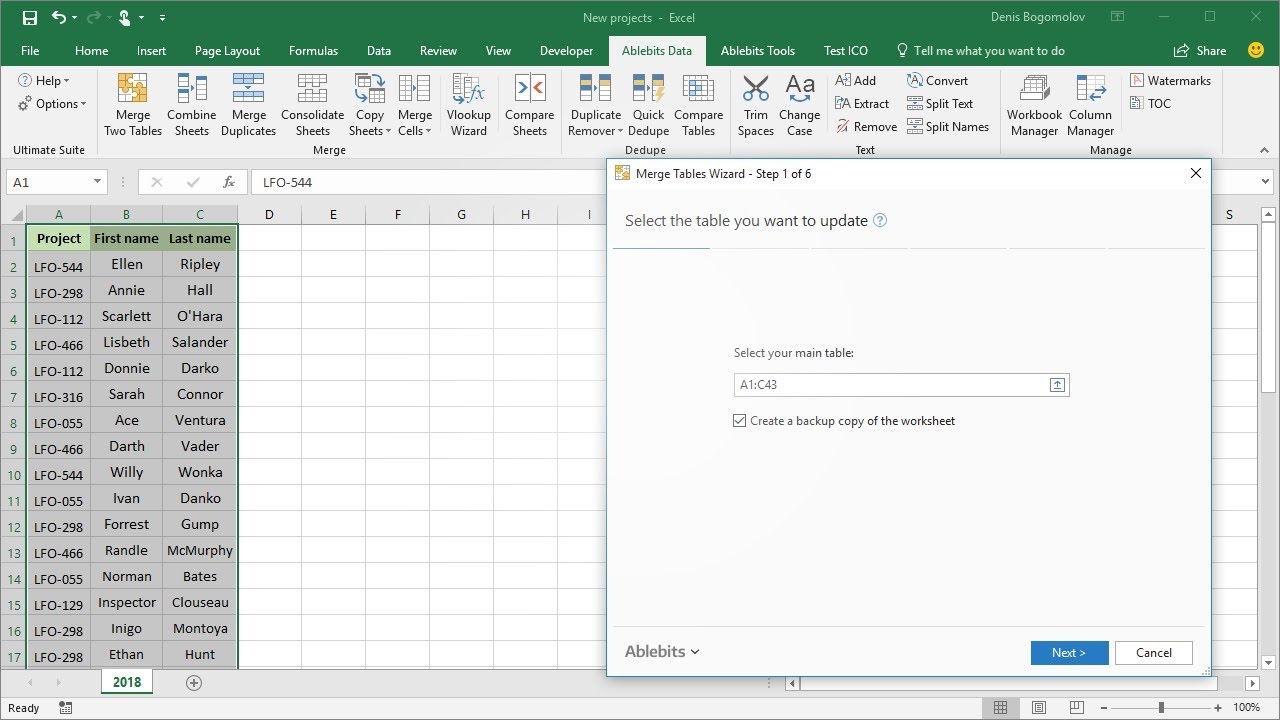
Method 2: Using Power Query

Power Query is an Excel add-in for data transformation and preparation. It's particularly useful for merging data from multiple sheets:
-
Import Sheets into Power Query:
- Go to Data > Get Data > From File > From Workbook.
- Select the workbook and then the sheets you wish to import.
- Each sheet will load as a separate table in Power Query.
-
Merge Queries:
- In Power Query Editor, select the first table.
- Go to Home > Merge Queries > Merge.
- Choose another table from the list and select the columns to match.
- Merge and expand as needed, selecting which columns to keep.
- Repeat for all tables.
-
Remove Duplicates:
- With all data merged, click Home > Remove Duplicates.
- Select columns where duplicates might occur.
- Click OK.
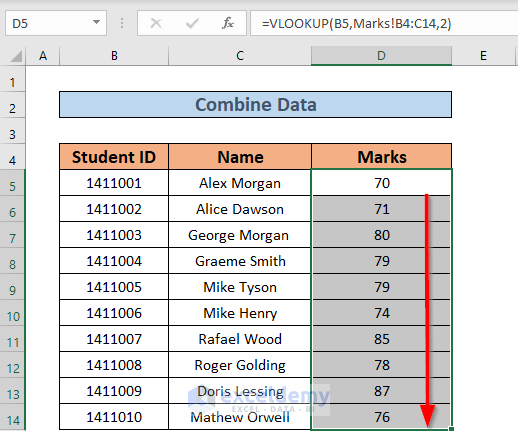
Method 3: Using VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH

If your sheets share a common key (like an ID or Name), you can use functions like VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH to merge them:
- VLOOKUP:
- In a new sheet, list all the IDs or keys you want to merge.
- Use VLOOKUP to pull data from other sheets.
- Example:
=VLOOKUP(A2,Sheet2!$A$1:$C$100,3,FALSE)retrieves the 3rd column value from Sheet2 where A2 matches.
- INDEX/MATCH:
- This method offers more flexibility than VLOOKUP.
- Combine INDEX and MATCH to pull data, which can handle arrays in both rows and columns.
Here’s how you would typically set this up:
| Sheet1 (A1:A100) | Sheet2 (A1:C100) | Merged Sheet (Column A = Keys, Column B = Data from Sheet2) |
|---|---|---|
| 1001 1002 |
ID | Name | Value 1001 | John | 1200 1002 | Jane | 1500 |
=VLOOKUP(A2,Sheet2!$A$1:$C$100,3,FALSE) =VLOOKUP(A3,Sheet2!$A$1:$C$100,3,FALSE) |
Method 4: Using Macros or VBA

For those comfortable with coding or automating repetitive tasks, Excel VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) can offer powerful solutions:
- Merge Sheets:
- Open VBA Editor (Alt+F11).
- Insert a new module (Insert > Module).
- Write VBA code to loop through sheets, copy data into a master sheet, and then remove duplicates.
- Example VBA Code:
Sub MergeSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim wsMaster As Worksheet
Dim lastRow As Long
Dim copyRange As Range
' Assume "Master" is the name of the sheet where data will be merged
Set wsMaster = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Master")
wsMaster.UsedRange.Clear
' Loop through each sheet, excluding the master sheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name <> wsMaster.Name Then
' Set the range to copy
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
Set copyRange = ws.Range("A1:B" & lastRow)
' Copy and Paste into Master Sheet
lastRow = wsMaster.Cells(wsMaster.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
copyRange.Copy Destination:=wsMaster.Range("A" & lastRow + 1)
End If
Next ws
' Remove duplicates
wsMaster.Range("A1").CurrentRegion.RemoveDuplicates Columns:=Array(1, 2), Header:=xlYes
End Sub
Method 5: Using External Tools or Add-ins
There are several third-party add-ins and tools designed for merging and deduplicating Excel data:
- Kutools for Excel: Offers a "Combine" tool for merging multiple sheets.
- Ablebits' Ultimate Suite: Includes a powerful tool for merging sheets with options to remove duplicates.
- Microsoft Power Automate (Flow): Create workflows to automate the merging of Excel files.
These tools often provide user-friendly interfaces and can manage large datasets with ease, reducing the manual effort significantly.
When wrapping up our exploration of merging Excel sheets and removing duplicates, it’s evident that there are numerous approaches available, each catering to different levels of user expertise and workflow needs. Whether you're a beginner who relies on Excel’s built-in functions or an advanced user comfortable with VBA and external tools, there’s a method for everyone. Each technique ensures your data remains clean, organized, and free of redundancy, which is vital for accurate analysis and efficient data management. Keep in mind the importance of maintaining data integrity and choosing the method that best fits your project’s scope and your own proficiency with Excel.
What is the easiest way to merge Excel sheets?

+
The simplest method for beginners would be using Excel’s built-in Data > Consolidate feature. However, for large datasets or more control, Power Query or third-party add-ins might be more efficient.
Can VBA handle multiple sheets with varying formats?
+
Yes, VBA can be programmed to loop through multiple sheets, but you might need to adjust your code to handle different column structures or data formats if they vary between sheets.
Do third-party tools require a subscription or one-time purchase?

+
It depends on the tool. Some like Kutools or Ultimate Suite from Ablebits offer lifetime licenses, while others might work on a subscription model or offer both options.