How to Easily Color Excel Sheet Tabs
Managing a complex Excel workbook with multiple sheets can be overwhelming. To make navigation easier and visually organize your data, coloring the tabs of Excel sheets is an effective strategy. This guide will walk you through the process, ensuring your workbook is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing.
Why Should You Color Excel Sheet Tabs?
- Improved Visibility: Color coding helps in quickly identifying the content or category of each sheet.
- Enhanced Organization: Different colors can represent different types of data or sections of a project, making it simpler to navigate through a large workbook.
- Visual Appeal: A well-organized, colorful workbook is more engaging and can boost productivity.
How to Color Excel Sheet Tabs
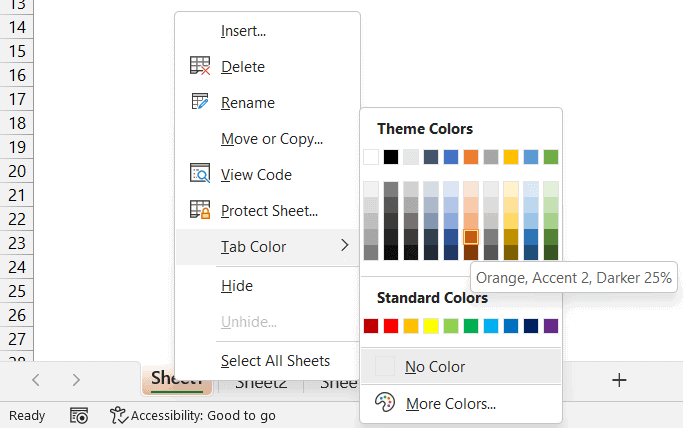
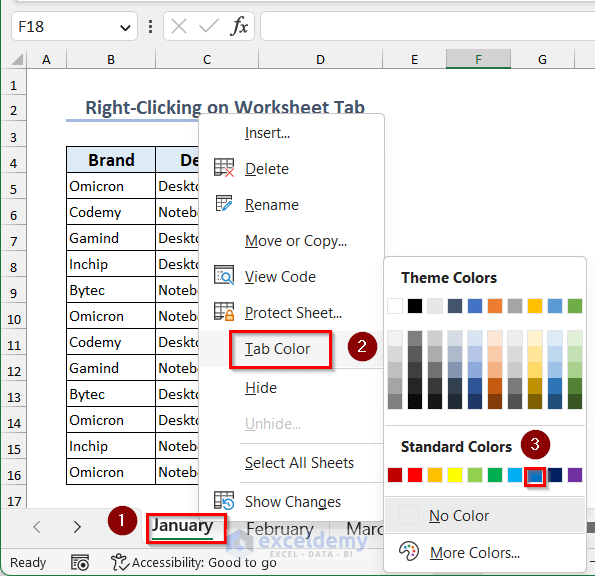
Here’s how you can easily color Excel sheet tabs:
Step 1: Select the Sheet
First, click on the tab of the sheet you wish to color.
Step 2: Right-Click to Open Context Menu

Right-click on the selected tab to open the context menu.
Step 3: Choose “Tab Color”
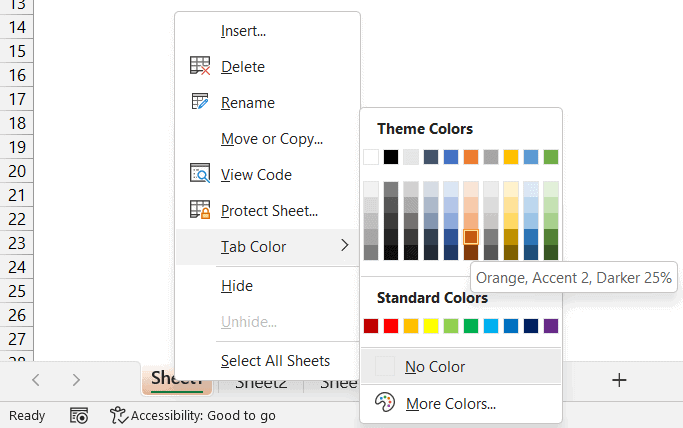
From the context menu, select the option labeled “Tab Color.”
Step 4: Pick a Color
Choose a color from the palette that appears. If you don’t find a color you like, click on “More Colors” for additional options.
Step 5: Apply the Color

Once you’ve selected your color, click on it to apply. The sheet tab will now reflect the chosen color.
✅ Note: You can apply multiple colors to different sheets within the same workbook to organize them further.
Tips for Efficient Color Coding
- Create a Color Legend: Maintain a key or legend to remember what each color signifies, especially in workbooks shared with others.
- Use Consistent Colors: Choose colors that have meaning or relation to the content of the sheet, and keep them consistent across workbooks.
- Consider Accessibility: Be mindful of color blindness when selecting colors; use patterns or icons if necessary.
Automating Tab Coloring with VBA

For users familiar with VBA, you can automate the process of coloring tabs:
Sub ColorTabBasedOnContent()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
Select Case ws.Name
Case “Summary”, “Total”, “Final”
ws.Tab.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0) ‘ Red for summary sheets
Case “Data*”
ws.Tab.Color = RGB(0, 255, 0) ’ Green for data entry sheets
Case Else
ws.Tab.Color = RGB(0, 0, 0) ‘ No color for others
End Select
Next ws
End Sub
💡 Note: Running this script will change the color of all tabs based on their names. Adjust the conditions to suit your needs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Color Not Showing: Make sure you’ve selected the correct sheet before right-clicking, and your Excel settings allow tab coloring.
- Limited Colors: If you need more color options, select “More Colors” for an expanded palette or consider using gradient fills (available in later versions of Excel).
To conclude, coloring Excel sheet tabs is a simple yet powerful way to enhance your workbook's usability and visual appeal. By following these steps and incorporating color coding strategies, you can streamline your data management process, making it more intuitive and less error-prone. The use of VBA for automation can further simplify the task for repetitive or large-scale workbooks, but always ensure you document changes to maintain clarity in shared environments. Remember, the key to effective color usage lies in consistency and planning, ensuring that each color carries a clear meaning within your workbook.
Can I apply colors to sheet tabs in all versions of Excel?

+
Yes, you can color sheet tabs in all modern versions of Excel. However, older versions like Excel 97 might not support this feature.
Is there a limit to how many sheets I can color?
+
No, there is no limit to how many sheets you can color, as long as your workbook does not exceed the Excel file size limitations.
How can I revert a sheet tab to its default color?

+
To revert to the default color, select “No Color” or “Automatic” from the color palette when changing the tab color.