5 Simple Ways to Calculate Work Hours in Excel

Introduction to Calculating Work Hours in Excel

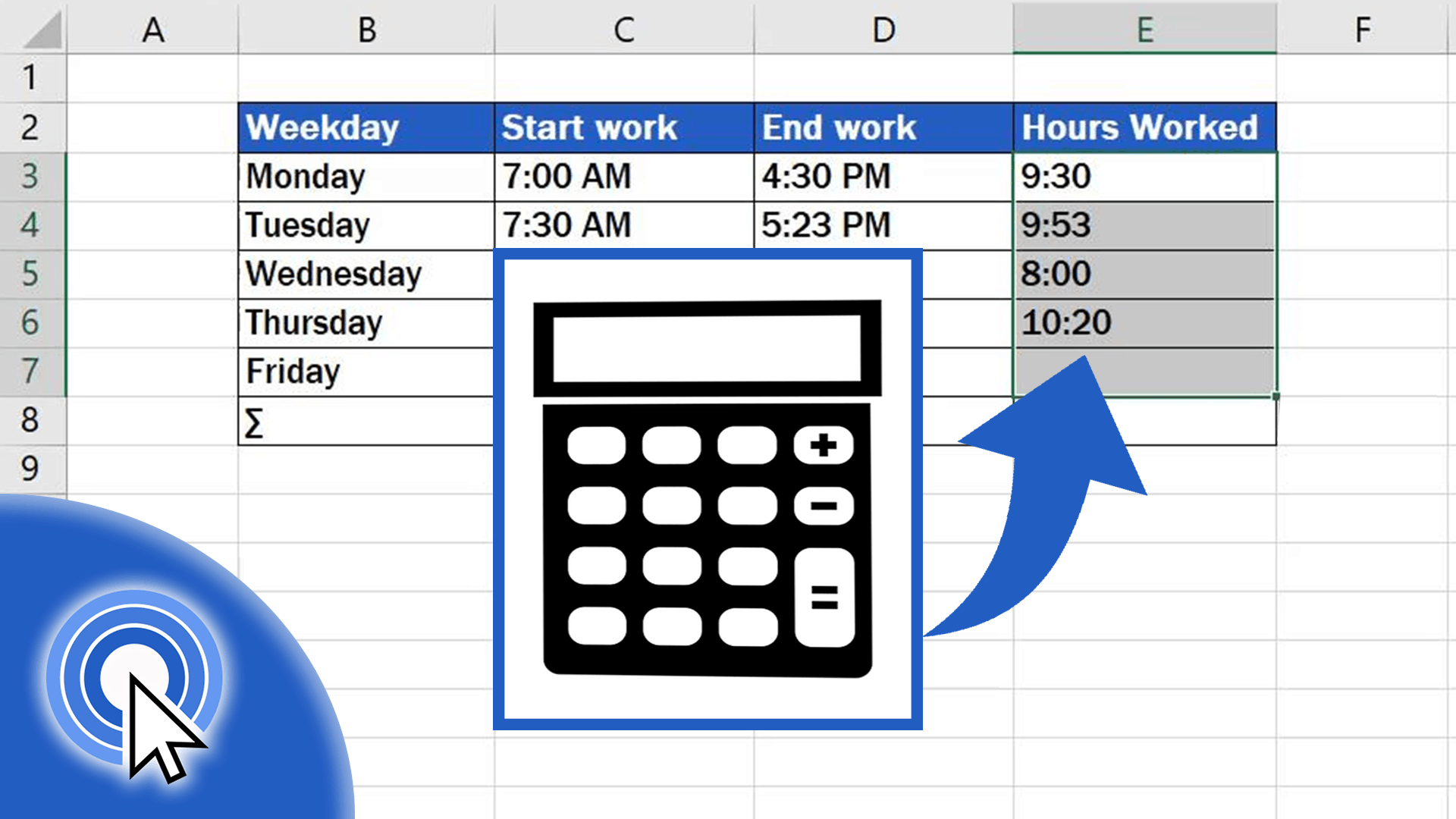
Calculating work hours can be an intricate task when managing a team or just tracking your own hours for invoicing or project management. Microsoft Excel provides a robust environment for performing these calculations with precision. Here, we’ll explore five simple methods to help you calculate work hours efficiently.

Method 1: Using Basic Formulas

The simplest way to calculate hours is through straightforward arithmetic:
- Input the start time in one cell (e.g., A2) and the end time in another (e.g., B2).
- Calculate the difference by subtracting A2 from B2:
=B2-A2
🔍 Note: Excel assumes 24-hour time format, so midnight to midnight would be 1.0 (or 24 hours).
Method 2: Calculating Overtime

If you need to calculate regular and overtime hours separately:
- Regular hours: Enter start and end times as before.
- Calculate overtime:
=IF(B2-A2>8,(B2-A2)-8,0)
Here, we’re assuming a regular workday is 8 hours; any time over this counts as overtime.
Method 3: Weekly Totals with Networkdays
For weekly timekeeping, you can use the NETWORKDAYS function:
- Calculate the number of working days:
=NETWORKDAYS(StartDate,EndDate)
=NETWORKDAYS(StartDate,EndDate)*8
📅 Note: The NETWORKDAYS function excludes weekends, but you can adjust it to include them with NETWORKDAYS.INTL.
Method 4: Using Time Functions for Invoicing

To create an invoice with hourly rates:
- Calculate total hours worked using method 1.
- Multiply this by the hourly rate:
=TotalHours * HourlyRate
Method 5: Advanced Time Tracking with Pivot Tables

Excel’s Pivot Tables offer advanced analysis capabilities:
- Import or manually enter data into columns for Date, Start Time, End Time, Project Name, etc.
- Create a Pivot Table by selecting your data and inserting a new pivot table.
- Use this to:
- Sum total hours per project.
- Show trends in work hours over time.
- Analyze overtime distribution across employees.
Tips for Accurate Time Tracking
Here are some tips to ensure accuracy in your time calculations:
- Format cells correctly to display hours, minutes, and seconds.
- Be mindful of AM/PM if not using 24-hour format.
- Use the
TIMEVALUEfunction to convert text into time values.
⏲️ Note: Excel might automatically adjust times if you enter a time greater than 24 hours, so check your cell formatting.
Excel's ability to handle time calculations makes it an indispensable tool for project managers, HR departments, and freelancers alike. By mastering these methods, you not only streamline your workflow but also gain insights into productivity and efficiency. Remember, while Excel is incredibly powerful, attention to details like formatting and understanding date-time functions are crucial for accurate results.
Can Excel handle time calculations over several months?

+
Yes, Excel can manage time calculations over extended periods, including months or even years, provided you set up your data and formulas correctly.
How do I account for breaks in work hours?

+
Subtract the duration of breaks from your total hours or use conditional formatting to highlight and adjust for breaks.
What if I work across midnight?

+
If your work spans midnight, ensure Excel recognizes this by using the 24-hour time format, or consider adding 24 hours to the start time manually.



