5 Simple Ways to Calculate Across Excel Sheets

5 Simple Ways to Calculate Across Excel Sheets
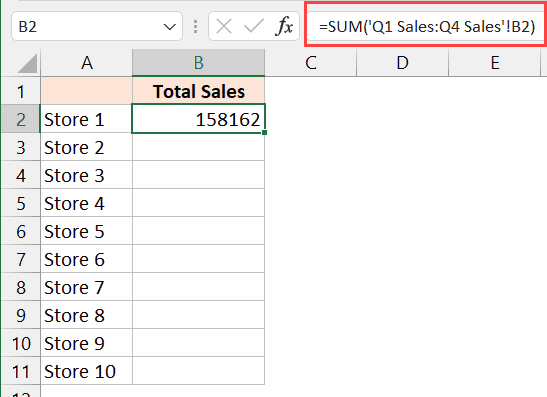
When it comes to working with Microsoft Excel, efficiency is key. Many users need to perform calculations not just within a single sheet but across multiple sheets. This can be quite an organizational challenge if you're not familiar with Excel's capabilities. In this post, we'll explore five simple methods to calculate across Excel sheets, improving both your productivity and data management.
1. Using 3D References

3D references in Excel allow you to reference the same cell or range across multiple worksheets within the same workbook. Here's how you can use them:
- Open your Excel workbook where you have several sheets.
- Let’s say you want to sum values from cell A1 across sheets named 'Sheet1', 'Sheet2', and 'Sheet3'. In the cell where you want the result, type:
=SUM(Sheet1:Sheet3!A1)
💡 Note: The 3D reference feature works only if the sheets are consecutive. If they are not, you might have to name the range or list out each sheet.
2. Indirect Function for Dynamic Sheet References

If you need to reference sheets dynamically or when the sheet names are not contiguous, the INDIRECT function is your go-to:
- In your formula, you can reference a cell that contains the sheet name, like this:
=INDIRECT("'"&A1&"'!A1")
3. Using Named Ranges

Named ranges can make your formulas more readable and easier to maintain:
- Create a named range for the cell(s) or range(s) you want to reference across sheets.
- Define the name in one sheet and then use it across other sheets.
- To sum a named range 'MyRange' from different sheets:
=SUM(Sheet1!MyRange, Sheet2!MyRange, Sheet3!MyRange)
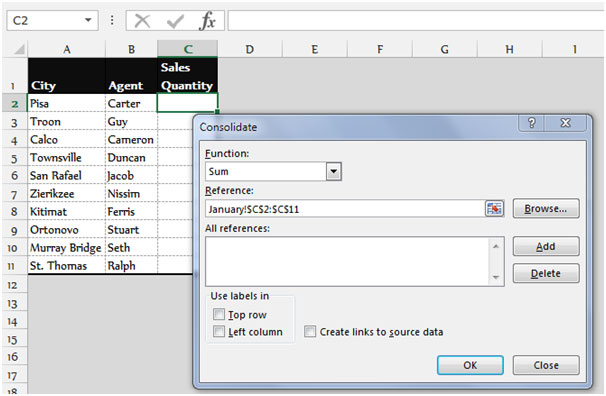
4. Consolidate Tool

The Consolidate tool allows you to combine data from multiple sheets or ranges:
- Go to the Data tab, and click on 'Consolidate'.
- Select the function you want to use (e.g., SUM) and then choose the ranges from your sheets.
- The results can be displayed in a new summary sheet or within an existing sheet.
5. VBA for Complex Calculations
For those needing more control or complex calculations, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) can be a powerful tool:
- Open the VBA editor by pressing Alt + F11.
- Create a new module by inserting a Module in your VBAProject.
- Write a macro that loops through sheets and performs your calculation:
Sub CrossSheetCalculate()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim total As Double
total = 0
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name <> "Summary" Then
total = total + ws.Range("A1").Value
End If
Next ws
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Summary").Range("A1").Value = total
End Sub
💡 Note: Ensure your macro security settings allow macros to run, and test your macro in a safe environment.
By mastering these methods, you can not only enhance your Excel skills but also make your work more efficient. Whether you're performing simple sum calculations or need more complex data manipulation across multiple sheets, Excel provides tools for every level of user from beginner to expert.
What is the best way to reference cells across sheets?

+
3D references are generally the simplest method for referencing the same cells across multiple sheets, especially if the sheets are named sequentially. For non-sequential sheets, using the INDIRECT function or named ranges might be more suitable.
Can I use VBA to perform calculations automatically?
+
Yes, VBA can automate complex calculations or repetitive tasks across multiple sheets with minimal user intervention once the script is set up.
Is there a limit to how many sheets I can reference in Excel?

+
There isn’t a specific limit to referencing sheets, but performance can degrade with extremely large workbooks. Also, Excel has a cap on the number of characters in a cell formula, which can limit the complexity of your references.



