5 Easy Steps to Import Multiple XY Coordinates from Excel

Working with geographical or spatial data often involves managing large sets of XY coordinates, which can be cumbersome when handled manually. Excel, a robust tool in data management, offers a straightforward solution to this problem. Here's how you can easily import multiple XY coordinates from Excel into various mapping or GIS software, enhancing your data visualization and analysis processes.
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
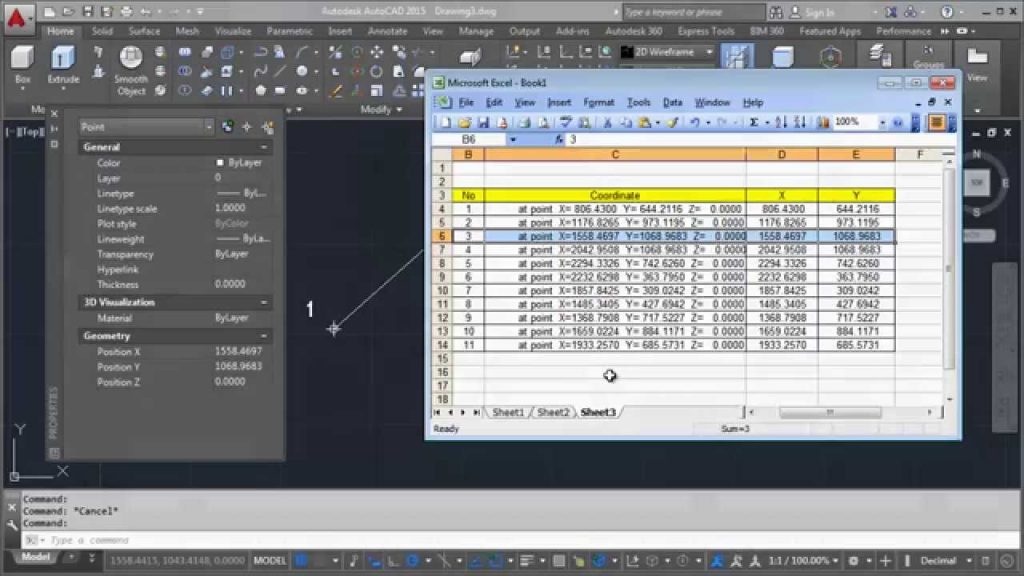
The first step in importing XY coordinates from Excel is to ensure your data is formatted correctly:
- Each pair of XY coordinates should be in separate columns, with X in one column and Y in another.
- Make sure there are no empty rows or cells between coordinate pairs, as this could disrupt the import process.
- Columns headers should be descriptive and simple, like “X” and “Y”.
- Verify that your coordinates are in the correct format for your GIS or mapping software (e.g., decimal degrees).
📝 Note: If your coordinates are in an unusual format or projection, consider converting them using online tools or GIS software before import.
Step 2: Export or Save Your Excel Data

Once your data is prepared:
- If your software supports direct Excel file import, you can save your workbook in the .xlsx format.
- For better compatibility, especially with legacy systems or different GIS software, export your data as a .csv (Comma Separated Values) file.
To save as a CSV:
- Go to
File > Save Asin Excel. - Choose
CSV (Comma delimited) (*.csv)from the list of file types. - Provide a file name and location.
- Click
Save.
📊 Note: CSV files retain your data without Excel's formatting or formulas, so be aware that any additional data like comments or formatting will not carry over.
Step 3: Importing into Your GIS or Mapping Software

The process to import data varies by software:
- QGIS:
- Go to
Layer > Add Layer > Add Delimited Text Layer. - Select your CSV file.
- Set the correct CRS (Coordinate Reference System) and specify which columns contain the X and Y data.
- Go to
- ArcGIS:
- Use
File > Add Data > Add XY Data. - Choose your file, then select the X and Y fields.
- Set the coordinate system if necessary.
- Use
- Google Earth:
- Import the CSV file through
File > Import. - Choose
Placemarksfrom the Import menu and map your columns to Latitude (Y) and Longitude (X).
- Import the CSV file through
Step 4: Verify Your Import

Once your data is imported:
- Check that all points are correctly placed on the map. If they appear as a single point or in the wrong location, review your data format or the import settings.
- Confirm that the projection or CRS matches the one used in your data.
- If necessary, join any supplementary data to your spatial data to enrich your map.
Step 5: Use Your Data Effectively

With your coordinates successfully imported, consider:
- Creating thematic maps to visualize data trends or patterns.
- Using spatial analysis tools to derive insights or solve complex spatial problems.
- Exporting your maps or visualizations for reporting or further analysis in other software.
The ability to import XY coordinates from Excel opens up a multitude of opportunities for spatial data management and visualization. Following these steps, you can seamlessly integrate your coordinate data into mapping and GIS platforms, unlocking the full potential of your spatial datasets. Whether for urban planning, environmental monitoring, or any other field requiring spatial analysis, this streamlined process ensures efficiency and accuracy in your workflow.
By keeping your data well-organized in Excel, converting it to a suitable file format, and using the appropriate tools to import into your mapping software, you can harness the power of location-based analysis with minimal hassle.
What format should my coordinates be in Excel?
+
Your XY coordinates should ideally be in a decimal degree format for most GIS software, or in the format compatible with the software you’re using.
Can I import coordinates in different projections or formats?

+
Yes, but you’ll need to ensure that the software you’re using supports the transformation or conversion to the desired projection.
What if some coordinates are missing?

+
Missing coordinates can result in mapping errors. Review and fill or remove incomplete coordinate pairs before import.