Mastering Multiple Sorts in Excel: A Simple Guide

Introduction to Sorting in Excel
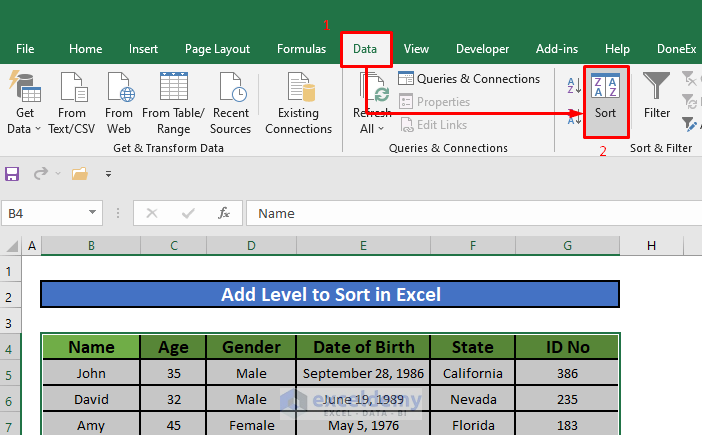
Sorting is an essential skill when working with spreadsheets in Excel, enabling you to organize and analyze your data efficiently. Whether you’re dealing with financial records, sales data, or personal contacts, knowing how to perform multiple sorts can significantly enhance your data management capabilities.
In this guide, we will explore the nuances of sorting multiple columns in Excel, ensuring you can:
- Understand the importance of sorting
- Use Excel’s sort feature with ease
- Perform multiple sorts to organize your data in complex ways
- Avoid common pitfalls associated with sorting
Why Sort Your Data?
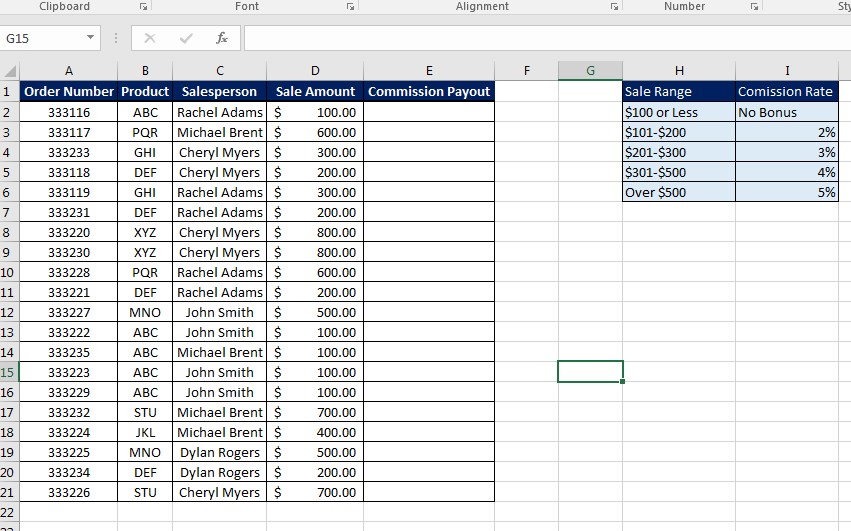
Sorting data can: - Improve data readability - Make it easier to locate and analyze specific information - Organize your data in a meaningful way for reports or presentations - Enable you to perform data analysis tasks like finding duplicates or summarizing trends
Basic Sorting in Excel

Excel’s sort feature is straightforward for single-column sorting. Here’s how to sort a column:
Select the Column: Click on the column header to select the entire column.
Access Sort Option: Go to the Data tab on the ribbon, and click on Sort & Filter.
Choose Sort Order: Select Sort A to Z for ascending or Sort Z to A for descending order.
This will sort the selected column, but what if you need to sort by more than one criterion?
Performing Multiple Sorts in Excel

When dealing with more complex data sets, you might need to sort based on multiple columns or conditions. Here’s how you can achieve multiple sorts:
Select the Range: Ensure your selection includes all the columns that need to be sorted.
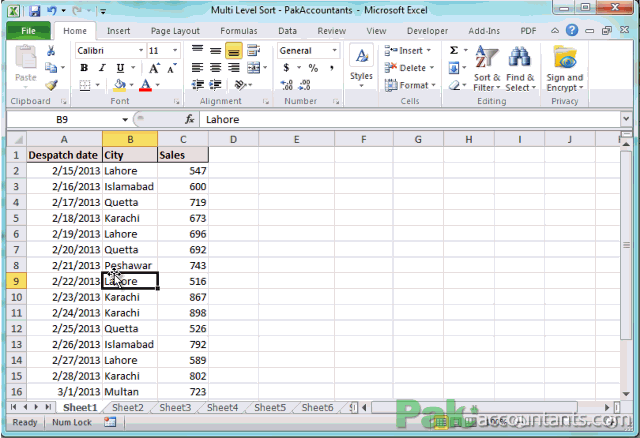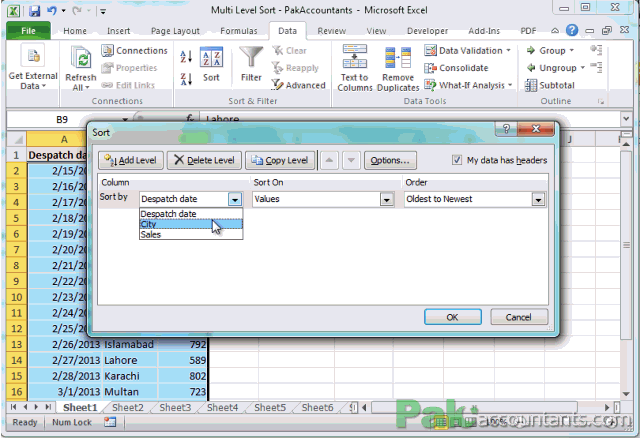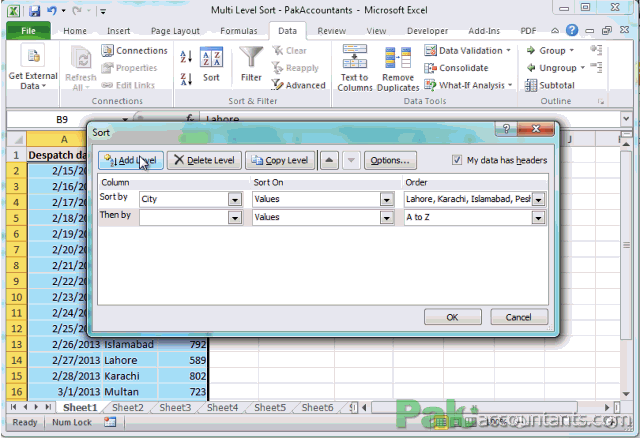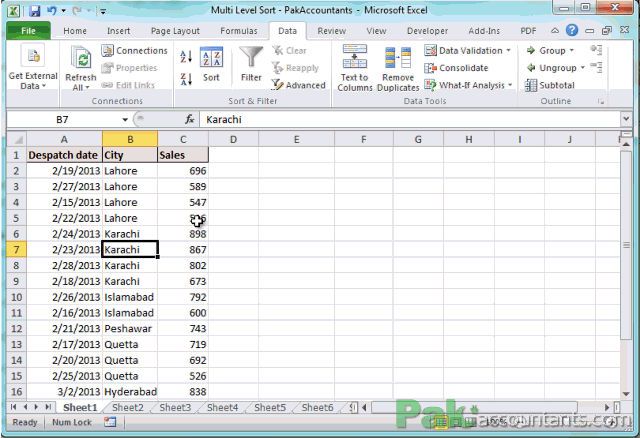
Open the Sort Dialog: On the Data tab, click on Sort.
Add Levels:
- In the sort dialog, click on Add Level to add another sorting condition.
- Define the primary column for sorting and its order (A to Z or Z to A).
- Add secondary or tertiary columns as needed.
Here’s an example:
| Employee ID | Department | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| E1001 | Marketing | 45000 |
| E1002 | HR | 50000 |
| E1003 | Marketing | 55000 |

Let’s say you want to sort this table by Department in ascending order and then by Salary in descending order within each department:
- Add Department as your first level in the Sort dialog, with Order A to Z.
- Add Salary as your second level, with Order Z to A.

📌 Note: When adding levels, Excel will sort from the top level to the bottom level sequentially.
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Sorting

- Use Headers: Make sure your data includes headers. Excel can use these as sorting references, making your sorting process clearer.
- Custom Lists: If you need to sort by categories that don’t follow alphabetical order (e.g., Low, Medium, High), create custom lists in Excel.
- Data Validation: Before sorting, ensure there are no merged cells in your selection, as this can cause data misalignment.
- Sorting Date and Time: Excel recognizes dates and times. Ensure they are in a format Excel can understand for accurate sorting.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
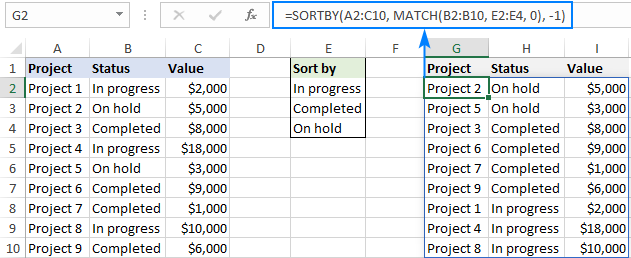
- Data Loss: When sorting, always select the entire row range. Failing to do so can lead to data from different rows becoming mismatched.
- Incorrect Sorting Levels: If you add sort levels in the wrong order, the results might not be what you expect. Double-check the order of your sorting criteria.
Advanced Sorting Techniques

For more sophisticated data management:
- Conditional Sorting: Use conditional formatting or filter rules before sorting to isolate and organize specific data sets.
- Sorting with Formulas: Employ formulas like SORT or SORTBY for dynamic sorting that changes as your data does.
- Macros for Complex Sorting: If you often perform the same multi-level sort, record a macro to automate the process.
Wrapping Up

By mastering multiple sorts in Excel, you unlock a powerful way to manage and analyze your data. Remember, the key is in the details:
- Understand your data structure
- Use headers and check for errors
- Utilize Excel’s sorting tools wisely
- Apply advanced techniques when necessary
This comprehensive guide should provide you with the knowledge needed to navigate through your data more effectively. Whether it’s for business analytics, financial reporting, or personal organization, Excel’s sorting features are indispensable tools for any user.
Frequently Asked Questions
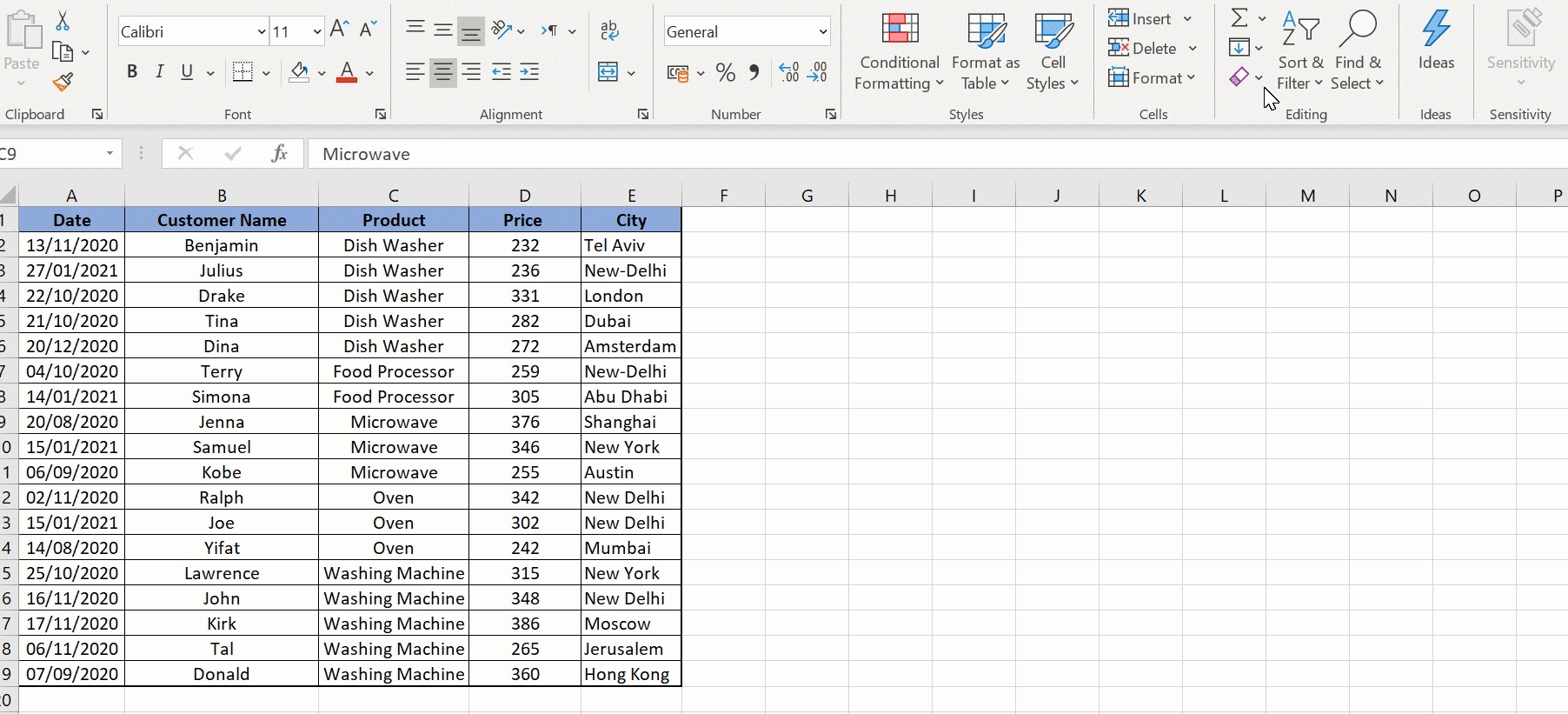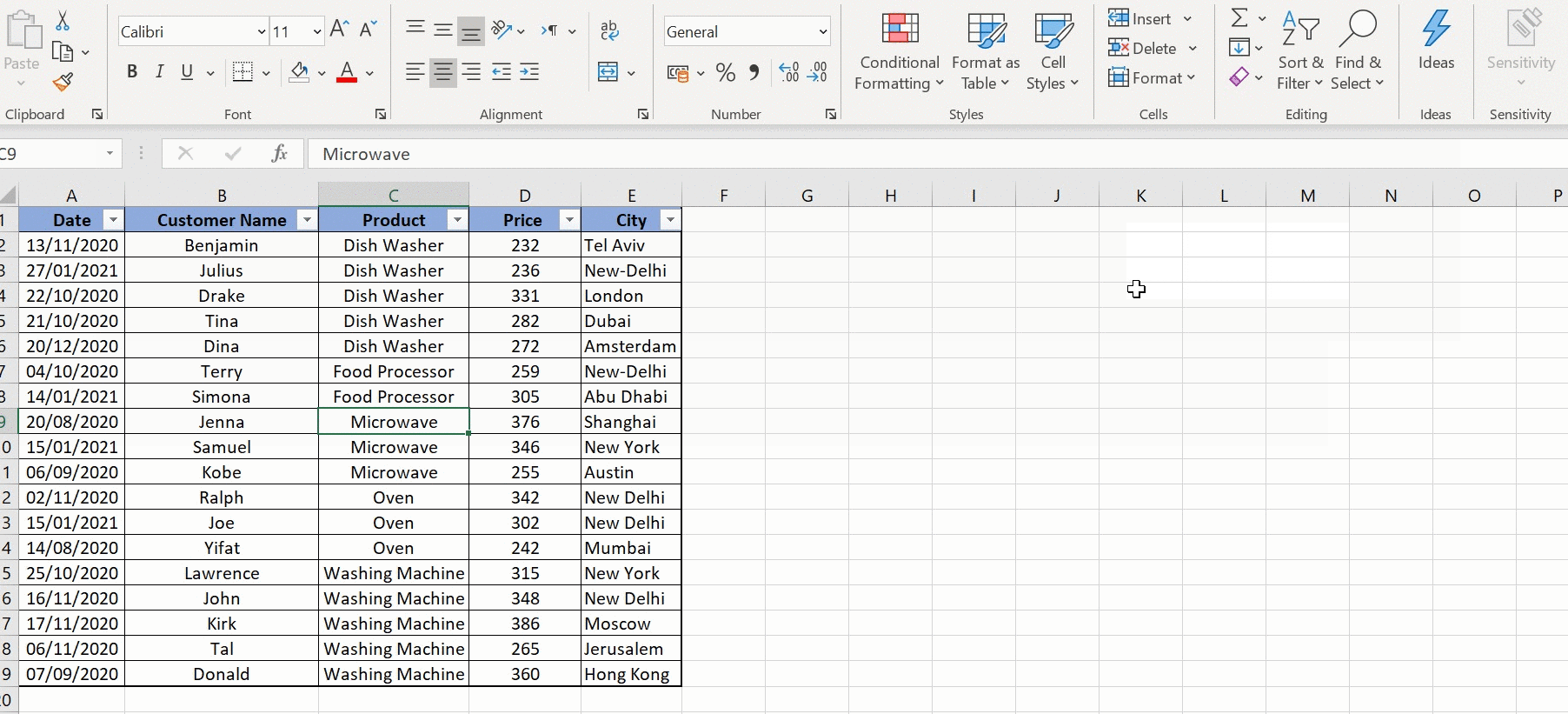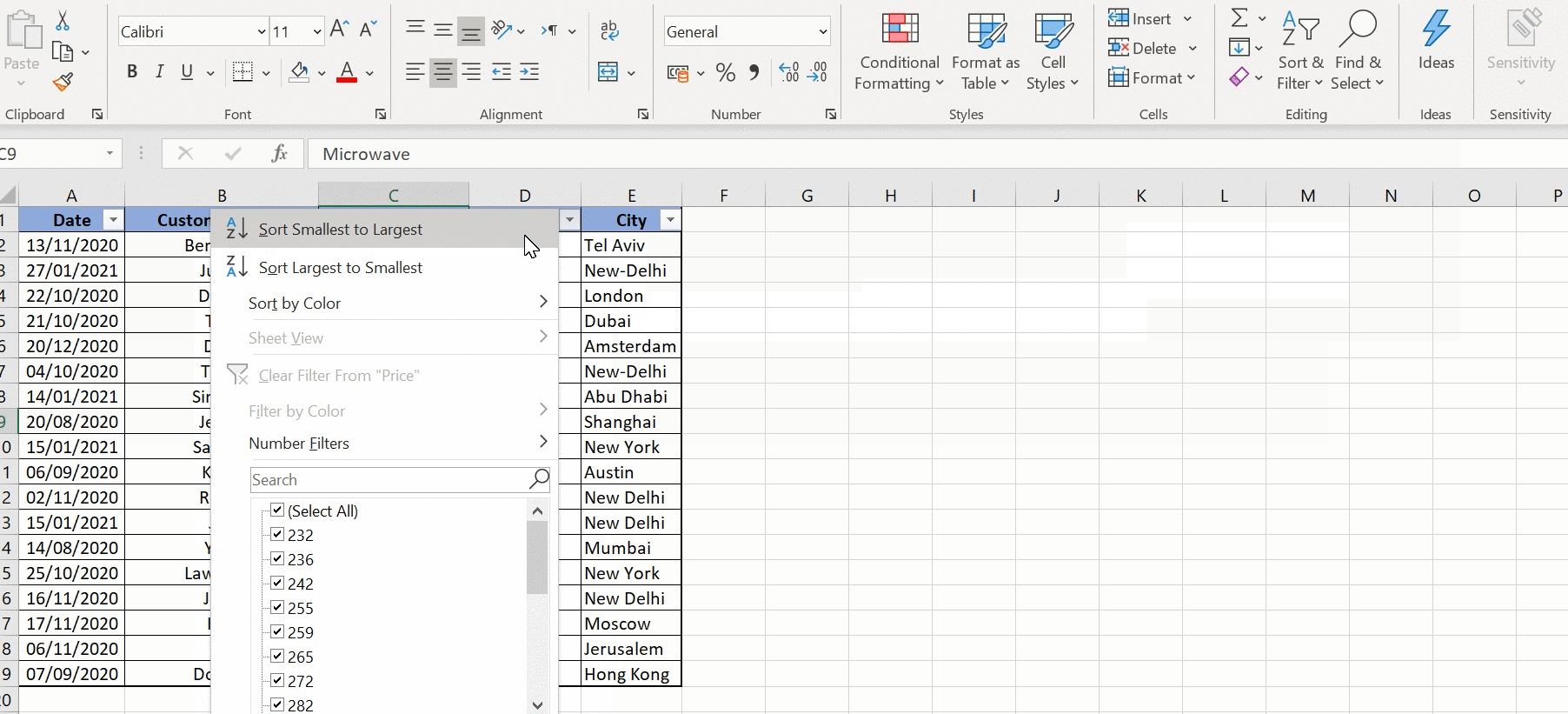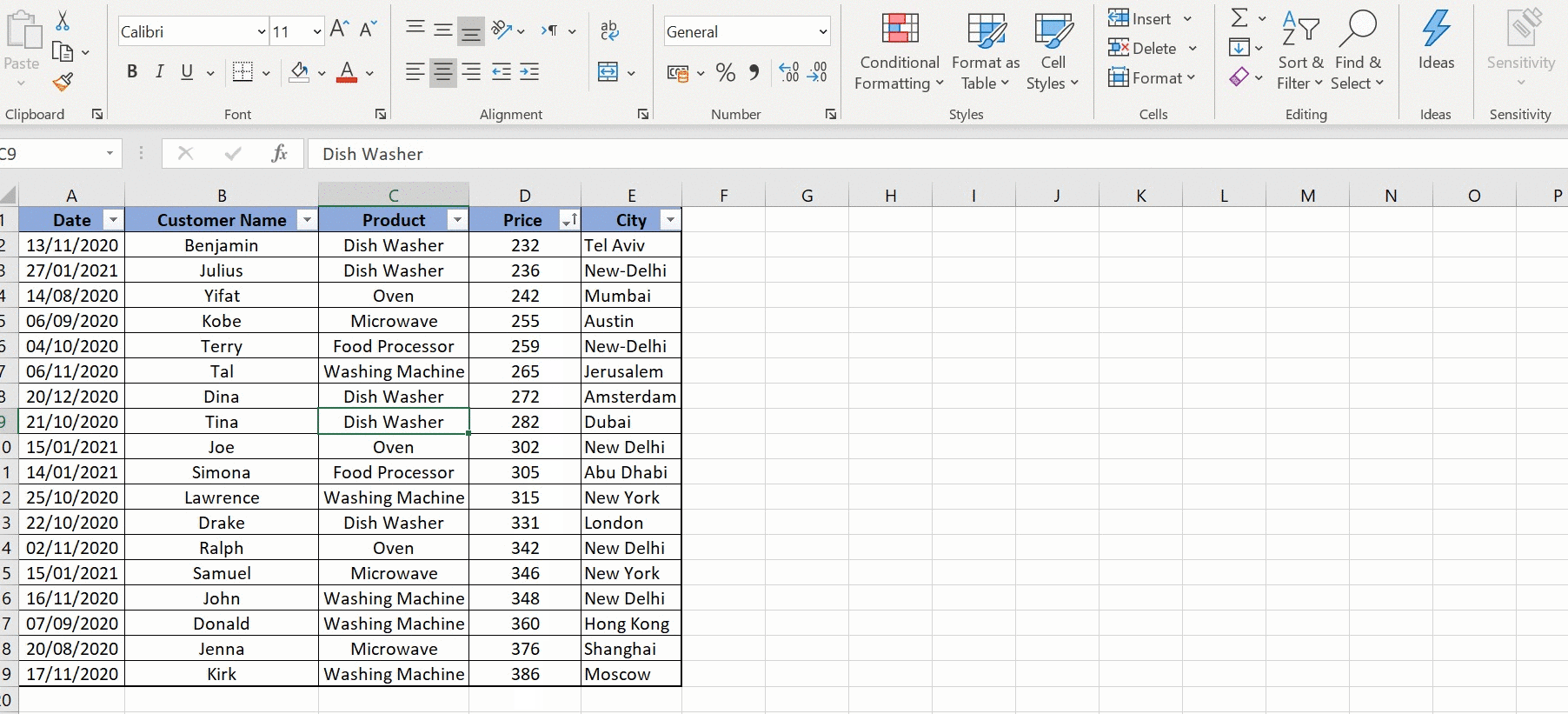
What happens if I don’t select all columns while sorting?
+
If you only select certain columns, Excel will sort those columns independently, potentially leading to data misalignment. Always select all columns to maintain data integrity.
Can I sort by color or icon in Excel?
+
Yes, Excel allows you to sort by cell color, font color, and even by icon sets. Go to Sort Options in the Sort Dialog, where you can choose to sort by cell color, font color, or icon.
How do I sort a list with custom ordering?

+
Create a custom list under File > Options > Advanced > General > Edit Custom Lists. After defining your custom order, select your data, and under Sort, choose the custom list for sorting.
Can I sort data with formulas?

+
Yes, with dynamic array formulas like SORT and SORTBY. These formulas allow you to sort data directly within a cell or range, updating dynamically as your data changes.
What should I do if my sort is not working as expected?
+
Check for hidden rows, merged cells, or ensure your data doesn’t span multiple sheets. Also, review the sort levels and their order to make sure you’ve set them correctly.