Write on Excel with Python: Quick and Simple Guide
Unlock the full potential of Excel data manipulation with Python, a powerful tool that enables you to automate repetitive tasks, analyze large datasets, and integrate Excel with other applications. This guide is designed for both beginners in Python programming and Excel users looking to leverage Python for enhanced data management. We'll cover the basics of using Python with Excel, from installation to executing common tasks.
Why Use Python with Excel?

Before diving into the technical details, it's essential to understand why Python is an excellent companion for Excel:
- Automation: Automate tasks that would otherwise be time-consuming in Excel.
- Data Analysis: Utilize Python's advanced data analysis libraries for complex operations not directly supported by Excel.
- Customization: Develop custom functions and tools tailored to your specific needs.
- Scalability: Handle larger datasets more efficiently than Excel alone can manage.
By integrating Python into your Excel workflow, you can significantly enhance your productivity and data handling capabilities.
Setting Up Your Python Environment
To begin, you'll need to set up your Python environment:
- Download and install Python from the official Python website if not already installed.
- Install pip, Python's package installer, if it's not part of your Python installation.
- Install the necessary libraries by running:
pip install openpyxl pandas xlrd
- Data Visualization: Integrate libraries like Matplotlib or Seaborn to generate charts directly from your Excel data.
- API Integration: Fetch or send data to external APIs, automating data updates.
- Web Scraping: Use Python to pull data from websites and populate Excel sheets.
- PyWin32: For Windows users, this library allows Python to interact with Excel.
- Excel Add-ins: Develop custom add-ins that call Python scripts.
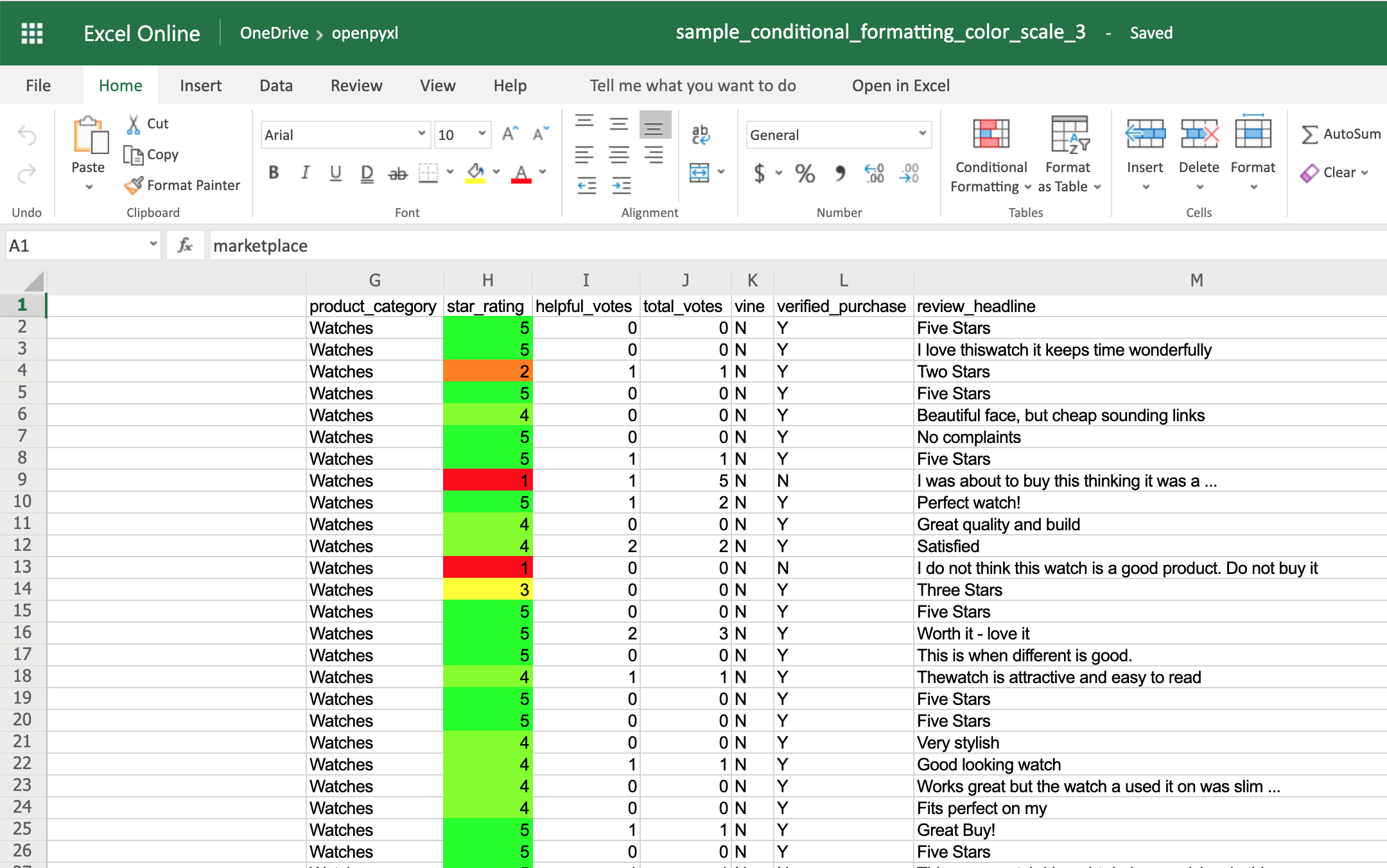
🛠 Note: Ensure your Python installation path is added to your system PATH for ease of access.
Reading Excel Files

One of the most common operations is reading data from an Excel file. Here's how you can do it using the openpyxl and pandas libraries:
Using Openpyxl

from openpyxl import load_workbookwb = load_workbook(‘example.xlsx’) sheet = wb.active
for row in sheet.iter_rows(values_only=True): print(row)
Using Pandas
import pandas as pddf = pd.read_excel(‘example.xlsx’, sheet_name=‘Sheet1’)
print(df.head())
Writing to Excel Files

Writing to Excel files from Python can be equally straightforward:
Using Openpyxl

from openpyxl import Workbookwb = Workbook() sheet = wb.active
sheet[‘A1’] = ‘Hello’ sheet[‘B1’] = ‘World’
wb.save(‘new_example.xlsx’)
Using Pandas

import pandas as pddata = {‘A’: [1, 2, 3], ‘B’: [‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘Z’]} df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_excel(‘output.xlsx’, index=False, sheet_name=‘NewSheet’)
Common Excel Operations with Python

Here are some common operations you might perform using Python:
1. Filtering Data

import pandas as pddf = pd.read_excel(‘example.xlsx’, sheet_name=‘Sheet1’) filtered_df = df[df[‘age’] > 30] filtered_df.to_excel(‘filtered_data.xlsx’, index=False)
2. Data Aggregation

grouped = df.groupby(‘category’).agg({‘sales’: ‘sum’, ‘quantity’: ‘mean’})
grouped.to_excel(‘aggregated_data.xlsx’)
3. Pivot Tables

pivot_table = pd.pivot_table(df, values=‘sales’, index=‘region’, columns=‘product’, aggfunc=‘sum’) pivot_table.to_excel(‘pivot_table.xlsx’)
These operations can be adjusted based on the structure of your data and your specific requirements.
Enhancing Excel with Python

Python's flexibility allows for the creation of complex analytical tools:
Scripting in Excel

You can script directly within Excel using:
🔍 Note: For a seamless Python and Excel integration experience, ensure compatibility between your Python version, Excel version, and the libraries you're using.
As we wind down, integrating Python into your Excel workflow not only saves time but also empowers you with analytical capabilities far beyond what Excel alone can offer. The power of Python lies in its ability to automate, analyze, and scale operations, which in turn can significantly enhance the way you manage and interpret data. With the techniques described here, you’re well on your way to harnessing the synergy of Python and Excel, making your data handling tasks more efficient, insightful, and scalable.
How do I install Python libraries for Excel?

+
You can install Python libraries using pip, Python’s package installer. Open a command prompt or terminal and run pip install openpyxl pandas xlrd to install libraries necessary for Excel manipulation.
Can I use Python within Excel?

+
Yes, you can either use Python scripting through add-ins like PyWin32 on Windows, or integrate Python scripts into Excel macros or add-ins for automation.
Is it possible to automate Excel without opening the application?

+
Absolutely! Using libraries like openpyxl or pandas, you can read from and write to Excel files without the need to launch the Excel application itself.
What are the limitations of using Python with Excel?
+
While Python can do much, certain Excel functionalities like complex charting or data validation rules might be challenging to replicate perfectly with Python. However, Python’s libraries can often bypass these limitations with alternative solutions.
Can I connect Excel to databases using Python?
+
Yes, using libraries like pandas or sqlalchemy, you can connect to various databases, pull data into Python, process it, and then export it to Excel or update existing Excel files.